
Key takeaways:
- Microsoft has published a roundup of all the new capabilities added to Windows Autopatch in the past few weeks.
- IT admins are getting finer control over Windows updates with the ability to pause and resume updates for specific Autopatch groups or rings.
- Microsoft added a new registry conflict detection feature, allowing IT admins to identify and resolve potential update-blocking conflicts.
Microsoft has rolled out a series of Windows Autopatch enhancements designed to redefine how organizations approach updates and device management. The major highlights include a new Autopatch deployment guide, finely-tuned update controls, registry conflict detection, and support for self-serve device deregistration.
Microsoft has created a new deployment guide that helps IT admins to plan their migrations to Windows Autopatch. It explains some common objectives and suggests a recommended deployment plan. Moreover, the Windows Autopatch deployment guide details some migration considerations for Windows Update for Business (WUfB) and Microsoft Configuration Manager. The guide also provides suggested business case benefits and stakeholder communications.

New IT controls for pausing Windows updates
Additionally, Microsoft has added a new feature that gives IT admins better control when pausing quality updates on Windows Autopatch-managed devices. It’s now possible to pause/resume updates for individual/multiple Autopatch groups or at the ring level. The feature lets IT admins view a list of all deployment rings that would be affected as a result of pausing Windows updates.
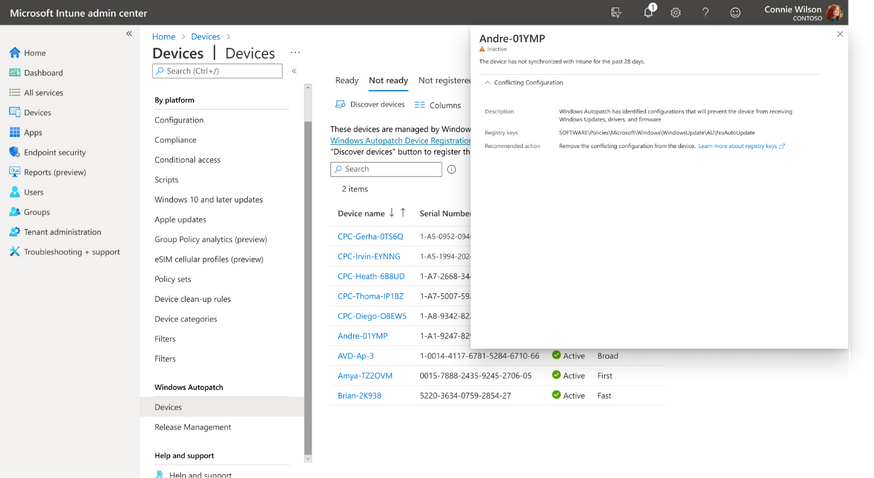
Registry conflict detection
Microsoft has introduced a new capability that helps administrators to detect conflicts during the device registration process. The device readiness check now lets IT admins search for registry settings that could block devices from getting Windows updates or working with Windows Autopatch. They will be able to view details about these devices as well as remediation suggestions in the “Not ready” tab of the Windows Autopatch Devices blade.
Self-serve device deregistration from Windows Autopatch
Lastly, Microsoft has made it easier to remove a specific device from Windows Autopatch management. However, the feature will move the device to the “Not registered” tab in the Devices blade instead of completely removing it from the Azure AD group.
Last month, Microsoft announced a slew of updates to celebrate the first anniversary of its Windows Autopatch service. The company added the ability for IT admins to create discrete Autopatch groups and opt out of Microsoft 365 updates and Expedited updates. The service now supports automated deployment of recommended driver and firmware updates on Windows devices.


