
Researchers have developed an exploit for a new critical vulnerability in the FortiGate firewall that affects around 336,000 Internet-exposed devices. The security advisory warned that IT admins have yet to install the patches released in June 2023.
The heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability (tracked as CVE-2023-27997) has a severity rating of 9.8 out of 10. It enables a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code and completely take over vulnerable devices. The security vulnerability affects multiple versions of FortiOS and FortiProxy SSL-VPN software.
Bishop Fox’s research team, who discovered the vulnerability, found that it affects all SSL VPN appliances running FortiOS. Fortinet quietly released security updates to address the flaw on June 8. At the time, the company confirmed that it may have been exploited in a limited number of attacks targetting government, manufacturing, and other critical infrastructure sectors.
69 percent of devices remain unpatched against FortiGate vulnerability
Bishop Fox researchers said that around 69 percent of affected devices exposed on the Internet still remain unpatched. They also discovered that the most vulnerable FortiGate devices hadn’t been updated for the past eight years. Bishop Fox researchers said that these machines are vulnerable to critical security flaws.
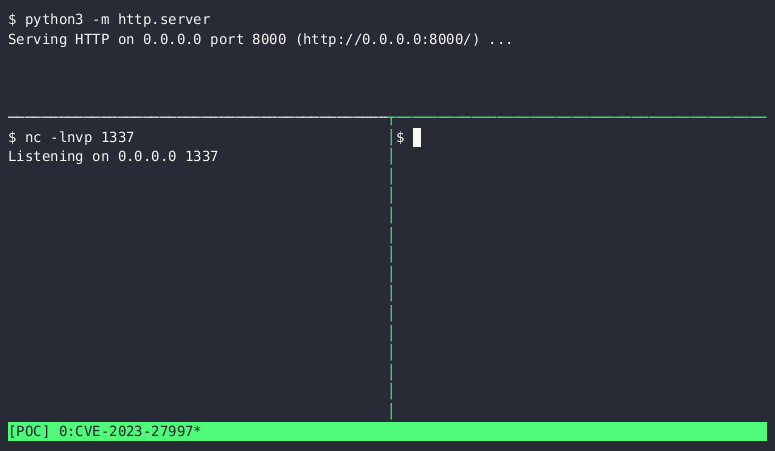
“Bishop Fox’s Capability Development team built an exploit for CVE-2023-27997 that we’re continuously using to test Cosmos customers. In the screen capture, our exploit smashes the heap, connects back to an attacker-controlled server, downloads a BusyBox binary, and opens an interactive shell,” said Caleb Gross, Director of capability development at Bishop Fox.
It’s highly recommended that IT admins should patch their firmware immediately to mitigate potential risks. If you’re interested, we invite you to check out Fortinet’s advisory for more details.


