Controlling Password Replication on Read-Only Domain Controllers
In today’s Ask the Admin, I’ll show you how to change which users can have their account credentials cached on read-only domain controllers (RODC).
Windows Server 2008 saw the introduction of RODCs to address some of the security risks of placing DCs in locations that lack the physical security of centralized datacenters. Read-only copies of the Active Directory (AD) database partitions and SYSVOL folder are hosted on RODCs to prevent attackers making global changes to AD.
When only a RODC is present on the local subnet, users are authenticated against a writeable DC, even if it’s located across a wide area network. But it’s possible to cache credentials of accounts that use the local branch office networks to improve login speed and reduce network traffic. Additionally, there’s a deny list preventing password caching of sensitive AD accounts, such as the domain administrator account.
For more information on RODCs, see Deploy a Read Only Domain Controller on the Petri IT Knowledgebase. You can also modify which AD attributes are replicated to RODCs using the filtered attribute set (FAS).
Cache credentials on an RODC
To perform the instructions below, you must have an existing AD domain with at least one RODC.
- Log in to any domain controller with an account that has permission to modify AD group membership.
- Open Server Manager from the Start screen.
- In Server Manager, select Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) from the Tools menu.
- In Active Directory Users and Computers, expand your AD forest and domain in the left pane, and click the Users container.
- In the right pane of (ADUC), double click Allowed RODC Replication Group.
- In the group dialog box, switch to the Members tab.
- Click Add at the bottom of the dialog, then enter the names of any users or groups you’d like to add to Allowed RODC Replication Group, and then click Check Names.
- If matching accounts are found in AD, the names will appear underlined in the dialog box after clicking Check Names.
- Once you’re done adding accounts, click OK.
- Click OK in the group dialog box to complete the process.
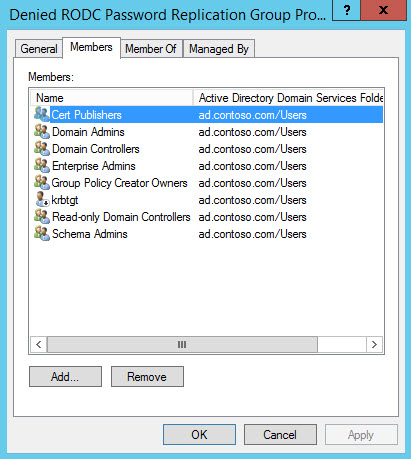
Don’t forget that you can block credentials being cached by adding the relevant accounts to the Denied RODC Replication Group using the same process as above. And as with most permission scenarios, deny permissions override allow permissions. The Denied RODC Replication Group has the following members by default:
- Enterprise Domain Controllers
- Enterprise Read-Only Domain Controllers
- Group Policy Creator Owners
- Domain Admins
- Cert Publishers
- Enterprise Admins
- Schema Admins
- Domain-wide krbtgt account
In this article I showed you how to configure which user and computer accounts can be cached on a RODC using built-in groups in Active Directory.




