Enhancing Cloud Security: Microsoft Details Best Practices to Thwart Identity Compromise

Key Takeaways:
- Microsoft emphasizes the need to move away from Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) due to significant security risks.
- Organizations using hybrid authentication should avoid syncing privileged admin accounts from Active Directory to Microsoft Entra ID.
- Microsoft advises using phishing-resistant methods to safeguard privileged accounts.
Microsoft has released a comprehensive guide to assist IT administrators in promptly and effectively responding to security breaches within their organizations. The Microsoft Incident Response team detailed best practices to protect workloads in cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments.
Decommission AD FS
Microsoft explained that the Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) could pose a significant risk to enterprise environments. This service enables users to access multiple systems or applications with a single set of credentials across security boundaries. However, Microsoft has warned that a single misconfiguration could compromise the entire identity infrastructure.
Additionally, threat actors have been targeting on-premises federation servers to steal Token Signing Certificates. This allows hackers to create forged SAML tokens and gain unauthorized access to Microsoft Entra ID. To mitigate this risk, Microsoft recommends that organizations move away from AD FS and adopt an Entra ID-based authentication method instead.
“Microsoft IR strongly recommends moving to native Microsoft Entra ID authentication and decommissioning AD FS (or other federated identity providers) where possible. This reduces the overall complexity of the organization’s identity plane and makes it easier to secure identities,” Microsoft explained.
Avoid syncing privileged admin accounts from Active Directory
Organizations that use hybrid authentication mechanisms usually synchronize their user accounts and groups from Active Directory to Microsoft Entra ID. However, this method presents security risks and is not advisable, especially when dealing with privileged administrative accounts.
Microsoft recommends that organizations should use native Entra ID accounts for admin accounts. Additionally, the company advises customers to use phishing-resistant methods such as Conditional Access and Privileged Identity Management (PIM).
Block token theft of privileged accounts
Microsoft notes that cybercriminals use malware or adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) attacks to steal tokens from endpoint devices. These tokens can be used to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) and gain access to sensitive data.
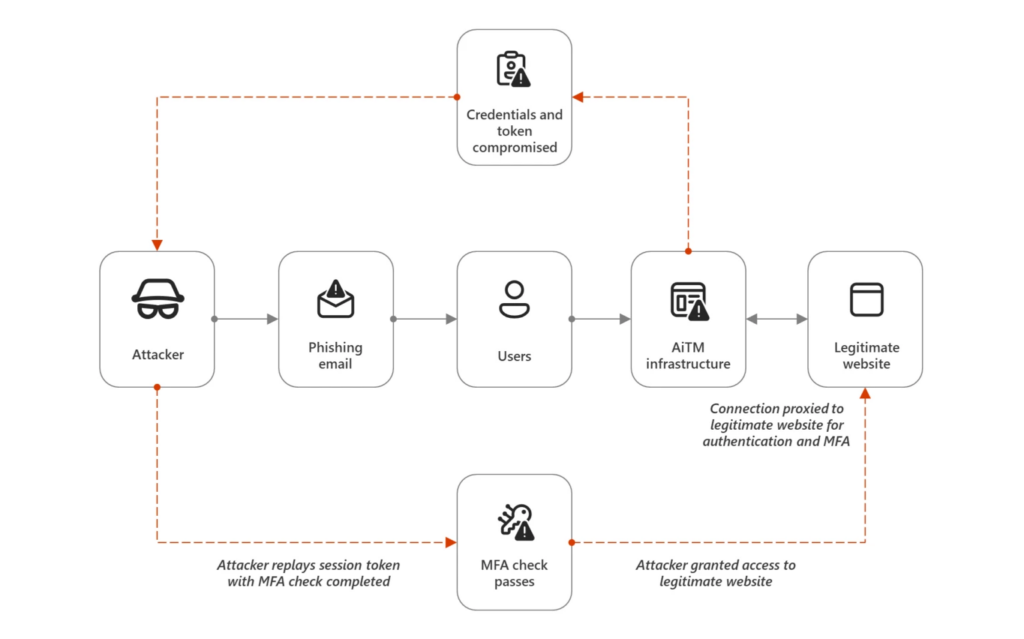
To combat this issue, organizations should use FIDO2 keys, certificate-based authentication, and other phishing-resistant methods to protect highly privileged accounts. IT admins can also access the Microsoft Entra ID Portal and other management solutions with privileged access workstations.
Microsoft has launched a token protection solution that binds issued tokens to a specific device. This solution is currently available in preview in Microsoft Entra Conditional Access.
Restrict workload identity privileges and monitor CA misconfigurations
According to Microsoft, some organizations tend to give excessive permissions to workload identities. A workload identity refers to a non-human identity assigned to specific applications or services operating in the cloud. To prevent security risks, Microsoft suggests that IT admins must ensure that these app identities follow the principle of least privileges.
Moreover, organizations should create alerts for new credentials, malicious sign-in activities, and the assignment of additional privileges to existing applications. They can also use Conditional Access for workload identities to block access based on elevated risk patterns.
Last but not least, Microsoft urges customers to require multifactor authentication when joining or registering a device. It’s highly recommended to configure alerts in order to prevent unauthorized changes to Conditional Access policies. Microsoft also suggests using simple authentication and authorization mechanisms within enterprise environments. It’s also important to audit privileged role assignments regularly.



