How do I install and configure a new Windows 2000 DNS server to prepare for a new AD Domain?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the Active Directory locator in Windows 2000. Active Directory clients and client tools use DNS to locate domain controllers for administration and logon. You must have a DNS server installed and configured for Active Directory and the associated client software to function correctly. This article guides you through the required DNS configuration.
NetBIOS name resolution (WINS server, LMHOSTS file, or NetBIOS broadcast) is still required for earlier versions of Windows to resolve network resources on an Active Directory domain.
DNS Server Requirements for Active Directory Support
Microsoft recommends that you use Microsoft DNS Server as supplied with Windows 2000 Server as your DNS server. However, Microsoft DNS is not required.
The DNS server that you use:
Version 8.1.2 and later of BIND (a popular DNS server implementation) supports both the SRV RR and dynamic update. (Version 8.1.1 does support dynamic updates but it has flaws that were fixed in 8.1.2.) If you are using a version of BIND that does not support dynamic update, you need to manually add records to the DNS server.
Note: Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 Server DNS does not support the SRV record. Use DNS Server that is provided with Windows 2000 Server.
Starting with a Windows 2000-Based Stand-Alone Server
This server becomes a DNS server for your network. You can also promote it to the domain controller role at a later time.
In the first step, you assign this server a static Internet Protocol (IP) configuration. DNS servers should not use dynamically assigned IP addresses, because a dynamic change of address could cause clients to lose contact with the DNS server.
Configure TCP/IP
- Click Start, point to Settings and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Network and Dial-up Connections.
- Right-click Local Area Connection, and then click Properties.
- Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- Assign this server a static IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address. Enter the server’s IP address in the Preferred DNS server box.
- Click Advanced.
- Click the DNS Tab.
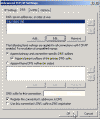
- Select “Append primary and connection specific DNS suffixes”
- Check “Append parent suffixes of the primary DNS suffix”
- Check “Register this connection’s addresses in DNS”. If this Windows 2000-based DNS server is on an intranet, it should only point to its own IP address for DNS; do not enter IP addresses for other DNS servers here. If this server needs to resolve names on the Internet, it should have a forwarder configured.
- Click OK to close the Advanced TCP/IP Settings properties.
- Click OK to accept the changes to your TCP/IP configuration.
- Click OK to close the Local Area Connections properties.
Note: If you receive a warning from the DNS Caching Resolver service, click OK to dismiss the warning. The caching resolver is trying to contact the DNS server, but you have not finished configuring the server.
Install the DNS Service
Continue to the next step to install Microsoft DNS Service:
Install and Configure Windows 2000 DNS Server
Next, after installing and configuring DNS, proceed to the next 2 steps:
Promote This Server to Domain Controller (Optional – Recommended)
Promote this server to the domain controller role by using the Dcpromo.exe utility.
After the server has been promoted to the domain controller role, the DNS server can use the Active Directory Storage Integration feature (this is the recommended path). Proceed to the next step if you want to use Active Directory Storage Integration for DNS.
Enable Active Directory Integrated DNS (Optional – Recommended)
Active Directory Integrated DNS uses the directory for the storage and replication of DNS zone databases. If you decide to use Active Directory Integrated DNS, DNS runs on one or more domain controllers and you do not need to set up a separate DNS replication topology.
- In DNS Manager, expand the DNS Server object.
- Expand the Forward Lookup Zones folder.
- Right-click the zone you created, and then click Properties.
- On the General tab, the Zone Type value is set to Primary. Click Change to change the zone type.
- In the Change Zone Type dialog box, click DS Integrated Primary, and then click OK.
- The DNS server writes the zone database into Active Directory.
- Right-click the zone named “.”, and then click Properties.
- On the General tab, the Zone Type value is set to Primary. Click Change to change the zone type.
- In the Change Zone Type dialog box, DS Integrated Primary, and then click OK.
Links
Promote and Demote Domain Controllers in Windows 2000 – 238369
HOW TO: Use DNS to Find Networked Resources in Windows 2000 Server – 300386
Setting Up the Domain Name System for Active Directory – 237675