
Microsoft has published an advisory about a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) malware called XorDdos that is targeting Linux endpoints and servers. The company has warned that its security researchers have detected a 254 percent surge in the malware’s activity during the last six months.
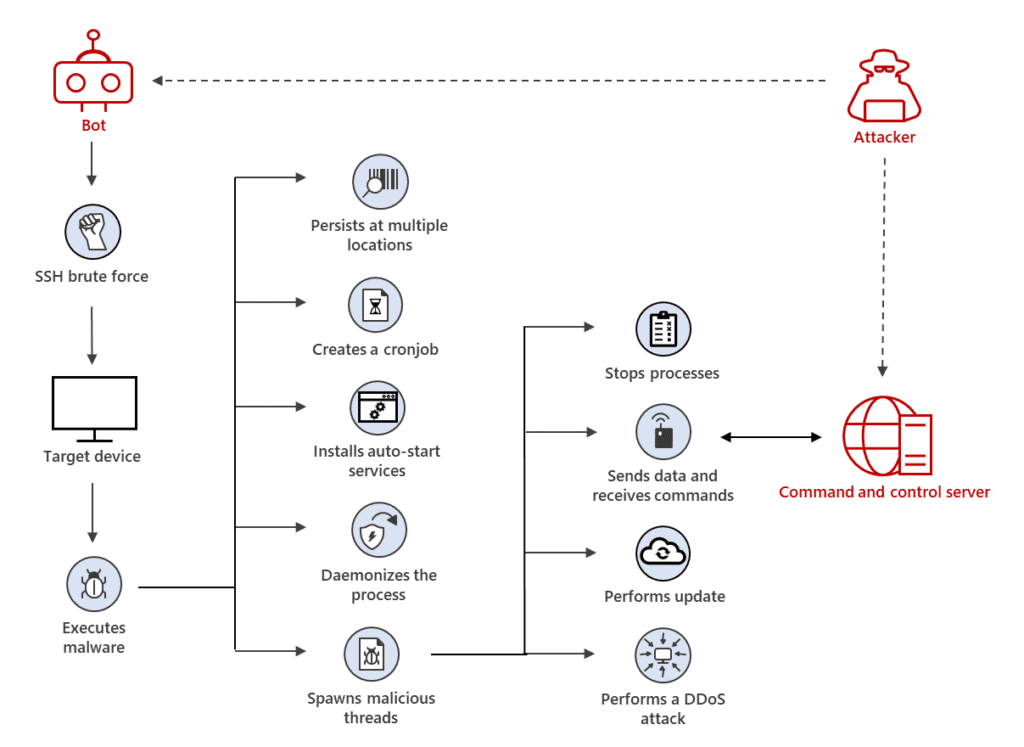
The security research group MalwareMustDie first discovered the XorDDoS malware back in 2014. The Linux botnet enables the attackers to scan the network for unprotected Linux-based servers. The primary goal is to find the matching admin credentials on Secure Shell (SSH) servers and then use root privileges to deploy the malware on a Linux machine. Once done, the botnet lets the attacker gain full control over the target device.
More recently, Microsoft threat researchers noticed a massive increase in the XorDDoS malware attacks. The company highlights that the Linux botnet utilizes its kernel rootkit component to hide its ports and processes from malware detection tools. The XorDdos malware uses numerous persistence mechanisms to target different Linux distributions such as ARM, x86, and x64.
“Its evasion capabilities include obfuscating the malware’s activities, evading rule-based detection mechanisms and hash-based malicious file lookup, as well as using anti-forensic techniques to break process tree-based analysis. We observed in recent campaigns that XorDdos hides malicious activities from analysis by overwriting sensitive files with a null byte,” the Microsoft 365 Defender Research Team.
Microsoft provides mitigation strategies to protect against Linux threats
Microsoft has provided a couple of mitigation strategies to help IT Pros protect their organizations against the emerging XorDdos malware attacks. It advises customers to use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and enable cloud-delivered protection in Microsoft Defender Antivirus.
Additionally, the Microsoft research team also urges employees to use Microsoft Edge or any web browser that is compatible with Microsoft Defender SmartScreen. We invite you to check out the Microsoft Security blog for more details.



