PowerShell Problem Solver: Get Local Active Directory Group Members with PowerShell
- Blog
- PowerShell
- Post
In some recent articles we have looked at retrieving members of an Active Directory group with PowerShell, with an eye toward exporting to a CSV file. Of course, our servers and desktops also have groups, and it might be useful to know what users and groups are in those local groups. The local administrator’s group comes immediately to mind, but you can query any local group using the techniques I’m going to show you.
I’m going to assume that you are running in a domain environment with credentials that have administrator rights on any servers you plan to query. Most of what I am going to show you doesn’t support alternate credentials. Although, you can probably take many of my examples, wrap them in a file or script block, and execute with Invoke-Command where you can specify an alternate credential as last resort.
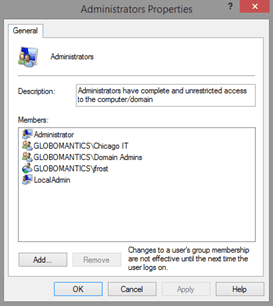
I am going to run all of my commands from a Windows 8.1 desktop running PowerShell under a domain administrator credential. I am going to get the members of the Administrators group on CHI-Core01.
As you can see the group has a mix of local and domain users and groups. I’ll define some variables to use with my examples.
$group = "Administrators"
$computername ="chi-core01"
If you were developing a script or function, these could become parameters eventually.
Using ADSI
The first option takes us back to the days of VBScript and ADSI.
Set wshShell = WScript.CreateObject( "WScript.Shell" )
strComputerName = wshShell.ExpandEnvironmentStrings( "%COMPUTERNAME%" )
Set objLocalAdmins=GetObject("WinNT://" & strComputerName & "/Administrators,Group")
Set memberList=objLocalAdmins.Members
For Each member In memberList
WScript.Echo member.name
Next
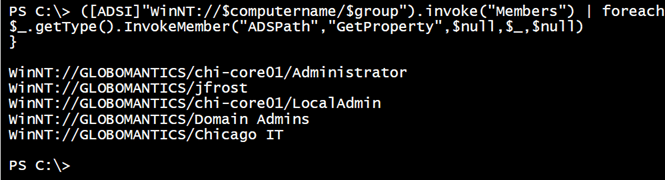
We can accomplish the same things in PowerShell using the ADSI type accelerator. Unfortunately, we still have to work with COM objects. There is nothing intuitive or easy about this approach, although it works once you figure it out. The following is technically a one-line command:
([ADSI]"WinNT://$computername/$group").invoke("Members") | foreach {
$_.getType().InvokeMember("ADSPath","GetProperty",$null,$_,$null)
}
Note that the WinNT moniker is case-sensitive. The result is a collection of strings.
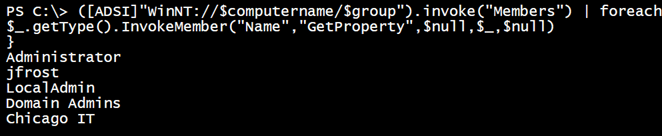
I am using the ADSPath member to distinguish domain from local accounts. You could use “Name” instead but then you would only get the last part of each member.
The [ADSI] type accelerator is a shortcut to creating a System.DirectoryServices.DirectoryEntry object. Unfortunately, I’ve never found a good .NET class for working with local users and groups. This is the best choice. Instead of using ADSI, I can do this:
$d = new-object "System.DirectoryServices.DirectoryEntry" "WinNT://$computername/$group"
Sadly, we still have the same COM issues. Using the Foreach method from PowerShell v4, the results will be the same:
$d.members().foreach({$_.gettype().InvokeMember("ADSPath","GetProperty",$null,$_,$null)})
Using CIM and WMI
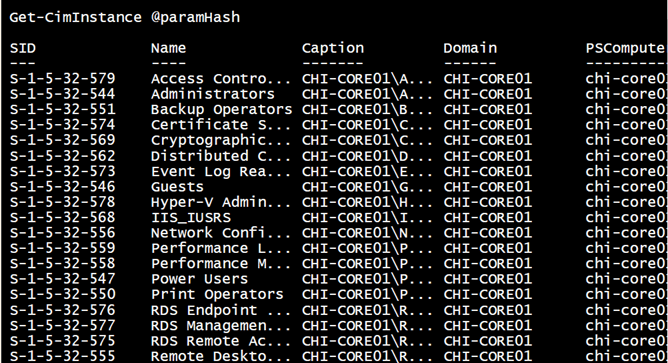
Another approach is to use WMI. You can use either the WMI or CIM cmdlets. First, let’s take a brief sidetrip and list all of the local groups on the server.
$paramHash = @{
ClassName = "win32_group"
filter = "localaccount = 'True'"
ComputerName = $computername
}
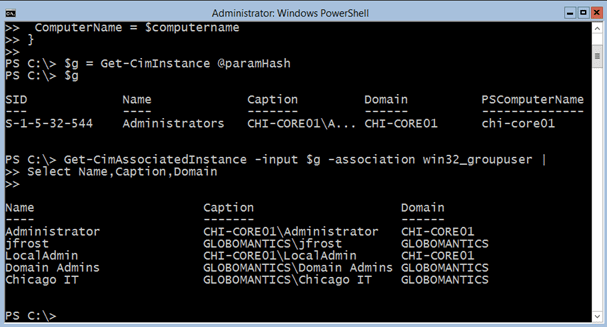
Get-CimInstance @paramHash
When querying a server that is a member of a domain, you need to filter for local accounts. Otherwise, you will list all of the domain based groups.
But I already know I want to query members of the Administrators group. To do that, I first need the group itself from WMI.
$paramHash = @{
classname = "Win32_group"
filter = "LocalAccount = 'True' AND Name = '$group'"
ComputerName = $computername
}
$g = Get-CimInstance @paramHash
Now, here’s the tricky part. Many objects in WMI are related or have what we refer to as associations. One of the associations for the Win32_Group class is Win32_GroupUser, which represents the members. Retrieving these associations is the job of Get-CimAssociatedInstance.
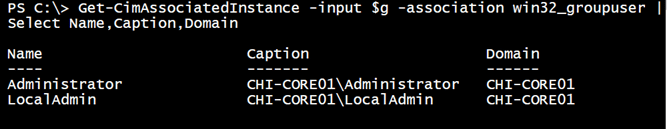
Get-CimAssociatedInstance -input $g -association win32_groupuser | Select Name,Caption,Domain
However, this is where it gets extra tricky. Here’s the result querying the server from my desktop.
No domain accounts. Yet look at the result of the same command run at the console on CHI-Core01.
Now I get the domain-based accounts. If you think about it, this makes sense. In my first command, I am making a remote connection to another server. But retrieving the domain members of the associated class appears to require another hop to a domain controller. By default Windows, and thus PowerShell, don’t like that second hop because it can’t be authenticated. This is where setting up CredSSP can help. Or you can employ a workaround.
In order for this to properly work, I need a way to authenticate to the second hop. One way to accomplish this is to use the legacy NET USE command and map a drive using credentials. I’ll need to wrap everything up in a scriptblock that I can execute using Invoke-Command.
$sb = {
param(
[string]$Group,
[System.Management.Automation.PSCredential]$credential)
#map a connection to a domain controller
$user = $credential.UserName
$pass = $credential.GetNetworkCredential().password
net use Q: \\chi-dc01\c$ /user:$user $pass | Out-Null
if (Test-Path "Q:\") {
$paramHash = @{
classname = "Win32_group";
filter = "LocalAccount = 'True' AND Name = '$group'";
}
$g = Get-CimInstance @paramhash
Get-CimAssociatedInstance -input $g -association win32_groupuser
net use Q: /delete | Out-Null
}
}
else {
Write-warning "Failed to create authenticated connection."
}
} #close scriptblock
I have hard-coded the name of the domain controller that holds the PDC emulator role in my scriptblock. At least in my network, this seems to be the most reliable method. I’ve also hard coded a drive letter to make it easier to remove the temporary drive mapping. I will pass a credential object over the wire so the password is not sent in the clear. On the remote computer, I can pull the plaintext password from the credential and use it with my drive mapping. The rest of the code consists of my CIM commands. To execute, I’ll define the credential to use and invoke the scriptblock.
$cred = Get-credential "globomantics\administrator"
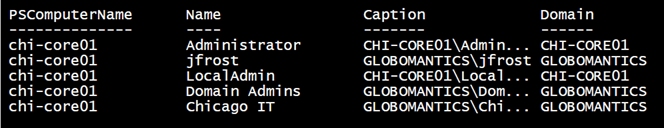
Invoke-Command -ScriptBlock $sb -ComputerName chi-core01 -ArgumentList Administrators,$cred |
Select PSComputername,Name,Caption,Domain
.
Legacy Tools
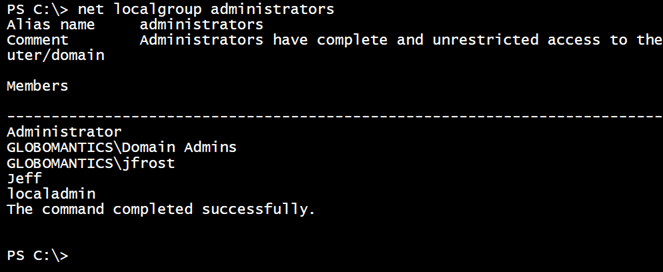
The final technique is to take advantage of the legacy NET LOCALGROUP command. Here’s how it works locally.
If all you want is a quick look, this may be all you need. Otherwise, we can use some PowerShell tricks to parse the text output and wrap it up with Invoke-Command to execute remotely.
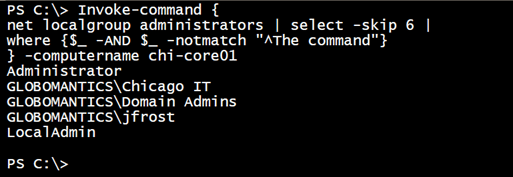
Invoke-command {
net localgroup administrators | select -skip 6 |
where {$_ -AND $_ -notmatch "^The command"}
} -computername chi-core01
Just a list of strings, but it works.
It sure would be nice if we had a set of reliable cmdlets from Microsoft for working with local users and groups. But until that day, we will have to build own using some of the techniques I’ve shown here.