
Microsoft has officially supported running SQL Server in a container since SQL Server 2017. Today, most support is for SQL Server on Linux containers, and Microsoft only supports SQL Server 2022 on Linux containers for production workloads. In this article, I’ll show you how to configure SQL Server Docker containers on Linux.
Why would you want to install SQL Server containers with Docker?
Over the past several years, containerization platforms like Docker have emerged as a popular way to run various applications. Containers are essentially like virtualization at the application level. Unlike a virtual machine that provides virtualization at the hardware level, containers provide virtualization at the application level, and all containers that run on a given system share the same underlying hardware and operating system. This makes containers a much lighter-weight implementation than a VM.
One of the big advantages of running an application like SQL Server in a container is that no installation process is required. A SQL Server database instance can be up and running as soon as the container starts. Another big advantage is the container image is always the same whenever the container starts. Applications like SQL Server persist data outside of the container by using external volume storage.
For SQL Server 2022, SQL Server deployments in Windows containers are not supported. You can create your own custom SQL Server Windows containers but they should be restricted to development and testing.
Installing Docker on Ubuntu 20.04
Ubuntu is one of the most popular platforms for managing Docker and Kubernetes containers. Ubuntu does not come with Docker preinstalled, but installing Docker on Ubuntu is simply a matter of running a few commands in the Terminal window.
- First, you need to update the system repository by running the following command. The sudo command ensures that you are running with the elevated privileges required to modify the system. Using the sudo command will require you to enter the root or systems administrator’s password:
sudo apt update
- Next, you need to Install Docker using the following command:
sudo apt install docker.io -y
- Finally, you need to install the Docker dependencies with the command below:
sudo snap install docker
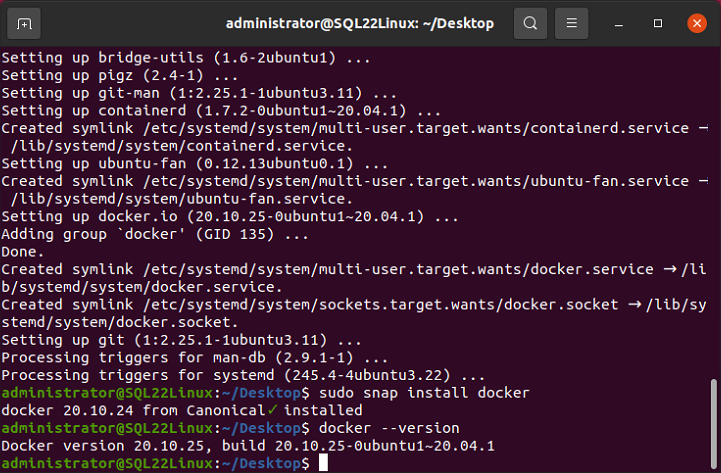
This completes the installation for the Docker engine on Ubuntu. You can verify the installation simply by running the following docker command:
docker –version
You can see the results of this installation process in the figure below.
Pulling the SQL Server Docker image
After Docker has been installed on Ubuntu, you’re ready to go ahead and pull down a SQL Server image. The following command shows how to use Docker to pull the SQL Server 2022 (16.x) Linux container image from the Microsoft Container Registry.
sudo docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2022-latest
This command pulls the latest SQL Server 2022 (16.x) Linux container image because it’s using the latest tag. However, multiple SQL Server images are available to use on the Docker hub. Each SQL Server Docker image has a fully installed and ready-to-run instance of SQL Server.
Running the SQL Server 2022 container
To run the Linux container image with Docker, you can use the following command:
sudo docker run -e "ACCEPT_EULA=Y" -e "MSSQL_SA_PASSWORD= TempPa55wd#" \ -p 1433:1433 --name sql2022 --hostname sql2022 \ -d mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2022-latest
Let me explain what this command does in detail
- This command starts by using the docker run command to start the container image.
- Next, the ‘-e’ switch is used to supply two different environment keyword pairs.
- First ACCEPT_EULA=Y enables you to accept the license agreement. This is mandatory.
- Next, the MSSQL_SA_PASSWORD= environment variable enables you to supply an ‘SA’ (SQL Server System Administrator) password. Here, it’s important to point out that the SA password must meet SQL Server’s password complexity requirements or the container will not start.
- Next the -p switch allows you to map a TCP port on the host environment (the first value) with a TCP port in the container (the second value). Here you can see they both use the SQL Server default port of 1433.
- The ‘–name’ switch is not required, but it enables you to supply a custom name for the container rather than use a randomly generated name.
- Likewise, the ‘–hostname’ switch is also not required, but it allows you to supply a custom container hostname. If you don’t specify the hostname, the container host name will default to the container ID.
- The ‘-d’ switch specifies that the container will run in the background. If you omit this, then the container will run in your interactive terminal session, effectively stopping all other actions in that session until the container exits.
- Finally, the last parameter specifies the SQL Server Docker container image that you want to use.
This command runs the Developer edition of SQL Server 2022. To specify a different edition you need to use the ‘MSSQL_PID environment’ variable.
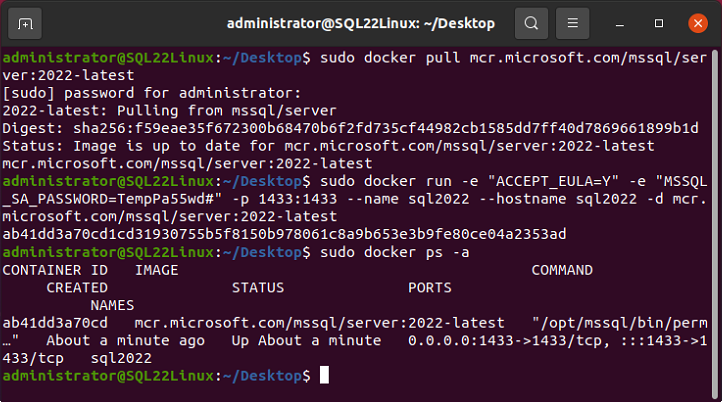
After the Docker container has been started you can use the following command to list the active containers:
sudo docker ps -a
You can see the commands to pull, run and list the SQL Server 2022 Docker container in the following figure.
You might notice all these examples are using the ‘sudo’ (Linux elevated root or Super User command) to run Docker commands. If you don’t want to use sudo to run Docker, you can configure a Docker group and add users to that group.
Connecting to the SQL Server Docker container
You can connect to the SQL Server instance running in a container exactly like connecting to any other SQL Server instance. However, you have the option of connecting from either inside the container or outside of the container.
All of the SQL Server Docker images have SQL Server command line tools (mssql-tools) installed, so you could start an interactive session using docker exec to run bash and then connect using command line tools. Alternatively, you can use regular SQL Server Management tools like SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and Azure Data Studio (ADS) to connect from outside the SQL Server container.
In order to connect to an SQL Server instance running in a Docker container with an external client tool such as SSMS, you need to know the container’s IP address. Every container will have a unique IP address much like a virtual machine would. You either need to register the container’s IP address and host name in your DNS, or you need to connect using the container’s raw IP address. Just using the IP address is generally simpler.
You can retrieve the IP address of a container using a command like the following.
sudo docker inspect -f '{{range .NetworkSettings.Networks}}{{.IPAddress}}{{end}}’ ab
172.17.0.2
Here, the docker inspect command is used in conjunction with the format switch to retrieve just the IP address of the container specified.
- In this example, the container name begins with the letters ‘ab’. However, your own container name will be different.
- If you refer back to the previous figure, you can see the container name is listed immediately following both the docker run and the docker ps commands.
- You might notice the full container ID is quite long. However, you only need to supply enough of the container ID to uniquely identify the container.
- In this case, since only one container was running, the letters ‘ab’ were enough to identify the container. The IP address of the SQL Server container was 172.17.0.2.
After getting the IP address of the container, you can use it to connect your SQL Server client tools to the container. In the following figure, you can see that we’re connecting Azure Data Studio to the running SQL Server 2022 Docker container.
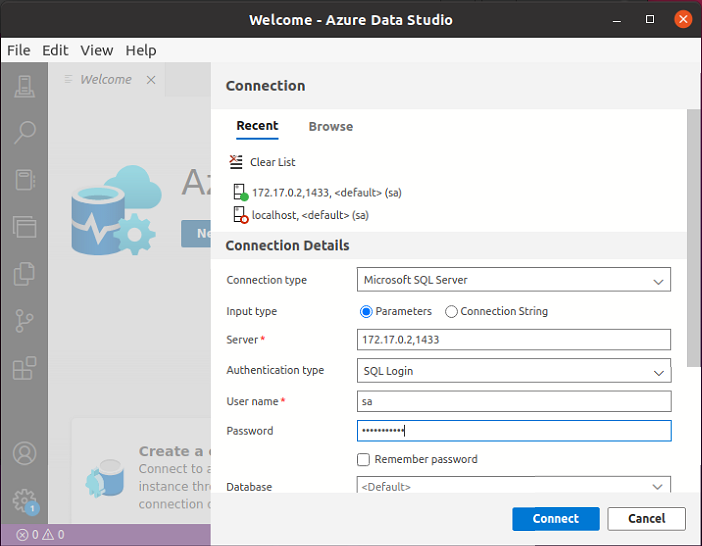
Here, I supplied the container’s IP address and the SQL Server port number followed by the SA user name and password that I supplied earlier as a part of the docker run command.
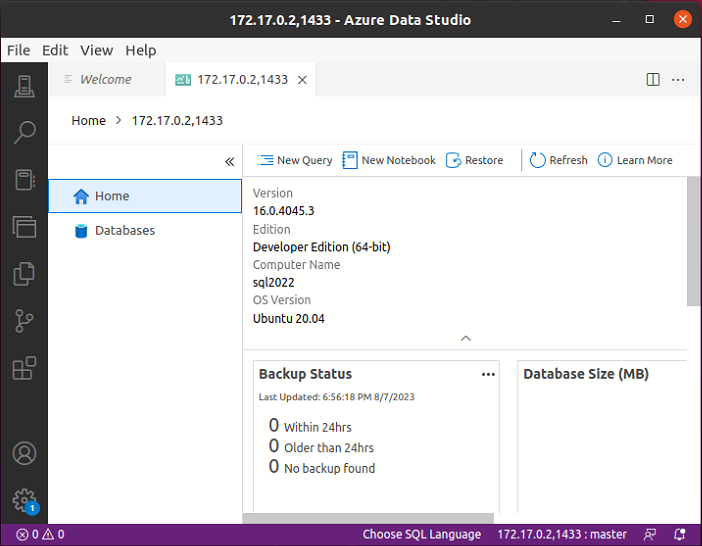
At this point, you can go ahead and use Azure Data Studio to navigate through databases, restore databases, and run queries exactly like any other SQL Server instance.
Summary
In this tutorial, you saw how to install, run and connect to a SQL Server Docker container on Ubuntu Linux. Running SQL Server from a container has several advantages over traditional VMs or physical hosts.
- First, containers are very lightweight and they are easy to start and stop.
- Containers provide a self-contained preinstalled application, so there is absolutely no need to go through all of the SQL Server setup steps in order to spin up a new SQL Server instance.
- Finally, container images are static, so if something happens to the running container, you can use the image to immediately start another instance that is identical to the previously running container at the time it was started.
Thank you for reading and please let me know in the comments if you have any questions about configuring SQL Server Docker containers on Linux.



