Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Rolls Out Offline Security Intelligence Update Feature for Linux Devices

Key Takeaways:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint has introduced the offline security intelligence update feature in public preview, catering specifically to Linux devices.
- It enables organizations to use a local hosting server to manage and distribute security intelligence updates.
- Administrators gain granular control over the update process, with options to manage the frequency of updates and test signatures before deployment.
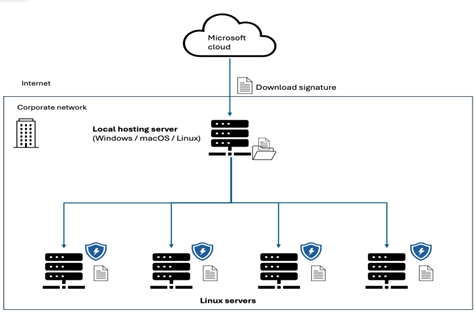
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint has added a new Offline Security Intelligence Update feature in public preview for Linux devices. This functionality enables organizations to update security intelligence even when internet connectivity is limited or unavailable, by utilizing a local hosting server.
Microsoft has highlighted several key benefits of the new offline security intelligence update feature for Defender for Endpoint customers. The feature lets administrators manage the frequency of signature updates downloaded on the local server. They can also test the downloaded signatures in a controlled environment before deploying them widely.
The offline security intelligence update feature offers a significant reduction in network bandwidth usage by consolidating downloads to a single local server. Moreover, the local server can operate on any operating system (Mac, Windows, Linux) and doesn’t require the installation of Defender for Endpoint. If the offline update fails, administrators have the option to opt for online updates from the Microsoft cloud.
How does the offline security intelligence update feature work?
First up, customers will need to set up a local Web/NFS server (Mirror Server) to connect with the Microsoft cloud for downloading updates. Then, administrators will execute a script to configure cronjob/task scheduler jobs on the local server. This automation enables Linux devices to retrieve updates at intervals defined by the user.
Microsoft says that the signature updates downloaded onto Linux endpoints must undergo verification to ensure integrity and compatibility before being loaded into the AV engine. Subsequently, IT admins will need to update the managed config JSON file on the Linux endpoints to configure the update process.
Currently, configuring the security intelligence update feature is limited to a managed JSON file. However, Microsoft plans to enhance this capability by allowing administrators to configure this setting through Security Settings Management in the future.
Prerequisites
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint version “101.24022.0001” (or higher) should be installed on the Linux endpoints. Additionally, connectivity to the local hosting server (Mirror Server) is required for the Linux endpoints. The local server should also support HTTP/HTTPS or a network share server and have access to the following Microsoft URLs:
- https://github.com/microsoft/mdatp-xplat.git
- https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2144709
Overall, the new feature is designed to enhance overall security posture and provides a robust mechanism for maintaining critical security measures in restricted environments. Microsoft notes that IT admins can head over to GitHub to get the offline security intelligence script. You can learn more about how to configure Linux Endpoints and the local server in this support document.


