Registering the Microsoft Hyper-V Volume Shadow Copy Service with Windows Server Backup

Overview
There are times when you will need to back up a virtual machine that needs to remain in a running state. Fortunately, Microsoft has provided a handy tool on its Windows Server platform that allows admins to make backups to volumes while applications continue to run and write to those volumes called Volume Shadow Copy Service.
Volume Shadow Copy Service
Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) is an infrastructure on Windows server platforms that enables applications to create shadow copies. These disk volume backups can be performed while applications continue to write to those volumes. There are basically 3 components that are involved in a VSS backup:
- A VSS requestor is an application that requests VSS services to create shadow copies. Typically, VSS requestors are backup applications such as Windows Server Backup. Requestors communicate with writers to gather system data and signal writers to prepare data for backup.
- A VSS provider manages storage volumes and creates shadow copies on demand.
- A VSS writer is an application or service that writes data to disk and cooperates with VSS providers and requestors. During backups, writers ensure that data is in the proper state for a shadow copy. Writers exist for several types of applications, such as Exchange 2007/2010, Hyper-V, NTDS and others.
In order to properly back up virtual machines that are in running state, a VSS-aware backup application (or requester) must be used, and that application must notify the VMs that they are being backed up.
This quote explains what VSS does pretty nicely:
“Backing up a Hyper-V virtual machine requires coordination between the Windows VSS instances on the host and the guest. To do so, the Hyper-V Integration Components installs code to every VM. This code allows the Windows VSS writer on the host to communicate with any registered VSS Writers inside running VMs to coordinate quiescence activities. This stacking of VSS instances ensures that applications successfully quiesce as virtual hard disk (VHD) files are backed up.”
–Windows VSS virtual machine backup strategies: Hyper-V vs. VMware
Because Windows Backup uses a VSS writer to create the snapshots, you will need to manually register the Microsoft Hyper-V VSS writer with Windows Server Backup before you can use Windows Server Backup.
If you do not manually register the Microsoft Hyper-V VSS writer, it may appear that the backup has completed successfully. However there is a chance that the VM might not be properly backed up if they were in a running state when the back up took place.
You can read more about this process in the following KB:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/958662
Registering Hyper-V VSS writer
Warning!
This document contains instructions for editing the registry. If you make any error while editing the registry, you can potentially cause Windows to fail or be unable to boot, requiring you to reinstall Windows. Edit the registry at your own risk. Always back up the registry before making any changes. If you do not feel comfortable editing the registry, do not attempt these instructions. Instead, seek the help of a trained computer specialist.
To register the Hyper-V VSS writer with Windows Server Backup, follow these steps:
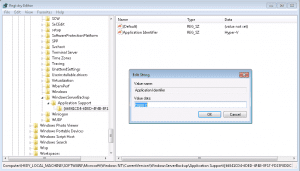
- Click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK. If you get a UAC prompt, acknowledge it.
- Navigate to the following registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion
- Right-click CurrentVersion, point to New, and then click Key. Type WindowsServerBackup, and then press Enter.
- Right-click WindowsServerBackup, point to New, and then click Key. Type Application Support, and then press Enter.
- Right-click Application Support, point to New, and then click Key. Type {66841CD4-6DED-4F4B-8F17-FD23F8DDC3DE}, and then press Enter.
- Right-click {66841CD4-6DED-4F4B-8F17-FD23F8DDC3DE}, point to New, and then click String Value. Type Application Identifier, and then press Enter.
- Right-click Application Identifier, and then click Modify. In the Value data box, type Hyper-V, and then click OK.
- Exit regedit.
BTW, you can create a text file with a .REG extension and paste the following information in it:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\WindowsServerBackup\Application Support\{66841CD4-6DED-4F4B-8F17-FD23F8DDC3DE}]
“Application Identifier”=”Hyper-V”
After saving, merge the file by double-clicking it.
Summary
And that’s it! Backing up a Virtual Machine that needs to remain in a running state can be a valuable skill and the first step is to first register Volume Shadow Copy Service on a Windows Server platform.