Boosting Efficiency: Microsoft’s New Feature Simplifies Management of Azure Role Permissions

Key Takeaways:
- Microsoft’s new tool called “AuthorizationResources table” provides organizations with real-time visibility into Azure role permissions.
- The tool offers clear insights into role assignments and user allocations, helping organizations optimize resource utilization within strict assignment limits.
- Azure Cloud Services (classic) will retire in 2024, urging organizations to transition to Azure Cloud Services (extended support) within Azure Resource Manager for improved security and efficiency.
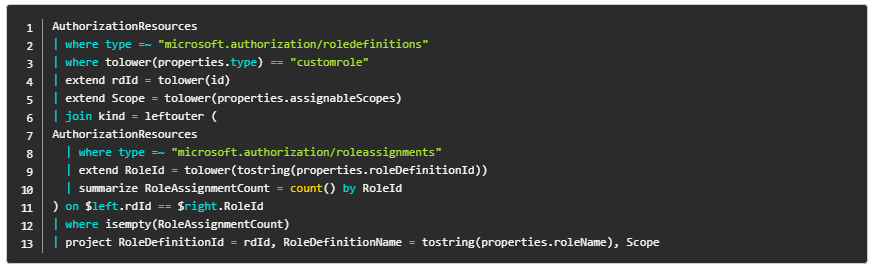
Microsoft has announced a new security tool that enables IT admins to clean up their Azure role-based access control (RBAC) permissions. The AuthorizationResources table, which is available via Azure Resource Graph (ARG), allows organizations to efficiently manage Azure access control permissions, optimize role assignments, and enhance security.
The AuthorizationResources table helps administrators to monitor the number of roles assigned and the users assigned to specific roles. Microsoft allows a maximum of 4,000 role assignments per Azure subscription and up to 5,000 custom roles within a directory. The AuthorizationResources ARG queries also help to determine how many roles are actually being used within an organization.
“With this table, you’ll be able to quickly answer questions such as “how many users are using a role definition?” or “how many role assignments are used?” or “how many role definitions are used?”. Then, you can act on the results to clean up unused role definitions, remove redundant role assignments, or optimize your existing role assignments using AAD Groups,” Microsoft explained.
Microsoft to retire Azure Cloud Services (classic) in 2024
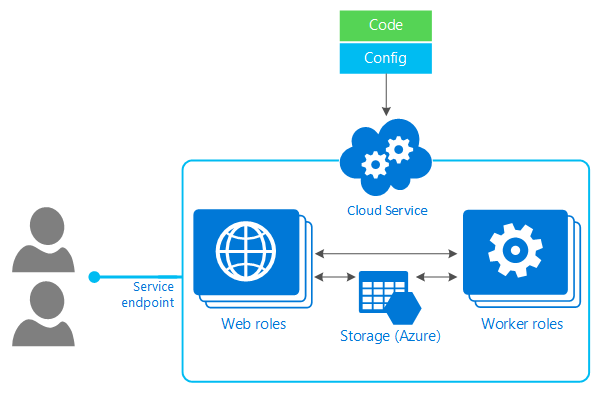
Microsoft has also reminded customers about its plans to shut down the Azure Cloud Services (classic) deployment model on August 31, 2024. The legacy model allowed customers to deploy and manage applications but was deprecated in favor of Azure Resource Manager. Microsoft says that organizations should use ARG to convert classic admins to role assignments.
Essentially, Azure Cloud Services (classic) supports classic admin roles, granting subscription-level administrators specific administrative privileges over Azure resources. However, it doesn’t support fine-grained security roles based on Azure RBAC (Role-Based Access Control). Azure RBAC is a modern access control system that allows administrators to define granular permissions for users and groups on Azure resources.
Migrate to Azure Cloud Services (extended support)
To continue to use cloud services, Microsoft recommends that organizations switch to Azure Cloud Services (extended support) in Azure Resource Manager before 31 August, 2024. The service offers various capabilities, such as role-based access control, regional resiliency, and support for deployment templates.
“Cloud Services (extended support) has the primary benefit of providing regional resiliency along with feature parity with Azure Cloud Services deployed using Azure Service Manager. It also offers some ARM capabilities such as role-based access and control (RBAC), tags, policy, and supports deployment templates,” Microsoft explained.
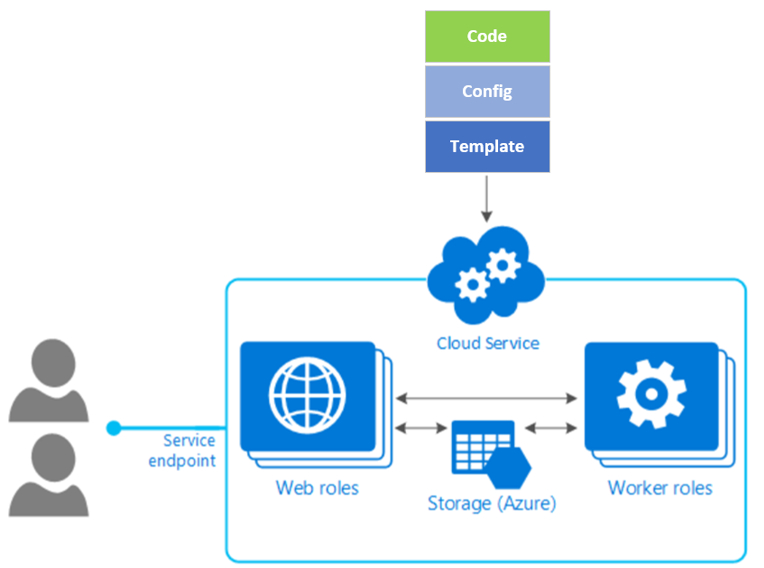
Microsoft notes that customers would need to make minimal changes to some configuration files in order to deploy Azure Cloud Services (extended support). Nevertheless, modifications to deployment scripts will be required to call the new Azure Resource Manager-based APIs, and you can find more details on this support page.



