Whatis Port 445 in W2K/XP/2003?
What is port 445 used for in Windows 2000/XP?
Among the new ports used by Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, is TCP port 445 which is used for SMB over TCP.
The SMB (Server Message Block) protocol is used among other things for file sharing in Windows NT/2000/XP. In Windows NT it ran on top of NetBT (NetBIOS over TCP/IP), which used the famous ports 137, 138 (UDP) and 139 (TCP). In Windows 2000/XP/2003, Microsoft added the possibility to run SMB directly over TCP/IP, without the extra layer of NetBT. For this they use TCP port 445.
At its simplest NetBIOS on your LAN may just be a necessary evil. NetBIOS on your WAN or over the Internet, however, is an enormous security risk. All sorts of information, such as your domain, workgroup and system names, as well as account information is obtainable via NetBIOS. It really is in your best interests to ensure that NetBIOS never leaves your network.
If you are using a router as your Internet gateway then you will want to ensure that it does not allow inbound or outbound traffic via TCP ports 135-139.
If you’re using a Firewall then you should also block the same ports – TCP ports 135-139.
If you are using a multi-homed machine i.e. more than 1 network card, then you should disable NetBIOS on every network card, or Dial-Up Connection under the TCP/IP properties, that is not part of your local network.
How to disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP?
In Windows 2000/XP/2003 you have the possibility to disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP. You do this by right-clicking on My Network Places and selecting Properties. Then right-click on the appropriate Local Area Connection icon, and select Properties.
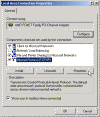
Next, click on Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and Properties.
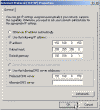
Now click Advanced, and select the WINS tab.
There you can enable or disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP.
The changes take effect immediately without rebooting the system.
You will get an event in your event log if you do not also disable the TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper Service service. You can Disable this service in Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services if desired.
Note: Computers that are running an operating system prior to Windows 2000 will be unable to browse, locate, or create file and print share connections to a Windows 2000/XP/2003 computer with NetBIOS disabled.
For more issues on this please read the Disable NetBIOS in W2K/XP/2003 page.
How to disable port 445?
You can easily disable port 445 on your computer. To do so follow these instructions:
- Start Registry Editor (Regedit.exe).
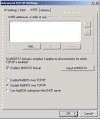
- Locate the following key in the registry:
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NetBT\Parameters
- In the right-hand side of the window find an option called TransportBindName.
- Double click that value, and then delete the default value, thus giving it a blank value.
- Close the registry editor.
- Reboot your computer.
After rebooting open a command prompt and in it type
netstat -an
See that your computer no longer listens to port 445.
Client/Server port usage
When does Windows 2000/XP/2003 uses port 445, and when it uses 139?
From now on I will refer to the “client” as the computer from where you map drives and other shared resources, and to the “server” as the computer with resources that are shared. I will also refer to NetBIOS over TCP/IP only as NetBT.
If the client has NetBT enabled, it will always try to connect to the server at both port 139 and 445 simultaneously. If there is a response from port 445, it sends a RST to port 139, and continues it’s SMB session to port 445 only. If there is no response from port 445, it will continue it’s SMB session to port 139 only, if it gets a response from there. If there is no response from either of the ports, the session will fail completely.
If the client has NetBT disabled, it will always try to connect to the server at port 445 only. If the server answers on port 445, the session will be established and continue on that port. If it doesn’t answer, the session will fail completely. This is the case if the server for example runs Windows NT 4.0.
If the server has NetBT enabled, it listens on UDP ports 137, 138, and on TCP ports 139, 445. If it has NetBT disabled, it listens on TCP port 445 only.