What is AWS Lambda?

AWS Lambda is an event-driven, serverless compute service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It enables developers to run code in response to events without having to manage the computing resources and infrastructure needed to run these applications. In this article, I’ll explain how AWS Lambda works and detail the best use cases for this platform.
What is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda allows developers to run event-driven code for almost every type of service, application, or framework. The platform can auto-scale to handle varied workloads and allow developers to focus solely on writing code for their applications.
AWS Lambda relies on Lambda functions, which can be written in different programming languages and triggered by events such as changes in data or user actions. The serverless architecture of AWS Lambda provides a cost-efficient platform to customers who will only be charged for the actual usage of their function without any idle time or upfront costs.
The major components of AWS Lambda
Here are the major components of AWS Lambda you should know about to get started with the serverless computing platform.
- Lambda functions: Lambda stores the code written by developers in a function that can be invoked by various triggers. Lambda functions define the logic and all the actions to be executed when the function is triggered, and they’re a crucial component of Lambda.
- Triggers: A trigger is an event that can synchronously or asynchronously invoke a Lambda function.
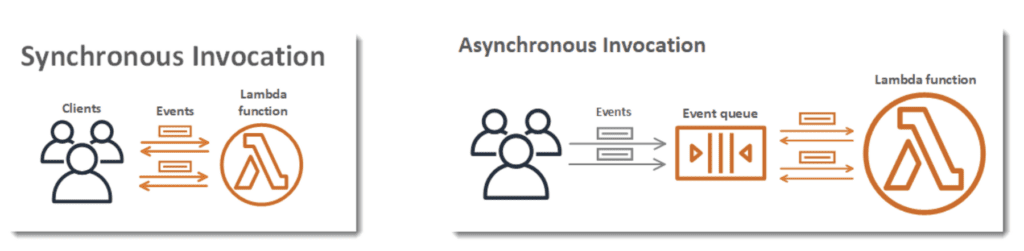
- Event Source: Lambda functions need an event source to trigger their execution. These events can include changes in data (possibly at scheduled time intervals), user actions, or events coming from other AWS products such as Amazon S3 buckets or Amazon API Gateway.
- Handler: Handler is a component within Lambda that acts as an entry point for the event source to trigger an event for the execution of a Lambda function.
- Execution environment: Every Lambda function provides a runtime environment for code execution. AWS Lambda supports multiple programming languages including Java, PowerShell, C#, Python, Node.js, and more.
- Execution role: The execution role is an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role that grants a Lambda function the necessary permissions for reading or writing data.
How does AWS Lambda work?
AWS Lambda leverages the aforementioned components to operate. Here’s how the platform works in practice.
Step 1: Creating an AWS Lambda function
The lifecycle of Lambda starts with the creation of a Lambda function using any of the supported programming languages in the AWS Lambda Console. This function acts as a container for the code that your Lambda function will run.
Step 2: Event trigger
The aforementioned Lambda function can be triggered using an event trigger. These triggers can be configured to activate following changes in data, user interactions, and more.
Step 3: Function invocation
When an event occurs, it triggers the invocation of the associated Lambda function. When this happens, AWS auto-provisions the Lambda function with the necessary permissions to run the code.
Step 4: Code execution
In this step, the Lambda function’s code starts executing within the runtime environment allocated by AWS. The data provided by the event trigger is processed for code execution.
Step 5: Scaling and concurrency
An AWS Lambda function can also auto-scale depending on the workload at hand. You can also execute multiple instances of the same function to process different jobs simultaneously. This is an optional step in the lifecycle of a Lambda function to ensure scalability and responsiveness.
Step 6: Response generation
In this step, AWS Lambda generates the output or finishes the execution of the code defined in the Lambda function.
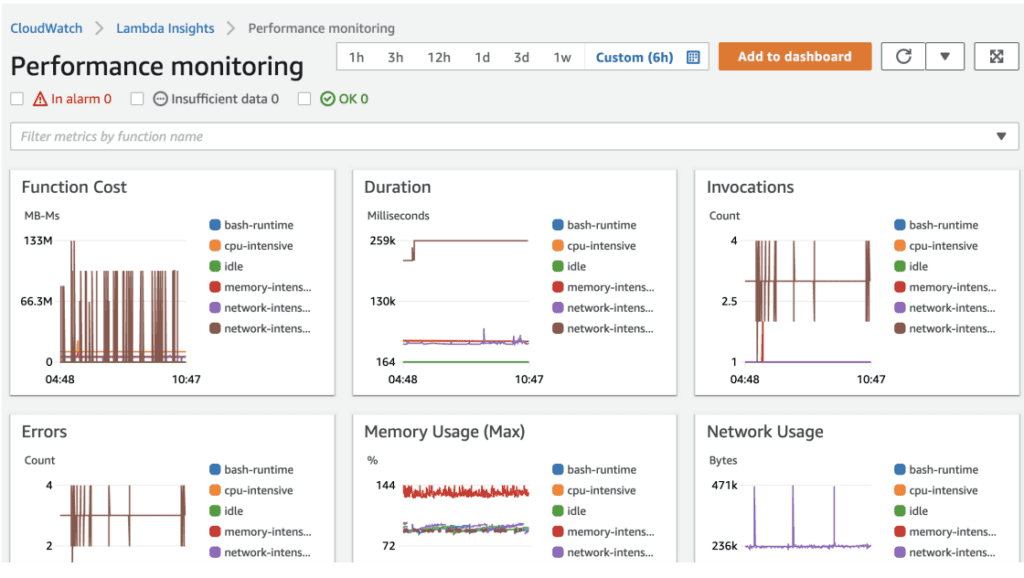
Step 7: Logging and monitoring
AWS Lambda provides built-in logging and monitoring features to track and debug the execution of Lambda functions. Developers can leverage this to build custom dashboards and alarms and monitor the performance of their Lambda functions via the AWS Management Console. Moreover, they can leverage dedicated AWS services such as Amazon CloudWatch to track logs.
[Image: Lambda Metrics]
What are the best use cases for AWS Lambda?
Lambda can serve as a versatile platform for several application scenarios. Here is a list of the best use cases for AWS Lambda.
Serverless applications
AWS Lambda powers the backend services of many serverless web and mobile applications on the market today. The platform can be used to manage core modules of applications such as authentication and authorization, database interactions, data processing, event handling, session management, and more.
Real-time file processing
AWS Lambda can be configured to perform real-time processing of all files and data flowing in from Amazon S3, Amazon DynamoDB, and other database systems.
Data processing and ETL
Developers can use AWS Lambda for data processing tasks including extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) in real-time or in batches. It can also perform several other data validations and trigger upstream or downstream workflows.
Analytics
One of the key use cases of AWS Lambda is real-time stream processing and data analysis. Lambda functions can be used to ingest, process, and transform data as it arrives, enabling real-time insights and actionable analytics.
Microservices
AWS Lambda makes it easy for developers to build microservice architectures that integrate with several AWS services to power applications of any size and scale.
Multimedia analysis
Another interesting use case for AWS Lambda is real-time multimedia analysis. As an example, Mediainfo, a popular tool used to display the most relevant video and audio file data can be run as an AWS Lambda function.
Function-as-a-Service
AWS Lambda is a popular application of the Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) cloud paradigm, as it provides a platform for executing serverless functions in response to events or requests.
Apart from these aforementioned common use cases, Lambda can also be used to schedule cron jobs and tasks, build data pipelines, handle the back-end code of applications, and even build intelligent chatbots and voice assistants. Overall, there’s a large field of opportunities for developers
The pros and cons of using AWS Lambda
Before you get started with AWS Lambda, let’s look at the main advantages and disadvantages of this serverless computing platforms
Advantages
- Scalability: Being a cloud service, Lambda can be scaled up and down to handle varying workloads while ensuring optimal performance. Lambda also supports various execution environments it can integrate with many AWS services.
- Language Flexibility: Supporting all the major programming languages including Java, Python, C#, Node.js, Ruby, PowerShell, GO, Rust, and others, Lambda is considered one of the most programmer-friendly serverless computing platforms on the market
- Cost-efficiency: Lambda eliminates the overhead of managing infrastructure, operating systems, and servers. Moreover, you will only be charged for the function execution time.
- Control: Developers can get flexible with AWS Lambda and create multiple functions to perform granular operations. They can also leverage this flexibility to build and debug complex systems.
While there are a ton of benefits that Lambda offers you, there are certain drawbacks that you need to be aware of before choosing this platform.
Drawbacks
- Limited Execution Environment: Every Lambda function comes with certain execution environment limitations such as memory and runtime library limitations. That can make Lambda functions not ideal for prolonged execution or long-running tasks.
- Cold Starts: When a Lambda function is triggered after being inactive for a while, it will need time to initialize its runtime environment and resources needed for its execution, which causes an increase in response times.
- Complexity: Using AWS Lambda for building, managing, and orchestrating complex applications can cause some organizational headaches. If you decide to set up and deploy hundreds of Lambda functions to build a large-scale application, that can become challenging pretty quickly.
- Statelessness: Lambda functions are stateless by design. This absence of a persistent state can add complexities when building applications that require session or state persistence.

How does AWS Lambda pricing work?
Getting started with AWS Lambda is free of cost. The AWS Free Tier provides a certain amount of monthly requests and compute time at no cost.
AWS Lambda offers every account holder 1 million free requests and 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time every month. However, beyond this free tier, the pricing for AWS Lambda depends on several factors such as the number of requests, memory usage, and execution time. Pricing also varies based on the AWS region where the function is executed.
Here are the three primary components that play a vital role in the pricing of AWS Lambda
Number of requests
The cost associated with the number of requests will vary depending on the AWS region where the service is being used. For instance, in the US East (N. Virginia) region of AWS, the price per 1 million requests is $0.20.
Memory
With AWS Lambda you can choose memory sizes in increments of 64MB, and the memory supported by each Lambda function can range from 128 MB to 10,240 MB (10GB). The cost per GB-second in the US East (N. Virginia) region of AWS is $0.00001667 per GB-second for 128 MB of memory.
Duration
Pricing also takes into account the execution time of a Lambda function alongside the total memory allocation. The cost per 100 milliseconds of execution time for 128MB in the US East (N. Virginia) region is $0.00001667.
Moreover, you can expect additional costs in your billing for data transfers, use of other AWS services in conjunction with Lambda, and storage. For a detailed breakdown of pricing or to request a pricing quote, visit the AWS Lambda Pricing page.
A versatile serverless computing platform
AWS Lambda combines the flexibility of cloud services with the efficiency of serverless computing. Its event-driven architecture and support for the major programming languages make it possible to build real-time applications with great flexibility. Last but not least, allowing developers to write code without having to deal with the overhead of environment, resource, and infrastructure management can be quite transformative.



