
Last week, the OpenSSL team patched two high-severity security vulnerabilities in its open-source cryptography tool. Microsoft announced yesterday that organizations can use Defender Vulnerability Management to detect vulnerable devices in their organization and monitor their patching process to reduce security threats.
OpenSSL is a popular cryptography library that provides open-source implementations of both SSL and TLS protocols. OpenSSL version 3.0.7 was announced last week to address both CVE-2022-3602 and CVE-2022-3786. The OpenSSL team explained that it’s a pair of buffer overflow vulnerabilities that could lead to crashes. The security flaws could be triggered by sending a malicious email with an X.509 certificate in client or server Linux builds.
The OpenSSL security team advised IT admins to monitor their environments for vulnerable instances and install the latest update. “We still consider these issues to be serious vulnerabilities and affected users are encouraged to upgrade as soon as possible,” the OpenSSL team said. “We are not aware of any working exploit that could lead to remote code execution, and we have no evidence of these issues being exploited as of the time of release of this post.”
Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management identifies vulnerable assets and tracks patching
According to Microsoft, the Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management solution enables IT admins to find flaws in the software installed on their machines. The service also provides an option to track the patching progress of exposed devices.
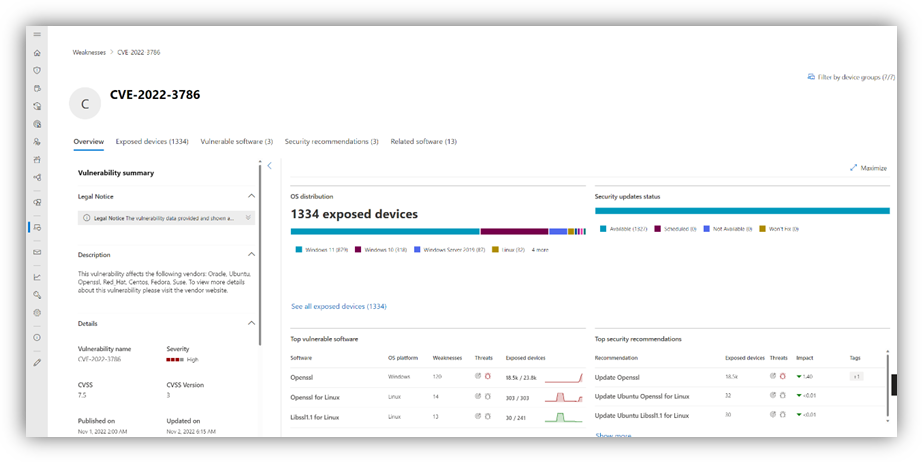
Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management is a set of tools that delivers continuous vulnerability assessment, risk-based prioritization, and remediation capabilities to help organizations minimize risks. The service is currently available in public preview for enterprise customers.
Microsoft has also provided a couple of advanced hunting queries to help IT Pros detect vulnerable devices in their environments. We invite you to check out Microsoft’s blog post for more details.



