Create Deployment Rings Using Windows 10 Update for Business
In today’s Ask the Admin, I will show you how to assign Windows 10-based devices to deployment rings using Windows Update for Business (WUfB).
WUfB is a new feature in Windows 10. It allows organizations to manage Windows updates without deploying Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) on-premises or using agent-based methods, such as Microsoft Intune for Windows 7.
WUfB is a set of group policy settings that can be used to manage how Windows 10-based devices receive updates from Microsoft’s servers. Using a combination of settings available in WUfB, such as servicing branch, deferring updates, and pausing updates, you can create deployment rings for groups of devices.
The Windows 10 Creators Update is an example of a Feature Update. A Quality Update does not bring any new features but it does bring more stability and security. You can use WUfB policy settings to create several deployment rings. For example, some devices might update on the Current Branch as soon as a Feature Update is released. Other devices might use the Current Branch for Business and a third ring defers updates for three months.
For more information on WUfB, see Understanding Windows Update for Business on the Petri IT Knowledgebase. WUfB options were changed in Windows 10 Anniversary Update. Details can be found in What Has Changed in Windows Update for Business.
Create a Deployment Ring Using Policy
If you are not familiar with Group Policy, take a look at How to Create and Link a Group Policy Object in Active Directory on the Petri IT Knowledgebase. This is a good primer on working with Active Directory Group Policy Objects (GPOs). For simplicity, I will set Windows Update configuration in local policy on a single device. The same settings can be used in Group Policy and applied across multiple devices. Create as many GPOs as you need deployment rings and target devices using Organizational Units (OUs).
- Log in to Windows 10.
- Type mmc into the search bar. Right-click mmc in the results and select Run as administrator from the menu.
- Enter a local administrator account name and password or give consent to elevate privileges.
- In the console window, click CTRL+M to add a snap-in.
- In the Add or Remove Snap-ins window, select Group Policy Object Editor under Available snap-ins. Click Add.
- In the Select Group Policy Object dialogue, leave Local Computer as the selected GPO and click Finish.
- Click OK in the Add or Remove Snap-ins.
- In the Group Policy Object Editor, expand Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Update > Defer Upgrades and Updates.
- In the right pane of the console, double-click Select when Feature Updates are received.
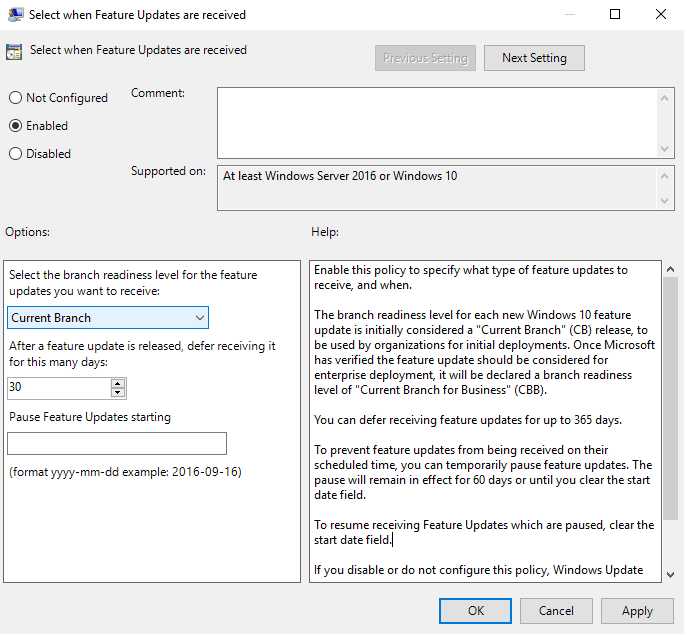
- In the Select when Feature Updates are received dialogue, change the status of the setting to Enabled.
- Select Current Branch or Current Branch for Business from the dropdown menu.
- Optionally, you can also defer updates in the chosen branch by up to 365 days. You can also pause updates for 60 days from the date entered in Pause Feature Updates.
- Click OK.
The new Windows Update settings will be deployed to computers that fall in the scope of the GPO or local policy object when Group Policy is refreshed.
In this article, I showed you how to use WUfB policy settings to create deployment rings for Windows 10 Feature Updates.




