Microsoft released a patch on November 11 to address a vulnerability in SChannel that could allow remote code execution. This patch included four new cipher suites for Windows Server versions 2003 through 2012 R2. Previously only Windows Server 2012 R2 had these cipher suites. On November 16, Microsoft updated the advisory stating that they found an issue with the new cipher suites they introduced. On November 18, Microsoft updated MS14-066 to remove the cipher suites from the default cipher suite list for Windows 2008 R2 and Windows 2012. Windows 2012 R2 does not get the update.
Microsoft has explained how to do this manually. The full list of cipher suites that are supported is also outlined by Microsoft. In addition, you can also follow these steps to manually enable these changes.
If you want to get the full list, read on. If not, skip to the next section.
The best practices cipher suite order:
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
- TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
The default cipher suite order:
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384*
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256*
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
- TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256_P256
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P256
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P256
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P521
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P384
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P256
- TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
- TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
- TLS_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
Note: Windows Server 2003 doesn’t support the reordering of SSL cipher suites offered by IIS. However, you can still disable weak protocols and ciphers. Also, Windows Server 2003 does not come with the AES cipher suite. Microsoft has a hotfix for this.
So how do you configure these protocol orders and ciphers without manually laboring each time?
Use IIS Crypto.
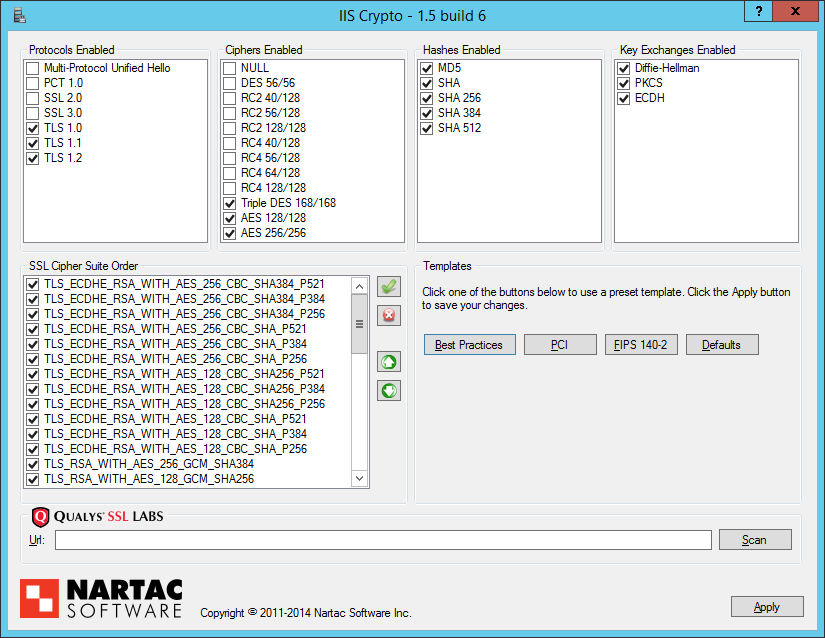
IIS Crypto was created to simplify enabling and disabling various protocols and cipher suites on servers running IIS, and it sets a few registry keys to enable/disable protocols, ciphers and hashes, as well as reorder cipher suites. All the changes are made following Microsoft’s best practices.
One of the nice things about IIS Crypto, in my opinion, is that it also supports pre-defined templates that can be set with a single button click:
- PCI. Disables everything except SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, RC4 128, Triple DES 168, AES 128, AES 256, MD5, SHA1, DH, and PKCS.
- FIPS 140-2. – Disables everything except TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, Triple DES 168, AES 128, AES 256, SHA1, DH, and PKCS.
- BEAST. The same as PCI, but also reorders the cipher suite.
Instead of making the changes manually or using some scripting to do this on multiple servers, you can simply use IIS Crypto to ease the task of properly configuring these web servers.
After downloading and running IIS Crypto, you will be able to select the following settings:
Once used, IIS Crypto modifies some registry key and child nodes. Each registry key has an “Enabled” value that is set, while protocols have an additional value named “DisabledByDefault” that is also set.
To enable/disable protocols, ciphers and hashes:
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL
To reorder the cipher suites:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Cryptography\Configuration\SSL0010002
It was tested on Windows Server 2003, 2008, 2008 R2 and 2012 and 2012 R2.
Note for servers running Remote Desktop Services (RDS): The default security layer in RDP is set to “Negotiate”, which supports both SSL (TLS 1.0) and the RDP Security Layer. However, if you set the security layer to SSL (TLS 1.0) and disable TLS 1.0 in IIS Crypto you will be unable to connect to RDP.
To check your settings, open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration in Administrative Tools and double click RDP-Tcp under the Connections group. If it is set to SSL (TLS 1.0), make sure that you do not disable TLS 1.0 in IIS Crypto.