Cybercriminals Compromise Senior Executives’ Azure Accounts – Everything You Need to Know

Key Takeaways:
- A sophisticated cyber campaign is actively targeting Microsoft Azure corporate accounts, posing a significant risk to organizations’ sensitive data and financial assets.
- The attack is particularly aimed at senior executives, with malicious tactics such as phishing emails and multi-factor authentication manipulation used to compromise their Azure accounts.
- Security researchers emphasized the need for continuous monitoring and proactive security measures to thwart potential cyber threats.
Cybersecurity researchers have revealed an ongoing campaign targeting Microsoft Azure corporate accounts. The malicious campaign is leading to the theft of sensitive corporate data and financial assets from numerous organizations.
Specifically, Proofpoint researchers first spotted the ongoing activity back in November 2023. The threat actors used malicious emails with shared documents to target employees with access to corporate resources across affected organizations. Some of these documents included embedded links that redirect users to malicious phishing pages.
“The affected user base encompasses a wide spectrum of positions, with frequent targets including Sales Directors, Account Managers, and Finance Managers. Individuals holding executive positions such as “Vice President, Operations”, “Chief Financial Officer & Treasurer” and “President & CEO” were also among those targeted,” Proofpoint researchers explained.
After the initial breach, the attackers utilize different forms of multi-factor authentication to prevent the victims from regaining access to their compromised accounts. In some instances, the hackers registered their own phone number or authenticator app to receive verification codes. They also perform lateral movement within affected organizations through Exchange Online.
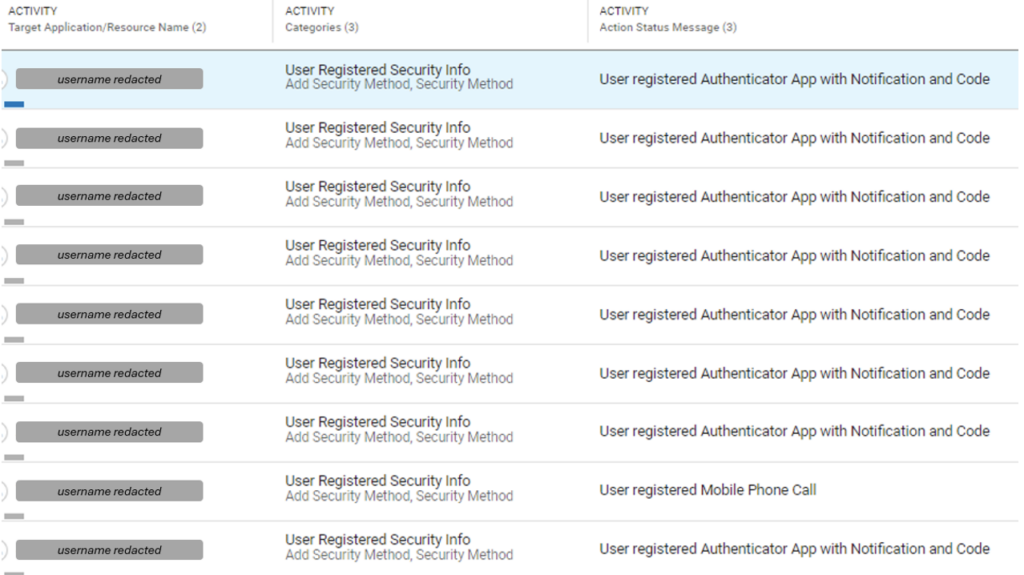
Additionally, the attackers managed to send customized messages to personnel in the HR and finance departments of the target organization. They were also able to steal sensitive corporate data such as user credentials, financial assets, and internal security protocols. The hackers created dedicated rules to delete any traces of their malicious activities from the victims’ mailboxes.
Best practices to protect Microsoft Azure accounts against cyberattacks
Proofpoint recommends that IT administrators should keep a close eye on user agents and source domains of incoming connections to employee accounts within their organizations. Customers should also track potential signs of initial access attempts and account takeovers.
Last but not least, organizations should enforce strict password hygiene to enhance the security of corporate accounts. It’s also advisable to implement auto-remediation policies to minimize the impact of any potential damage in case of a successful security breach.



