Enhancing Security: Microsoft to Phase Out Default Outbound Access for Azure VMs

Key Takeaways:
- Microsoft is deprecating default outbound access for Azure virtual machines (VMs) in September 2025 to boost protection against cyberattacks.
- New VMs will no longer have unrestricted Internet access by default and organizations need to use explicit outbound connectivity methods like Azure NAT Gateway or Azure Load Balancer outbound rules.
- Existing VMs with default outbound access won’t be affected, but IT admins are encouraged to transition to explicit methods for better control and to avoid disruptions.
Microsoft is introducing a significant change to Azure that will impact how virtual machines (VMs) connect to the Internet. Starting in September 2025, default outbound access for new VMs will no longer include unrestricted Internet access.
In Microsoft Azure, outbound Internet access is enabled by default for resources within a virtual network (VNet). This default configuration permits virtual machines and other Azure resources to establish connections with external services and websites on the Internet. For example, it enables a web browser to perform TLS/SSL certificate revocation checks or allows a DNS server to make queries to external authoritative DNS servers.
Microsoft has decided to disable default outbound access to enhance security and protect organizations from ransomware attacks and other security threats. This measure prevents threat actors from exploiting vulnerable virtual machines to establish connections with malicious destinations, which could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data and system encryption.
Furthermore, Microsoft maintains control over the default outbound access Internet Protocol (IP) (which may change), and any dependency changes could lead to future complications. Therefore, it is advisable to employ an explicit connectivity method of public connectivity.
On September 30, 2025, all new virtual machines will no longer be able to use public IP addresses. “After this date, all new VMs that require Internet access will need to use explicit outbound connectivity methods such as Azure NAT Gateway, Azure Load Balancer outbound rules, or a directly attached Azure public IP address,” Microsoft explained.
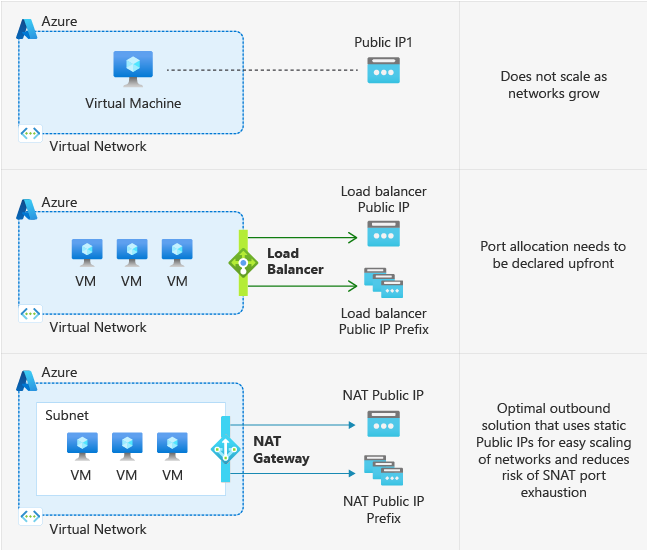
Microsoft suggests transition to explicit outbound access
A NAT Gateway allows multiple devices within a local network to share a single IP address while accessing resources on the Internet. However, it’s important to note that the deployment of NAT gateways in different availability zones could cause complexity and potential issues. Meanwhile, Azure Load Balancer outbound rules allow users to control the outbound network connections that are made from resources within a virtual network.
Microsoft mentioned that this change won’t impact existing virtual machines that use default outbound access. The company recommends administrators to switch to an explicit outbound method to avoid any disruptions in the workflow. It will help organizations ensure that public IP address changes won’t impact their existing workloads.



