How to Secure Unmanaged Devices with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Security Management with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is a new feature that can be used to apply security configuration to devices that do not enroll into Microsoft Endpoint Manager. In this scenario, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint retrieves, enforces, and reports on policies deployed via Microsoft Endpoint Manager. The devices are joined to your Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and are also visible in the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center alongside other devices you manage with Intune and Configuration Manager.
Just released into Public Preview, Security Management with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint has a number of prerequisites and steps that must be taken in order to get started. This post will go through each of these in detail so that you can get up and running right away.
- Ensure appropriate licensing for Security Management with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Configure Enforcement Scope within Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Configure Endpoint Security Profile Settings within Microsoft Endpoint Manager
- Onboard target devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Apply required tags to onboarded devices – this is only required during the Public Preview
- Create and configure Azure AD Groups for Security configuration targeting
- Assign policies for Security configuration
- Review onboarded and managed devices
Ensure appropriate licensing for Security Management with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Security Management with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is available to all tenants that are licensed for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Whilst Microsoft currently suggest that all Microsoft 365 licenses will grant access to this feature, our testing has shown that only tenants that are licensed for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (P2) are able to leverage the automated Azure AD Join feature that allows policies to be targeted.

Configure Enforcement Scope within Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
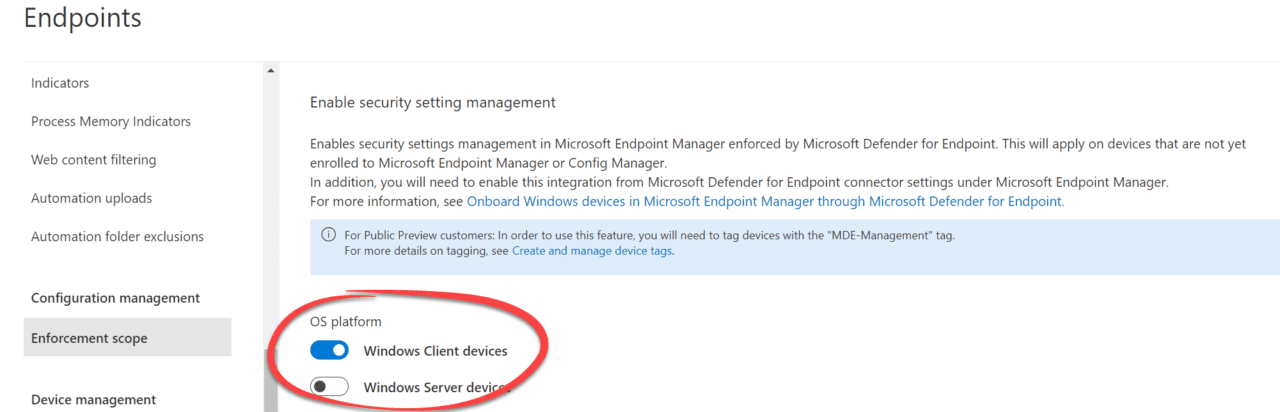
Within the Microsoft Security Portal > Settings > Endpoints > Configuration Management > Enforcement scope, it is possible to “Enable security setting management” on selected OS platforms.
In the example below, Security setting management has been enabled for Windows Client devices, but not Windows Server devices. In this post, we’ll focus on Windows client devices.
Configure Endpoint security profile settings in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
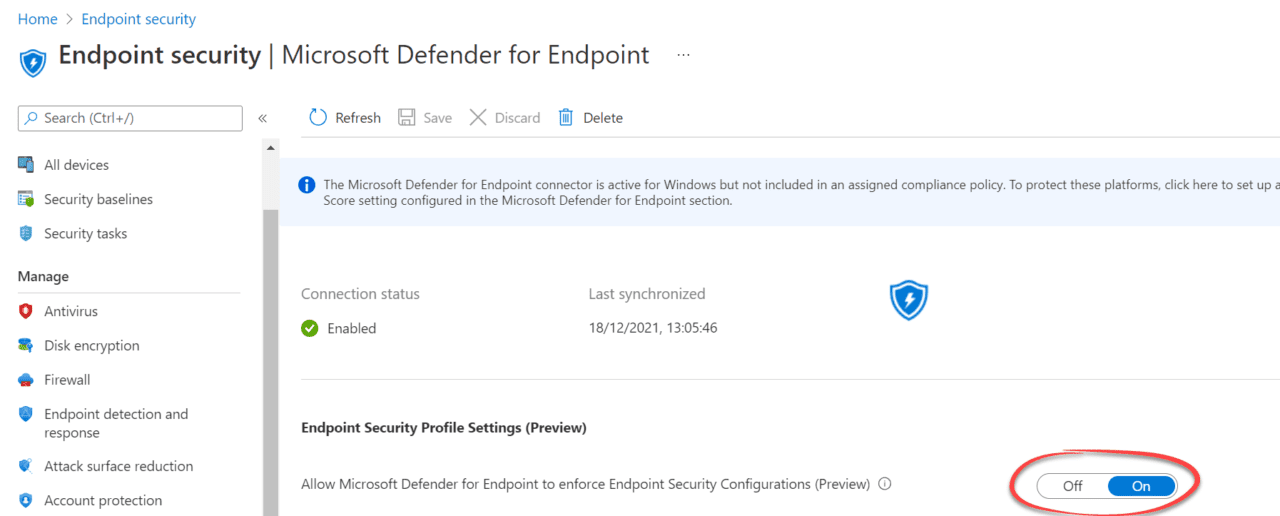
At the Endpoint Security Settings within Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center, we are presented with the option to Enable Security Profile Settings. This feature will allow Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to enforce Endpoint Security Configurations independently of the device being managed by Mobile Device Management (MDM) or Configuration Manager (ConfigMgr).
Enabling this setting allows supported agents to report the status of applied profiles to Microsoft Endpoint Manager, and agents will appear in device views and reports relevant to Endpoint Security profile management.
Complete the following steps to enable endpoint security profile settings:
- In Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center browse to Endpoint Security > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Within Endpoint security | Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, navigate to Endpoint Security Profile Settings (Preview) and locate the setting Allow Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to enforce Endpoint Security Configurations (Preview) and set this to On, as shown below.
Onboard target devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
In order for devices to be able to receive Security Settings policy from Microsoft Endpoint Manager, devices must be onboarded to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. It is not required for devices to be Azure AD Joined before onboarding, but devices will be Azure AD joined (or Hybrid Azure AD Joined) as part of the configuration process for Security Management with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. There are multiple ways to onboard devices into Microsoft Defender for Endpoint:
- Local Script (up to 10 devices)
- Group Policy
- Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager
- System Center Configuration Manager
- Mobile Device Management / Microsoft Intune
- VDI onboarding scripts
Not all methods are appropriate in the scenario we’re describing here. In fact, in an environment that is completely unmanaged, only Local Script onboarding is viable. Microsoft advise that the Local Script method is only to be used for less than 10 devices and that another method should be leveraged for rollouts of a larger scale. This is due to the increased overhead when using the Local Script method.
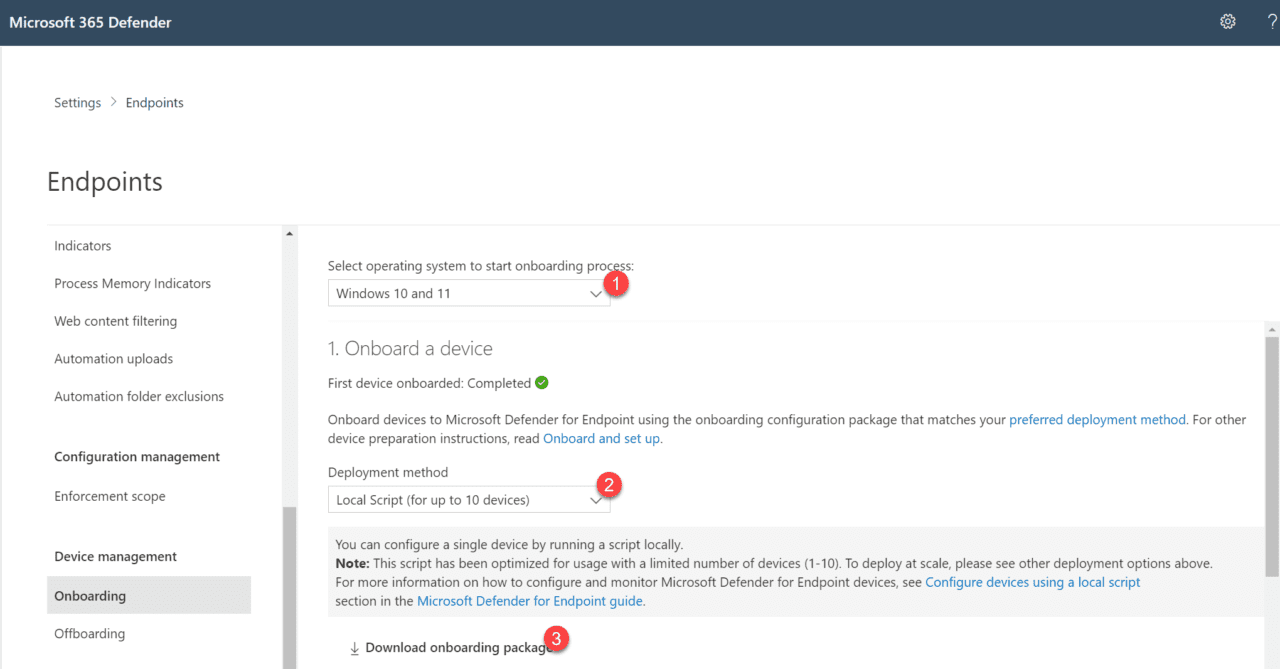
- Open the Microsoft 365 Defender portal and choose Settings > Endpoints > Onboarding
- At the Onboarding blade, select Windows 10 and 11 from the Select operating system to start onboarding process dropdown, then choose Local Script as the Deployment method and navigate to Download onboarding package
- Once downloaded, copy to the target device, extract the package and run the WindowsDefenderATPOnboardingScript.cmd file from an administrative command prompt.
During public preview, only onboarded devices that are tagged (in Defender for Endpoint) with the MDE-Management tag will be joined to Azure AD and enrolled in the Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint configuration management channel. This is important, as an Azure AD computer object is required to target Security Configurations from Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
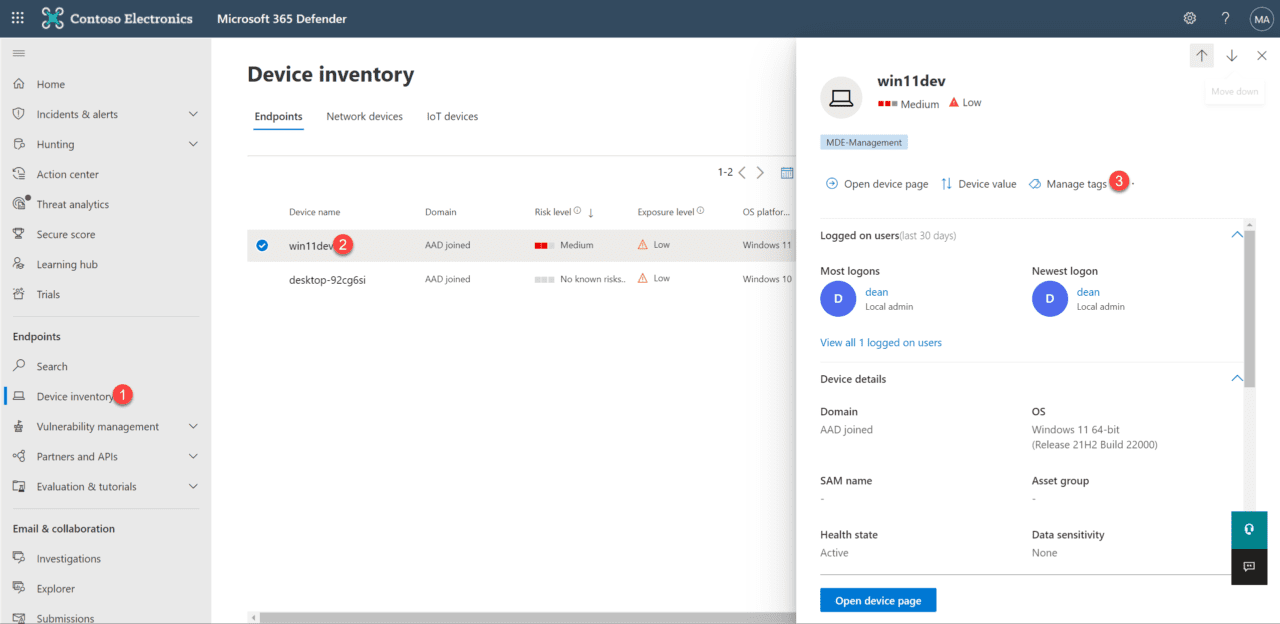
- In the Microsoft Defender Portal choose Device inventory
- In the Endpoints section, choose Device inventory, select the onboarded device and click Manage tags
- On the Manage machine tags page, enter MDE-Management as a new tag and click Save
Create and configure Azure AD Groups for security configuration targeting
In order to target Security Policy to onboarded devices, they must be a member of an Azure AD Group. To reduce administrative overhead, it is recommended to create an Azure AD Group with Dynamic Device Membership, so that newly onboarded devices automatically receive policy.
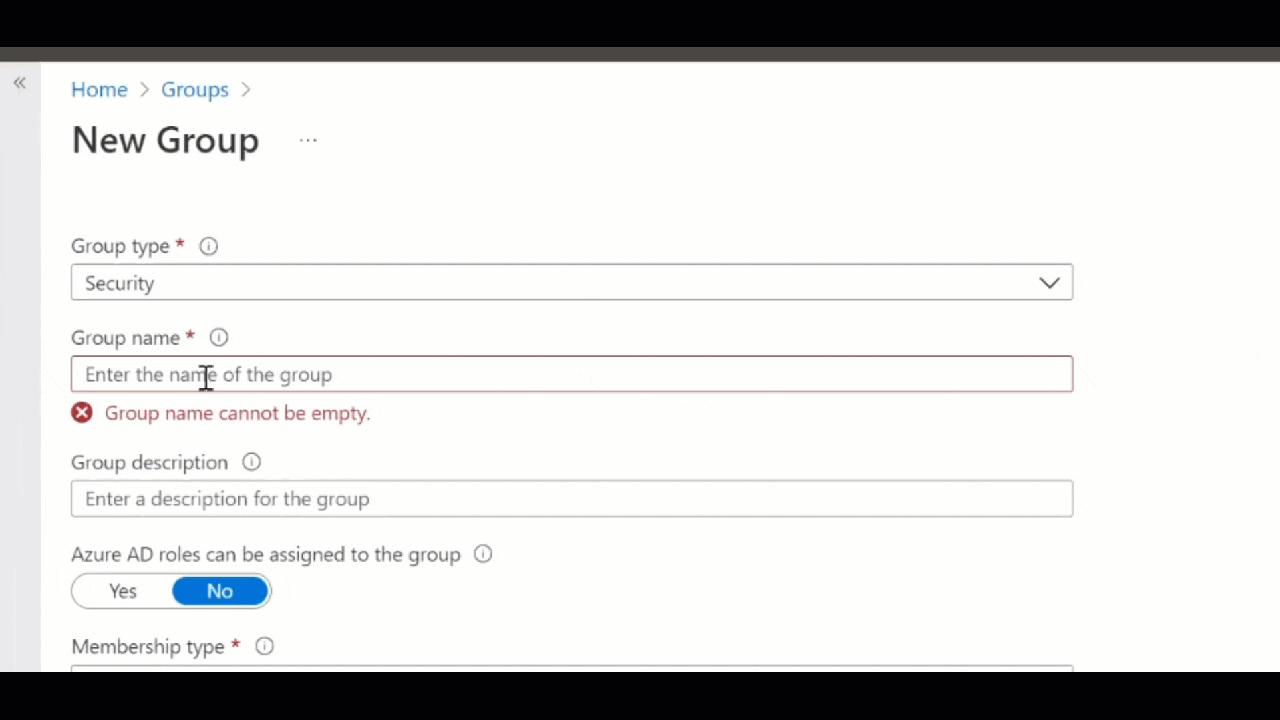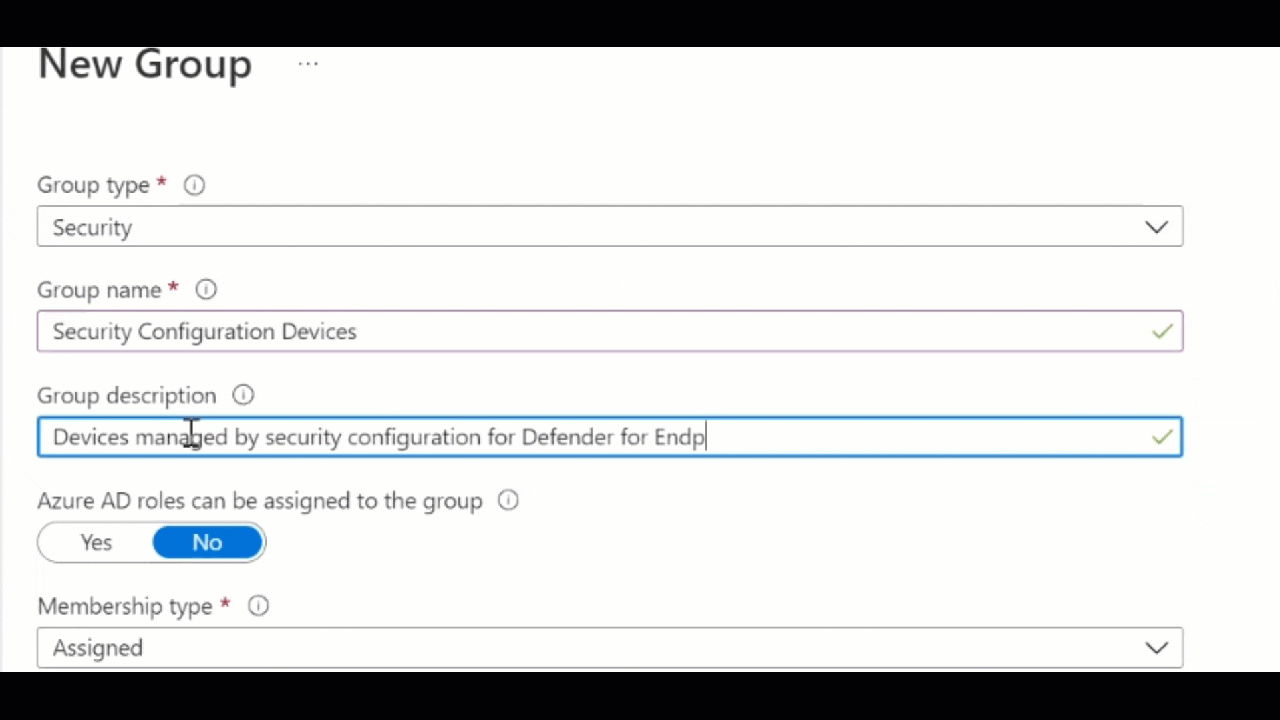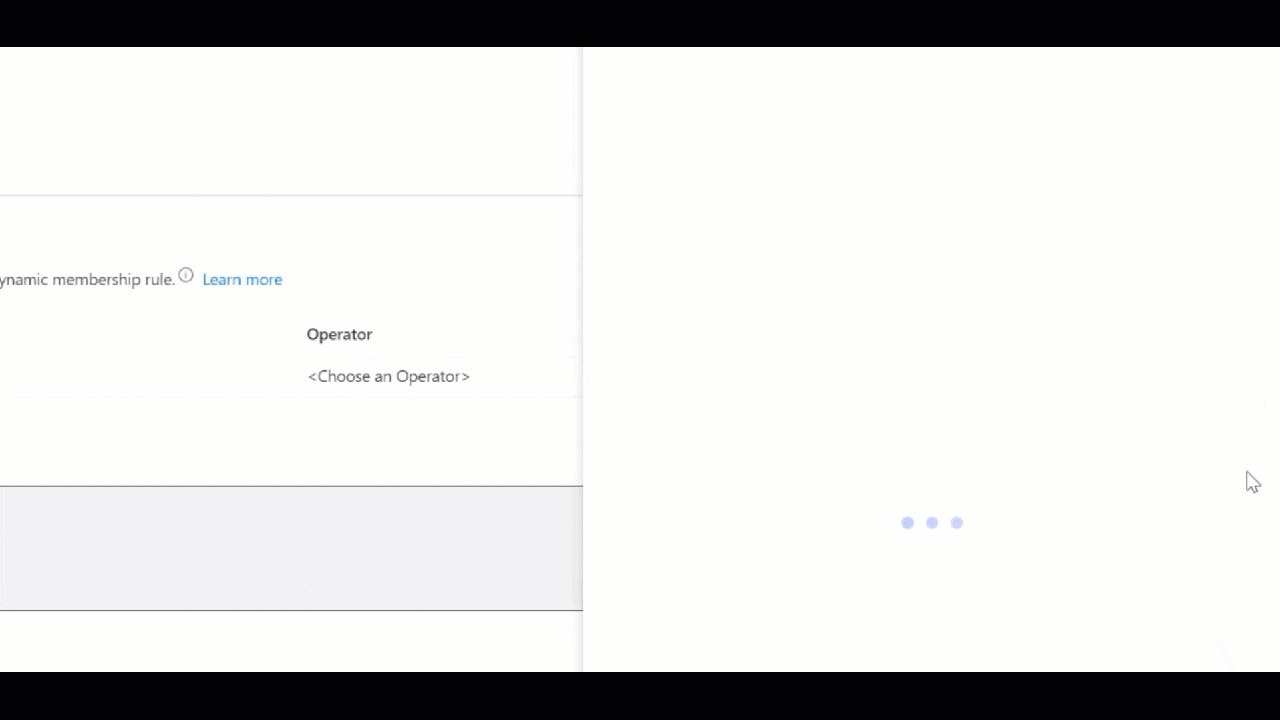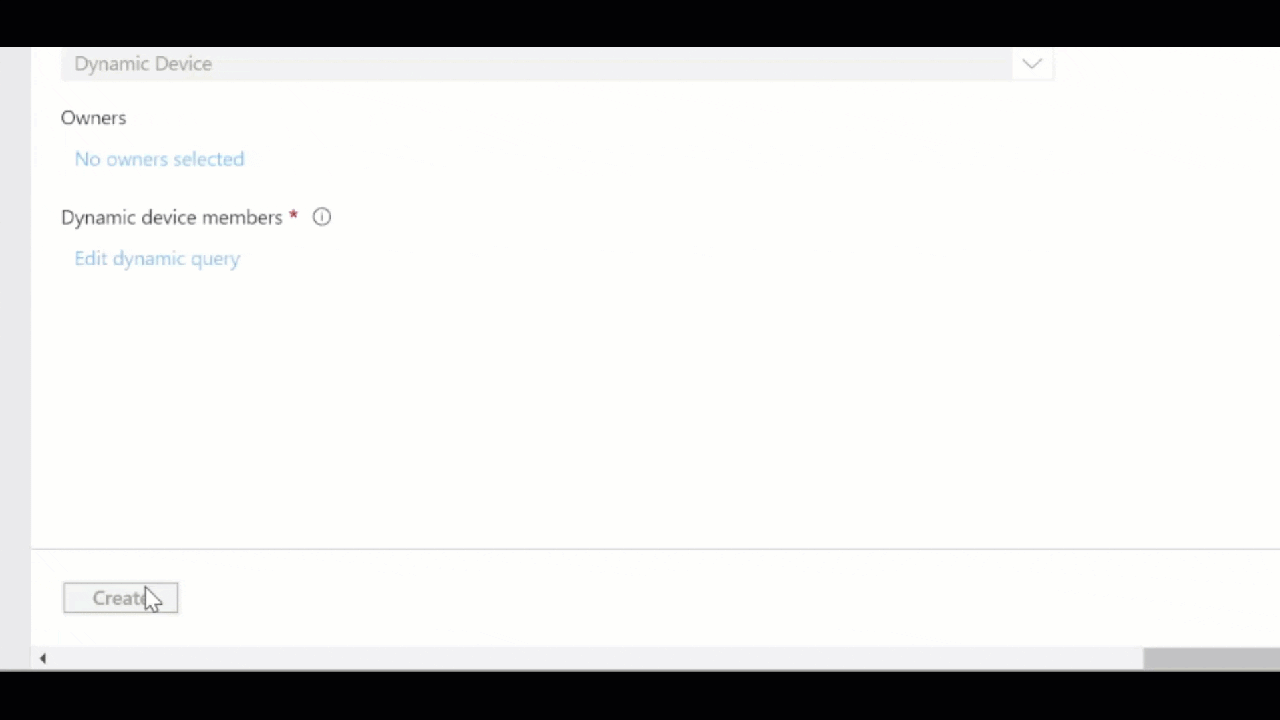
- From the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center portal browse to Groups > New Group
- On the Groups | All groups page, click New group
- On the New group page, provide a Group name, description if required and choose Dynamic device as the Membership type
- Once Dynamic device is chosen, the next options change. Choose Add dynamic query
- On the Dynamic membership rules page, choose to Edit the Rule Syntax and add (device.managementType -eq “MicrosoftSense”) with the Rule syntax and click Save
Assign policies for security configuration
Now let’s assign policies for security configuration.
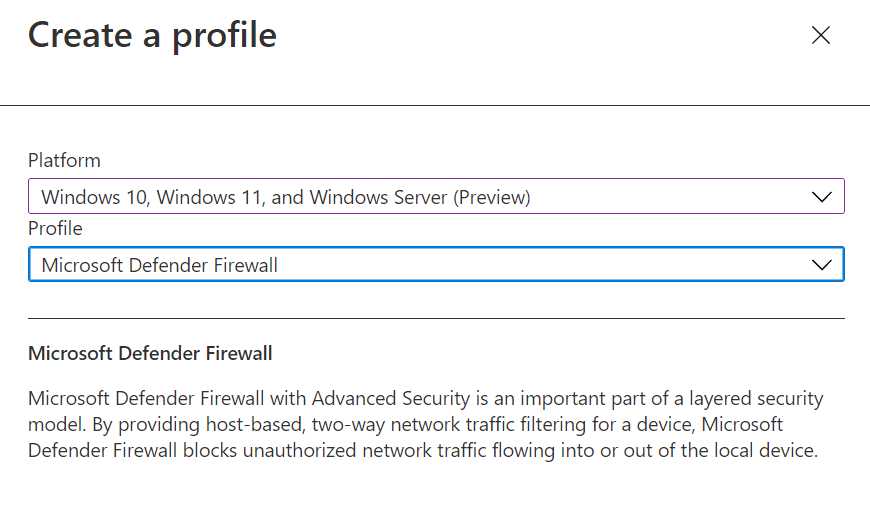
- From the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center portal browse to Endpoint security > and select one either Antivirus, Firewall, or Endpoint Detection and Response from the Manage list.
- Within the Create a profile pane, under Platform select Windows 10, Windows 11 and Windows Server (Preview) select the Profile and click Create
- On the Basics pane, configure the basic elements and choose Next
- On the Configuration settings pane, choose and configure the appropriate settings for your use case, then choose Next
- On the Assignments pane, target your new dynamic group, and choose Next
- On the Review + create pane, choose Create
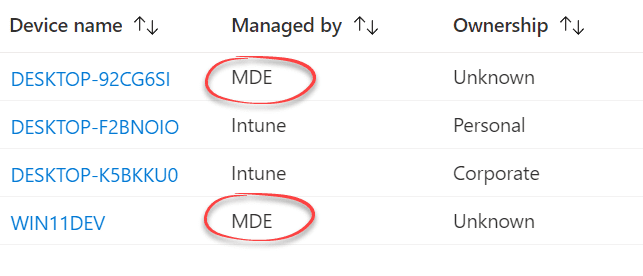
Review onboarded and managed devices
Devices that are onboarded into Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint can be viewed and interacted with in multiple ways. For example, in the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center portal, devices are listed as being Managed by “MDE”, as below.
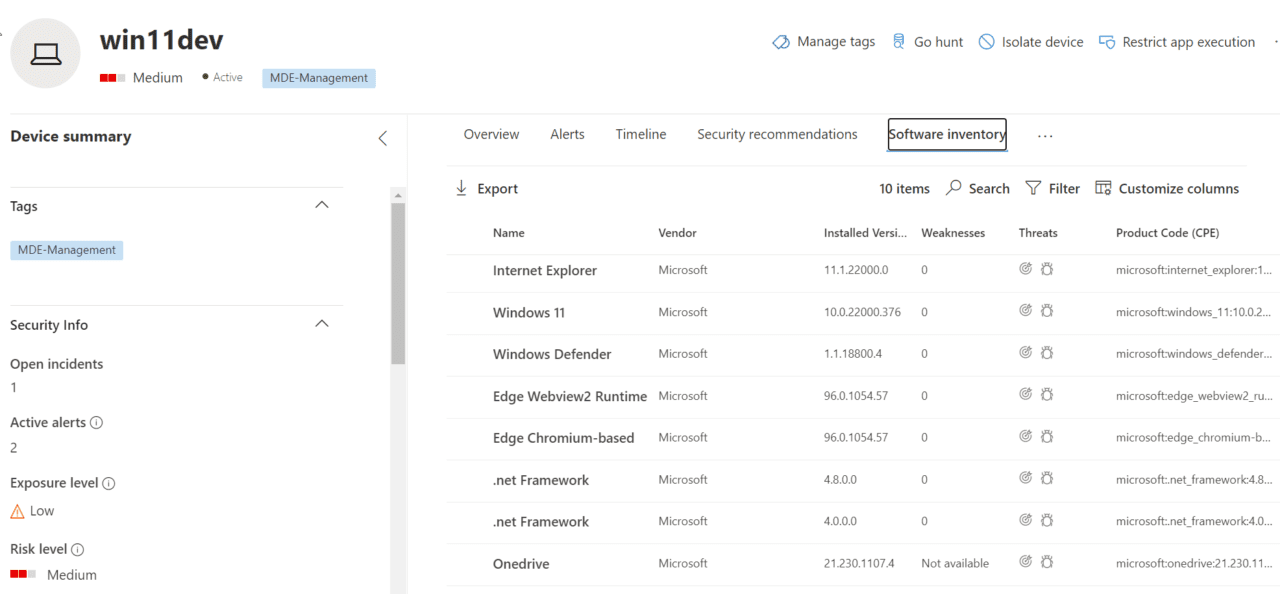
In the Microsoft Security Center, onboarded devices provide a rich set of information that would normally only be available from devices managed by Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
Insights such as Security Recommendations, Alert timelines and Software Inventory are made available.
Summary
Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint extends the Microsoft Endpoint Manager Endpoint Security surface to devices that aren’t capable of enrolling into Microsoft Endpoint Manager. With this capability, devices that aren’t managed by Microsoft Intune or ConfigMgr can receive security configurations for Microsoft Defender directly from Endpoint Manager.
Whilst this overview focused on unmanaged Windows 10 and 11 devices, devices that are part of a Windows Server Active Directory Domain Services domain are able to leverage this capability, as are Windows Server devices.
Related articles:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint – Important Service and Endpoint Settings You Should Configure Right Now
- Understanding Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and How It Protects Your Data
- Microsoft Defender for Business Brings Enterprise-Grade Endpoint Security to SMEs
- Securing Enterprise Devices: Embracing Zero Trust Security
Table of contents
- Ensure appropriate licensing for Security Management with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Configure Enforcement Scope within Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Configure Endpoint security profile settings in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
- Onboard target devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Apply required tags to onboarded devices – this is only required during the public preview
- Create and configure Azure AD Groups for security configuration targeting
- Assign policies for security configuration
- Review onboarded and managed devices
- Summary




