
Microsoft has released a new firmware analysis feature for Microsoft Defender for IoT. The new capability conducts an automated analysis of a binary firmware image that runs on an IoT device to identify potential security threats and vulnerabilities.
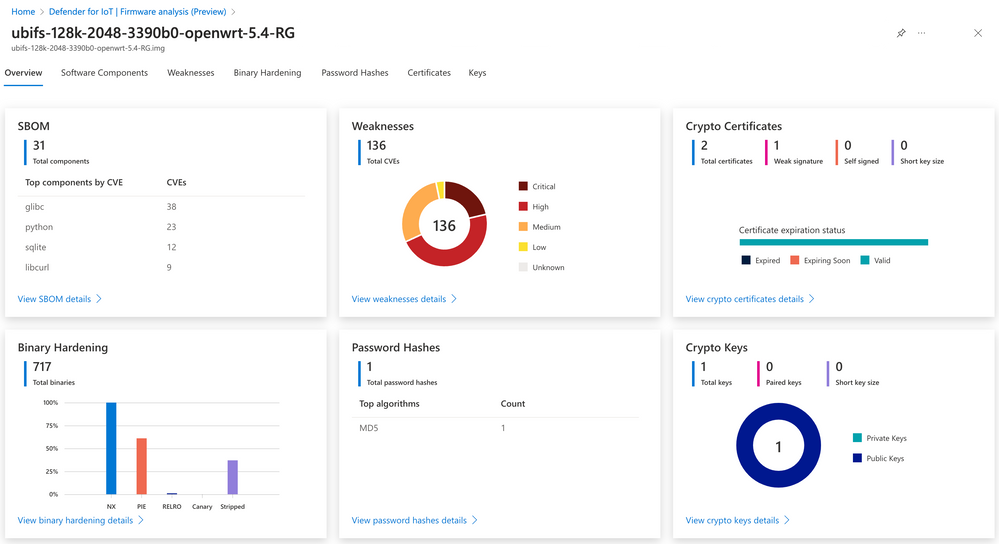
With firmware analysis, IT admins can view a detailed listing of open-source packages found in the firmware image. The feature helps security teams to scan the firmware components for publicly known Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs). This information can then be passed on to organizations and device manufacturers.
Secondly, the firmware analysis feature detects binaries that haven’t enabled select security flags during the compilation process. These include position-independent executables, buffer overflow protection, and other popular binary hardening methods.
Firmware analysis detects weak user accounts
In Microsoft Defender for IoT, the firmware analysis capability detects built-in user accounts and the cryptographic algorithms used for the encryption of password hashes. It enables IT admins to detect vulnerable IoT devices in corporate networks. Firmware analysis also makes it easier to identify cryptographic material embedded in the devices.
“Adversaries commonly target these materials as entry points. For example, expired, revoked, or self-signed SSL certificates can compromise communication from a device to a cloud service, potentially leaking organizational data or opening the device up to exploitation. Another potential threat vector are public and private keys that were inadvertently left in the device by the developers and grant attackers access to the device or cloud service,” Microsoft explained.
Getting started with firmware analysis
To get started with firmware analysis, IT admins will need to navigate to the Firmware analysis (preview) blade in Microsoft Defender for IoT. Then, upload an unencrypted Linux-based firmware image received from the device vendor.
Microsoft says that the new firmware analysis capabilities are available in public preview for enterprise customers. It should help organizations to better protect their IoT environments against emerging threats.


