Free Disk Space in Windows 10 by Automating Disk Cleanup
In a previous article, I explained how to use the Disk Cleanup utility to clean up temporary files on your Windows 10 machine. If you’re an administrator of a network that contains multiple computers, then running manual configuration tasks can be very time consuming. In this article, I’ll show you how to automate this process for larger environments.
Automating Disk Cleanup: One Approach
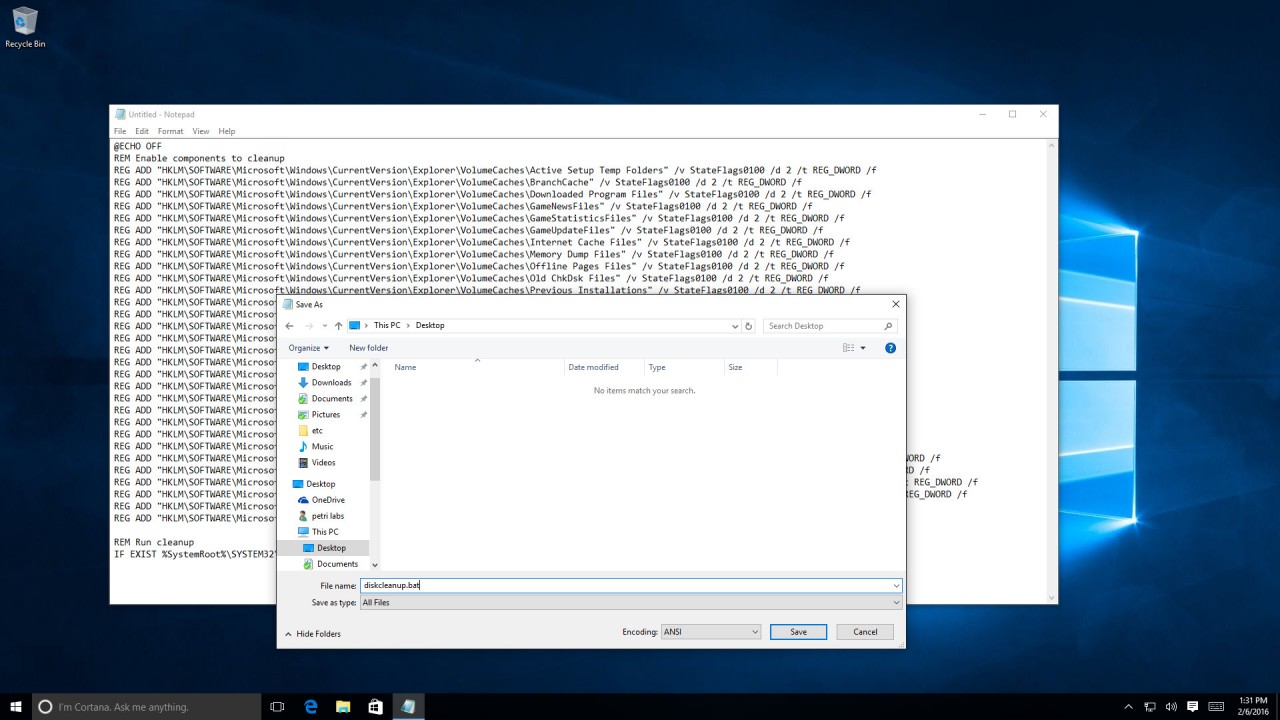
If you want to pre-configure these options on a remote computer and offer the user the ability to execute a script that will clean their disk, then you can use the following instructions to create .BAT file, place it on the computer’s desktop or anywhere you like, and execute it with elevated permissions:
@ECHO OFF REM Enable components to cleanup REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Active Setup Temp Folders" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\BranchCache" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Downloaded Program Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\GameNewsFiles" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\GameStatisticsFiles" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\GameUpdateFiles" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Internet Cache Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Memory Dump Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Offline Pages Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Old ChkDsk Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Previous Installations" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Recycle Bin" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Service Pack Cleanup" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Setup Log Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\System error memory dump files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\System error minidump files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Temporary Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Temporary Setup Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Temporary Sync Files" /V StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Thumbnail Cache" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Update Cleanup" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Upgrade Discarded Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\User file versions" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Windows Defender" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Windows Error Reporting Archive Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Windows Error Reporting Queue Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Windows Error Reporting System Archive Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Windows Error Reporting System Queue Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Windows ESD installation files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\VolumeCaches\Windows Upgrade Log Files" /v StateFlags0100 /d 2 /t REG_DWORD /f REM Run cleanup IF EXIST %SystemRoot%\SYSTEM32\cleanmgr.exe START /WAIT cleanmgr /sagerun:100
If you would like to schedule Disk Cleanup to run automatically, then you can do so using the Task Scheduler. Assuming you’ve pre-configured the system with the required settings to be cleaned by using the cleanmgr /sageset:100 command, or running the registry settings that are provided in this article, then the system will already know that if it runs cleanmgr /sagerun:100, and all the required files will be cleaned.
Now we need to create the scheduled task to run the command.
To do so, follow these steps:
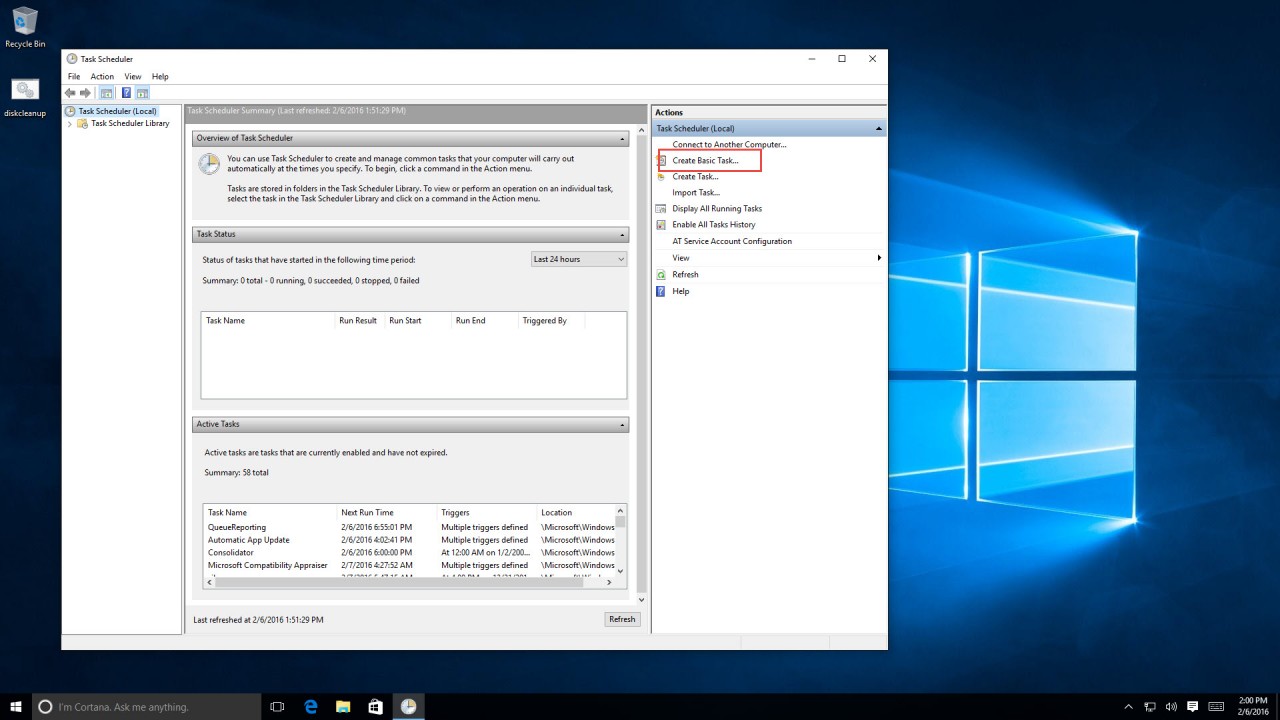
1. Open Task Scheduler from the Administrative Tools folder.
2. In the Task Scheduler window, click on “Create Basic Task.”
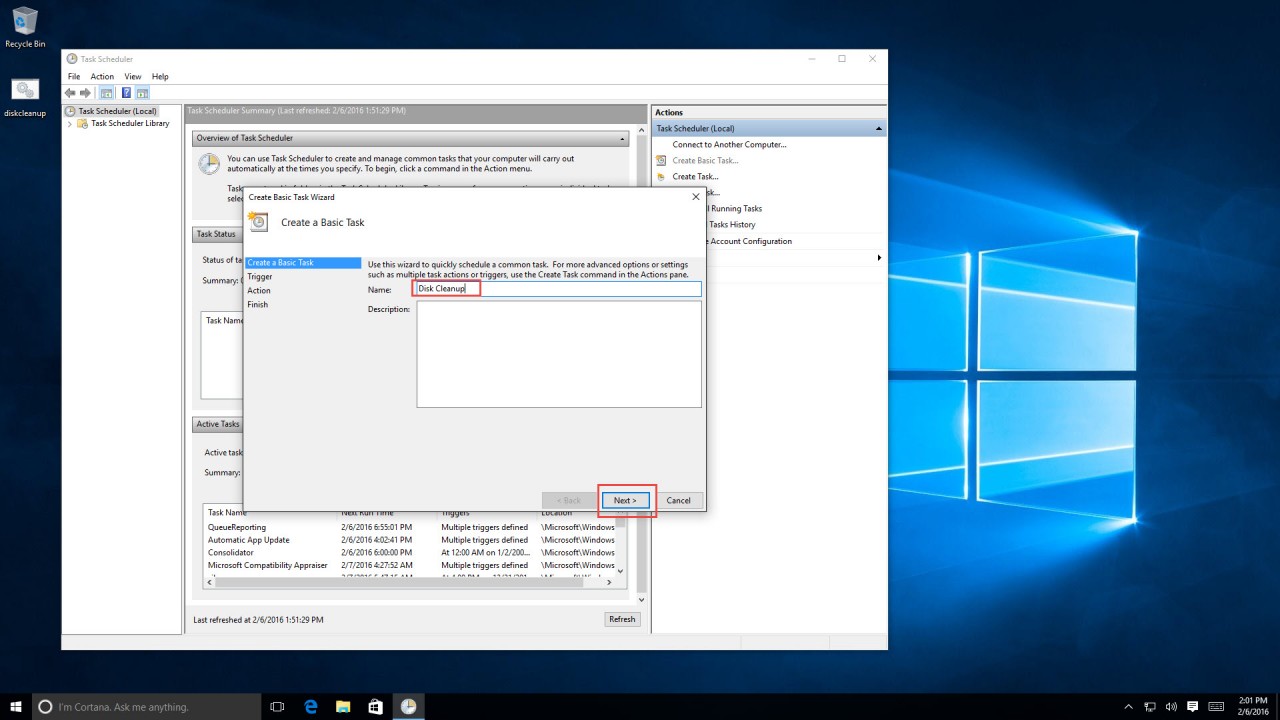
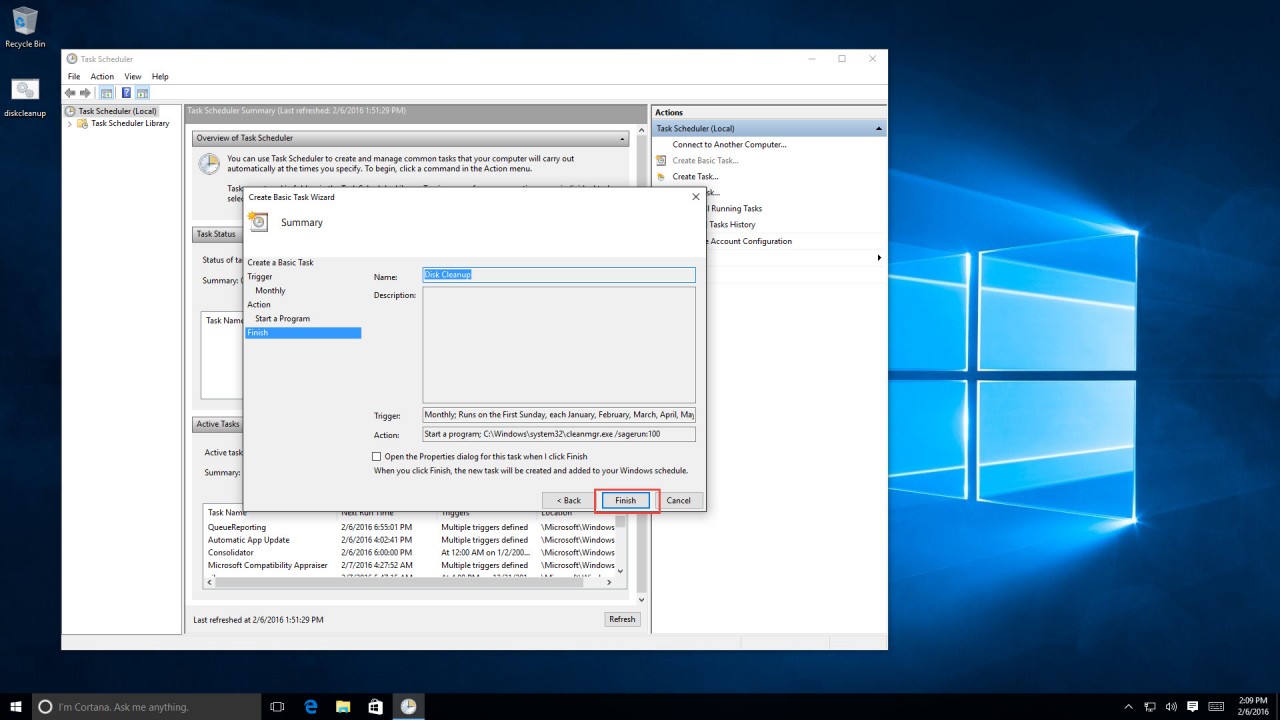
3. Give the task a name and description. Click “Next.”
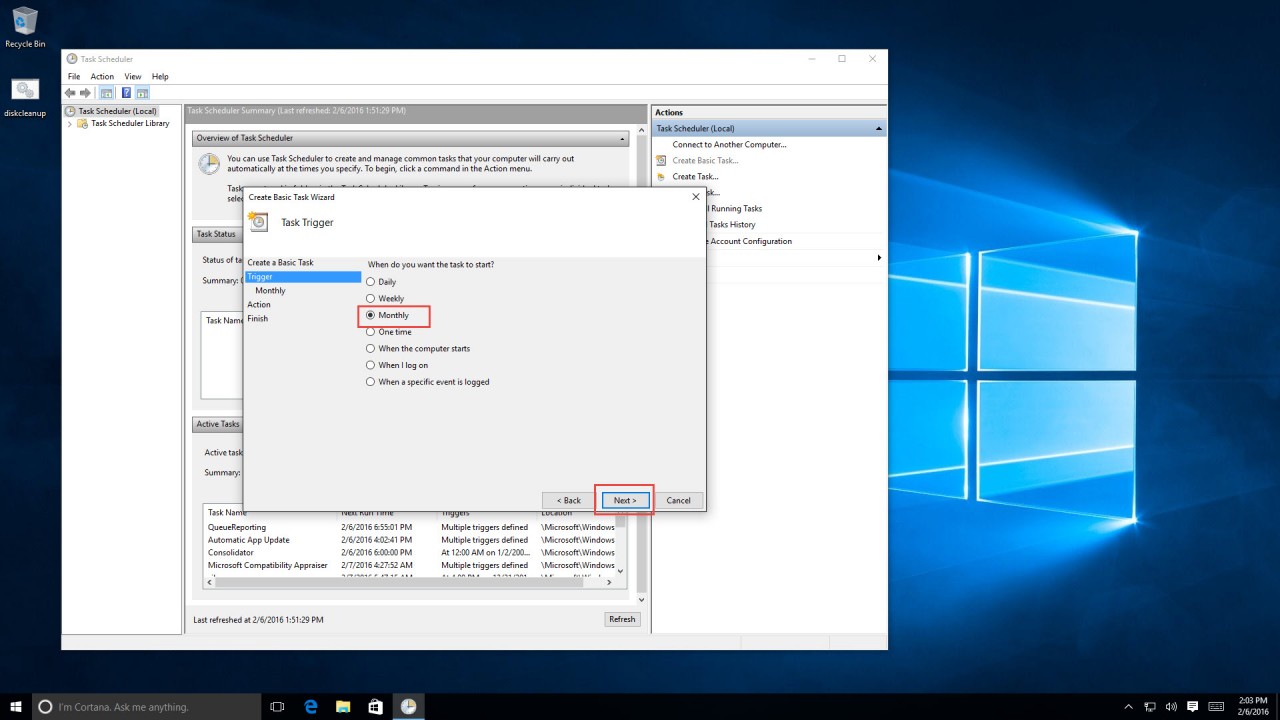
4. Select the option that best suits your needs. For this article, we’ll be using the monthly option. Click “Next.”
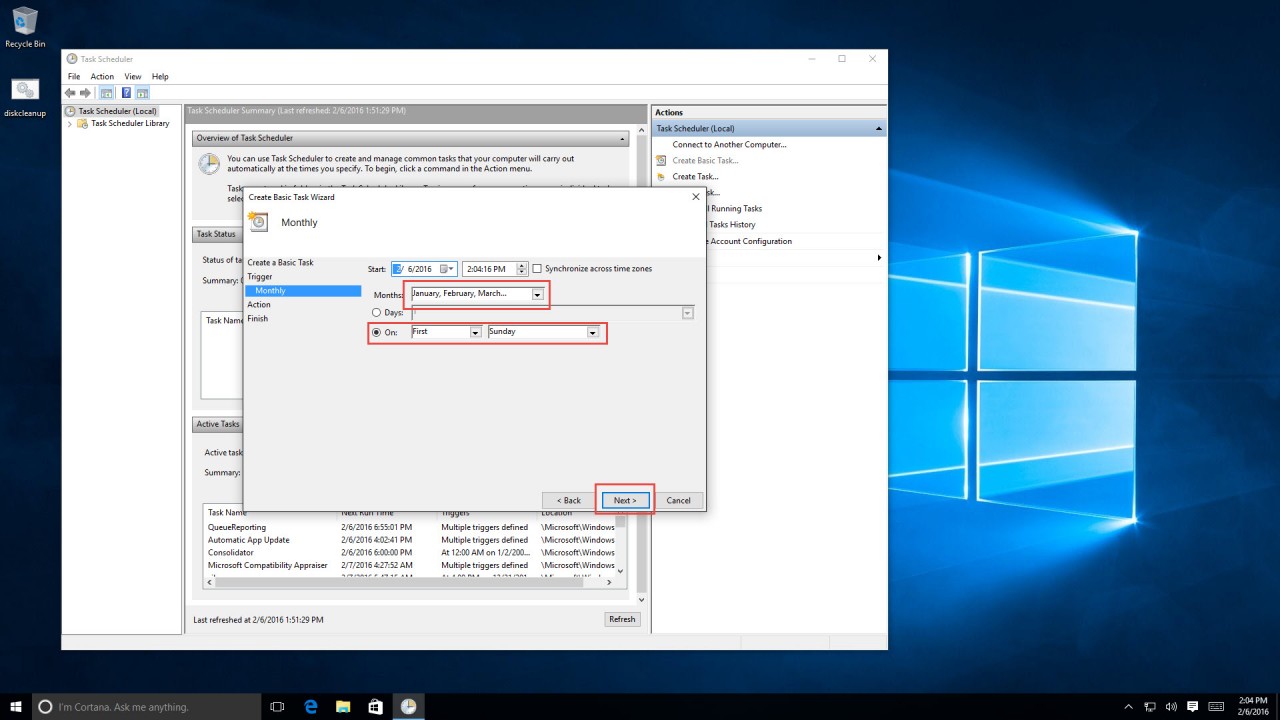
5. Select when you’d like to run the task. I chose the first Sunday of each month. Click “Next.”
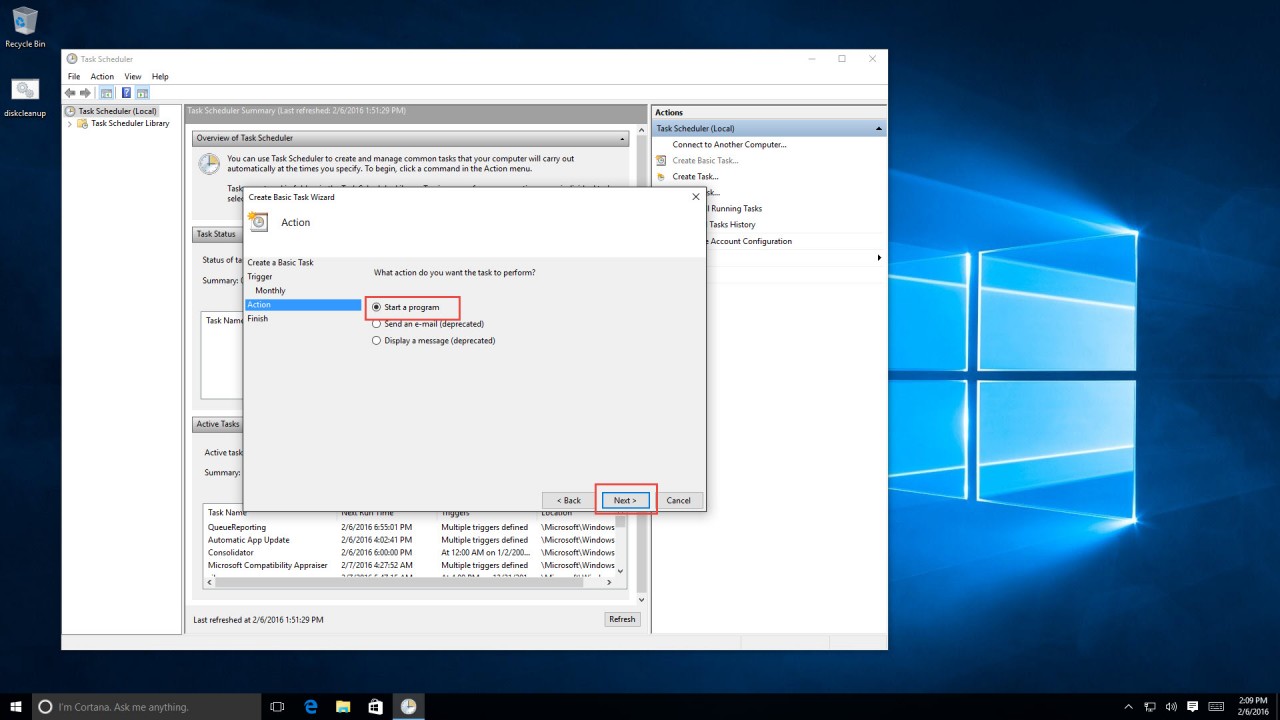
6. Now we need to give our task an action to execute. In this article, we’ll select “Start a program.” Click “Next.”
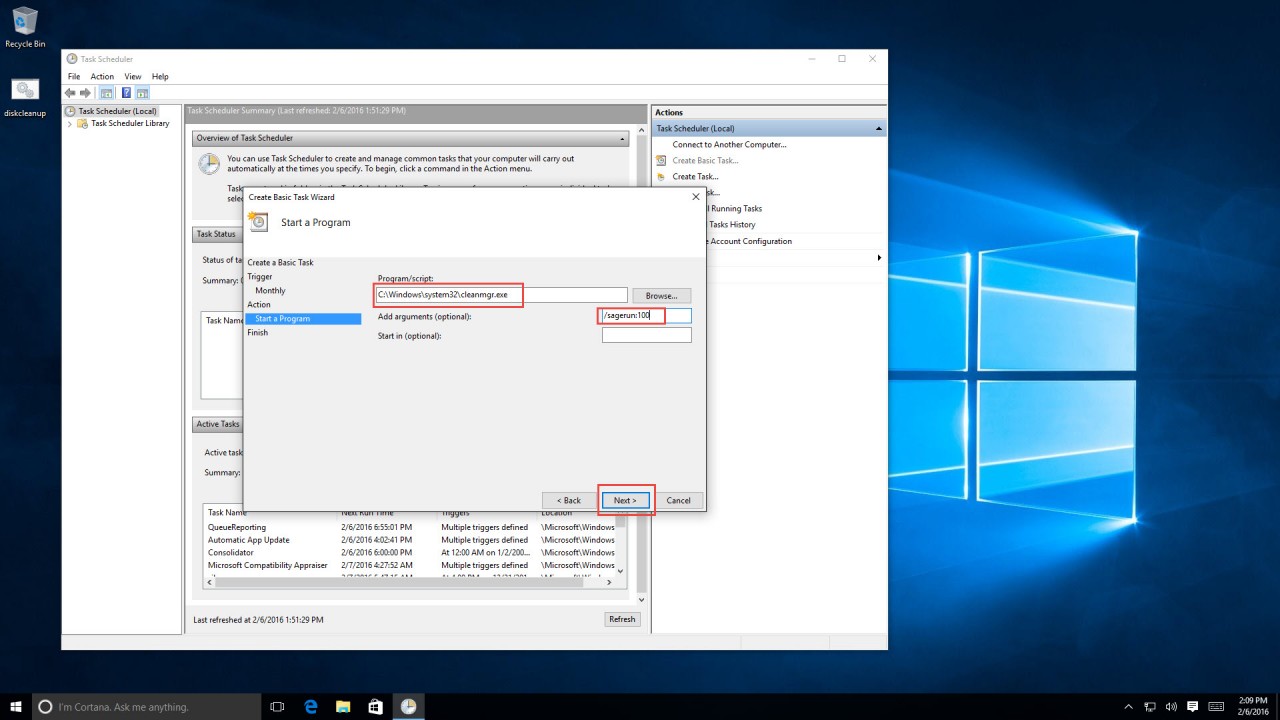
7. Use the following path:
C:\Windows\system32\cleanmgr.exe
Add argument as
/sagerun:100
Click “Next.”
8. To complete the creation of our task, click “Finish.”
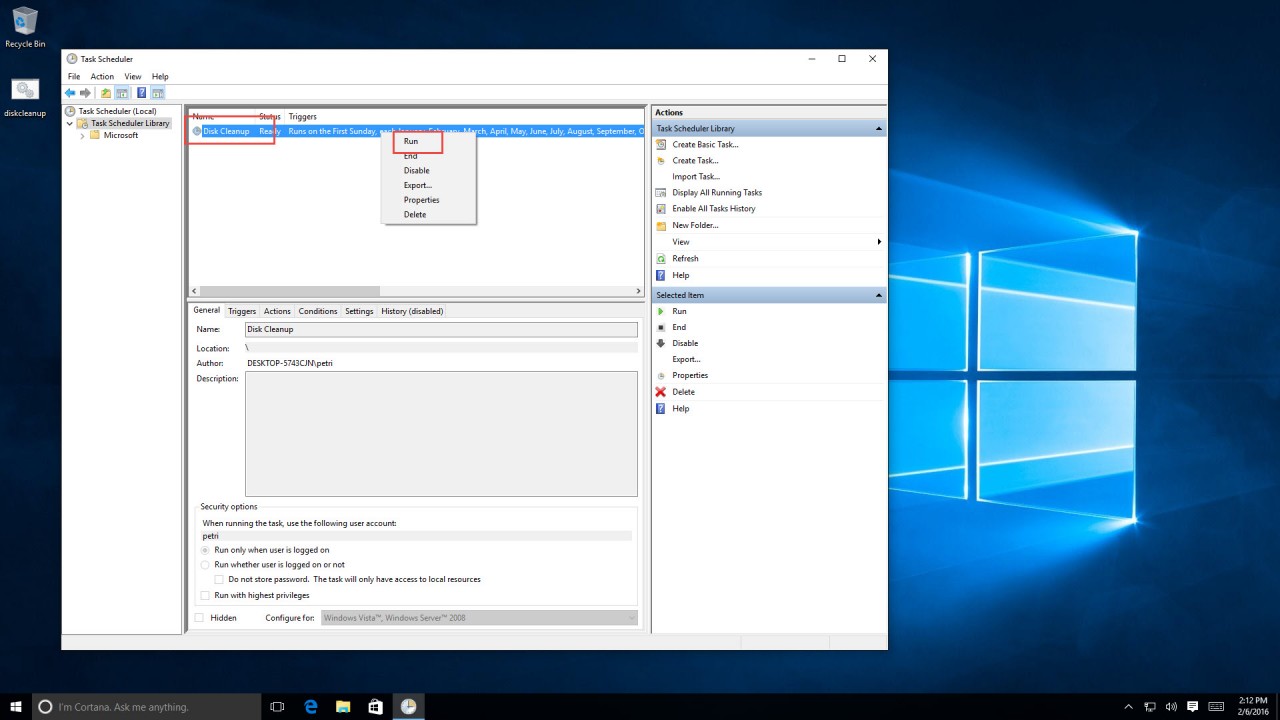
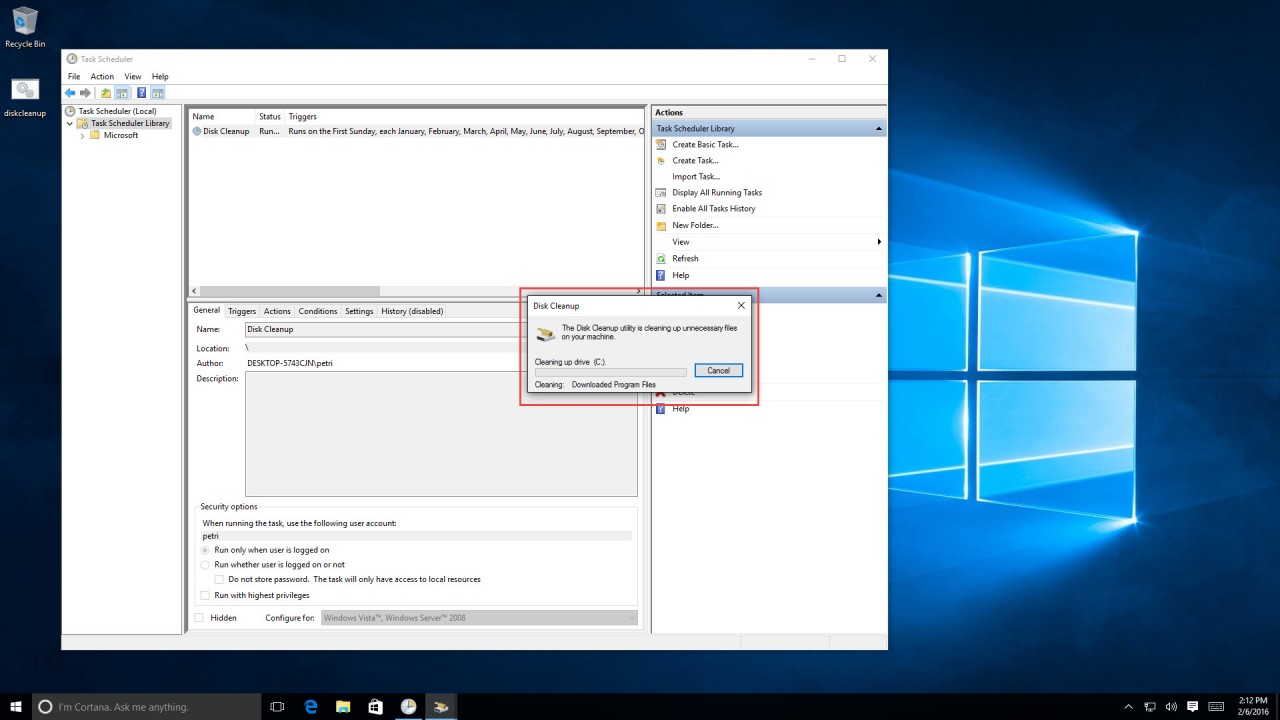
Now, either wait for the time of the task to arrive, or, if you want to check if it works right now, find it in the scheduled tasks library, right-click it, and select “Run.” If it runs, you’ll see it, and you can also check the last run status.