Note: This tip will work for the Alcatel (now Thomson) SpeedTouch Home ADSL modem that’s in use with most of the Israeli ISPs. I don’t know about it’s compatibility with European and other ISPs, but I’d love to hear your feedback on this issue .
Update: I’ve received a few notes from European based readers that say this guide helped them convert their modem, so I guess it does work after all 🙂 Read Upgrade from Alcatel SpeedTouch Home to Pro – Reader Notes for more info and use the Alcatel, Samsung and other broadband modems forums to post questions if you want.
This document describes how you can enable the ‘Pro’ software features on an Alcatel SpeedTouch Home ADSL modem. The most interesting feature that will be enabled is PPP. This means that you will not have to use PPTP anymore. This is great because PPTP really is sub-optimal and causes problems on platforms that do not come from Redmond.
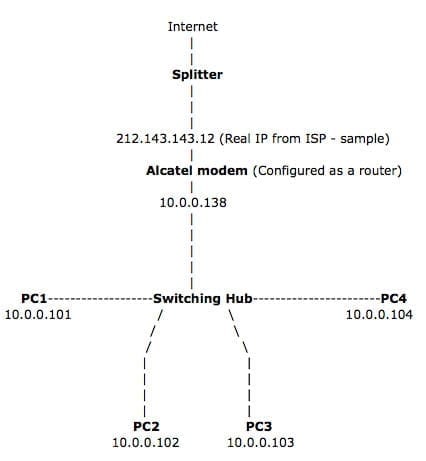
The modem will also act as a router with NAT/PAT which means that you can connect it to a hub/switch with as many computers as you want instead of just one. You will then be able to connect all your home computers to the Internet by using a simple hub/switch and simply configuring them to use the ADSL modem’s IP address as a Default Gateway.
Layout:
- The ADSL cable goes to the splitter.
- The ADSL modem is connected to the splitter.
- The ADSL modem is configured as a router.
- The Ethernet cable from the modem is connected to the switching hub.
- All PC’s are connected to the switching hub.
Read more: ADSL/Cable Home Network Configuration, Enable Alcatel SpeedTouch Pro with Static Port Mapping, Meaning of Lights in Alcatel SpeedTouch ADSL Modem.
All modifications are done in software. No hardware changes are needed.
For more information about the configuration, see the manual. All the ‘Pro’ features are described in the manual, so RTFM before you cry for help.
Warning: I do NOT support this operation, I will not answer your questions about it, and I will not help you get out of the mess you’ve gotten yourself into. You do have, however, the option of using my Alcatel, Samsung and other broadband modems forums.
Disclaimer & Warning
Messing with the software settings of your modem and/or messing with the registry or internal settings of your operating system can render your modem or operating system useless. Read the whole article and manual before you do any changes. Following these steps might work for you. It did for me and for many others, but that does not necessarily mean they will! I take no responsibility for anything bad that might happen to your OS or modem, and since you’re on your own – Do not ask me for help! It’s your modem!
Applying this hack will definitely VOID WARRANTY! If you are not experienced with tricks like these STOP NOW! Besides, some ISPs might stop supporting you if they find out that you messed up with your modem.
Don’t bitch me out if you do this and your modem turns into a furry animal that humps your leg and eats your cheetos.
Pre-Configuration
Connect your PC to the Home with a straight cable. Make sure the PC is clean! Do not use software like Zone Alarm, WinRoute, etc. Make sure you clean the PC of that kind of software, since it can interfere with the connection from your PC to your modem. Also make sure all dial-up connections are CLOSED.
TCP/IP Settings:
Set the network adapter settings for TCP/IP
- IP Address: . . . . . . . . . . . 10.0.0.X (Where X= any number between 1 and 254, but not 138)
- Subnet Mask: . . . . . . . . . . 255.255.255.0
- Default gateway: . . . . . . . 10.0.0.138
- Primary DNS: . . . . . . . . . . 10.0.0.138
Check your connection by pinging the modem.
Open a Command Prompt (CMD in W2K, XP, NT, Command in Win98) and type:
C:'WINDOWS>ping 10.0.0.138 Pinging 10.0.0.138 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 10.0.0.138: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Reply from 10.0.0.138: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Reply from 10.0.0.138: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Reply from 10.0.0.138: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Ping statistics for 10.0.0.138: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms
If you got 4 replies you’re OK. If not, check your IP settings, your network cable, your NIC lights and your NIC driver. Double check that no programs that might block communication are installed and running. Also make sure you check yourself by using the Ping command.
Active Directory warning: Those of you who are running home networks with Active Directory installed on Windows 2000 or Windows Server 2003s need to stop right here! Configuring the Alcatel modem as your DNS server will ruin your AD infrastructure. Do NOT configure your DC to use the Alcatel modem as their DNS servers! Keep the usual W2K DNS server and instead configure it to forward all queries to your ISP. Configure all other domain members to use the usual W2K DNS server. If you do not have AD on your network you can disregard this message. Read more about it on the Configure DNS Forwarding on Windows 2000 page.
Step One – Get the EXPERT password
Alcatel’s modems come in 2 flavors: Pro and Home. Both are using the same stripped down Linux kernel. All you need to do is configure the Home model to think it’s a Pro model and load it’s settings. To do so you must convert the modem to use the EXPERT mode because you need to make a change to a setting that is only available in the modem’s EXPERT mode.
The script
The PRO mode is protected by a numerical password that you can retrieve by using a script available here:
http://security.sdsc.edu/self-help/alcatel/challenge.cgi
(answer YES to all questions)
or here:
http://www.nzdsl.co.nz/howtos/Alcatel/pass.html
or even better, here:
http://www.bruring.net/alcapass.php
You can also download an executable version of the script to run on your own computer right HERE.
The “Challenge String”
For these scripts you need to obtain the “Challenge String” for your modem. The Challenge String is basically the same as the MAC address of the modem.
To obtain the MAC address (also called the “SpeedTouch string”) you can do one of the following:
- Telnet to your modem by using this command:
telnet 10.0.0.138
Log in as any user and the modem will show it’s logo screen.
There are a few types of software versions installed in the modems. To know what software version you have, type:
=>software [software]=>version Active : Gv8baa3.281 Passive : Gv8baa3.281 [software]=>
Warning: Updating firmware is NOT without risks and can render you modem useless! But if you do want to experiment with firmware upgrades – at your own risk – take a look here:
http://www.nzdsl.co.nz/software/alcatel/Default.htm
Look at the last 3 digits of the software version. If you have 253 or lower, type
=>EXPERT ========================DISCLAIMER========================= Access to expert mode is intended for qualified personnel only. Press ENTER to return to user mode. =====================END=OF=DISCLAIMER===================== 'SpeedTouch (00-90-DB-4A-FA-AF)' Password :
If you have a higher version (for example 281), type
=>td prompt ========================DISCLAIMER========================= Access to expert mode is intended for qualified personnel only. Press ENTER to return to user mode. =====================END=OF=DISCLAIMER===================== 'SpeedTouch (00-90-DB-4A-FA-AF)' Password :
Note: If you try to type EXPERT on a higher version you’ll get this error:
=>expert Unknown command. =>
That’s the MAC address of the modem.
- Ping your modem then check your ARP cache:
C:'WINDOWS>ping 10.0.0.138 Pinging 10.0.0.138 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 10.0.0.138: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Reply from 10.0.0.138: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Reply from 10.0.0.138: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Reply from 10.0.0.138: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Ping statistics for 10.0.0.138: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms C:'WINDOWS>arp -a Interface: 10.0.0.1 --- 0x2 Internet Address Physical Address Type 10.0.0.138 00-90-DB-4A-FA-AF dynamic
Take the MAC address, in this case 00-90-DB-4A-FA-AF (this is just an example of course), and write it down in the format of:
SpeedTouch (00-90-DB-4A-FA-AF)
Take this string and paste it into the script I gave you in the beginning. Do NOT paste it with the – ‘ – at the beginning and end of the string. It will work even if you put the – ‘ – but the password will be invalid. Also note that there is a space between the SpeedTouch and the – (…)
- You can also get the MAC address of the modem by opening an FTP session to it. Open a Command Prompt (CMD.EXE for NT, W2K and XP, or COMMAND.COM for Win9X) and type:
C:'WINDOWS>ftp 10.0.0.138 Connected to 10.0.0.138. 220 Inactivity timer = 120 seconds. Use 'site idle ' to change. User (10.0.0.138:(none)): 331 SpeedTouch (00-90-DB-4A-FA-AF) User '' OK. Password required. Password:
Copy the SpeedTouch (00-90-DB-4A-FA-AF) string and paste it in the scripts described at the beginning of step 1. You can safely close the FTP window without logging on.
You should then paste or enter the password that you obtained through the previous script.
Write this password down, because there is no easy way to get this code back without running the script again.
Step Two – Enable the Pro features
Note: You’ll have to disconnect from the ADSL service to configure the following settings, so maybe now’s a good time to print this screen.
Login to the modem using telnet.
telnet 10.0.0.138
The Speed Touch will prompt you with ‘User’. Just press Enter and the CLI (command line interface) banner will appear. You can login as any user with any password (if you haven’t changed it of course). It’s best that you use a username and password you can easily remember later.
Do you remember the OS version from step 1? Now do one of the following (like you did in step 1):
If you have 253 or lower, type:
=>EXPERT ========================DISCLAIMER========================= Access to expert mode is intended for qualified personnel only. Press ENTER to return to user mode. =====================END=OF=DISCLAIMER===================== 'SpeedTouch (00-90-DB-4A-FA-AF)' Password : ********** Switched to 'Trace & Debug' prompt.
If you have a higher version (for example 281), type:
=>td prompt ========================DISCLAIMER========================= Access to expert mode is intended for qualified personnel only. Press ENTER to return to user mode. =====================END=OF=DISCLAIMER===================== 'SpeedTouch (00-90-DB-4A-FA-AF)' Password : ********** Switched to 'Trace & Debug' prompt.
Return to Normal mode by typing <NORMAL>Either way, you are now in Expert mode. Next step is to upgrade the modem.
Type:
> rip rip> drv_read 2 1 b
and you’ll receive:
the data in hex is : 8604
or:
the data in hex is : 8704
depending upon your modem’s version.
For your general knowledge, the 8604 model is older than 8704 which also has an ATM port. If this is not the answer you’re getting – stop right away. Your modem has a version which is not compatible and you might cause damage to your modem if you go on.
Note for ISDN users: I’ve received reports that the Alcatel ISDN modem will report a version of 9600. Change it to 9606 and go on. It’s supposed to work (thanks Stathis Melistas, Belgium).
Note for PSTN users: Reader Flavio from Italy wrote that the PSTN Alcatel modem has a software version of KHDSAA.132 and his drv_read returned 8600. He changed it to 8606 and the modem was successfully switched to the Pro model. He also successfully upgraded the modem’s software version to KHDSAA.270 to avoid some NAT/PAT problems. Thanks!
You must now change the last digit to 6 and write it back.
rip> drv_write 2 1 b 8606
or
rip> drv_write 2 1 b 8706
depending on your version.
You should now reboot the box.
rip>exit >system system> reboot
That’s it! Your modem now has the Pro features!
Step Three – Configure your PC
Use the following settings on your PC/Mac/UNIX boxes:
IP Address – 10.0.0.X (where X must be any number from 1 to 254, but not 138) Subnet mask – 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway – 10.0.0.138 (The IP address of the Modem) Primary DNS – Use your ISP’s DNS (You can also use 10.0.0.138).
You can also connect a Router, Hub or Switch. PPTP is gone so you can connect any IP device. In case that you have more than 1 computer your IP addresses must be unique on each computer. Keep the X part of the IP address unique.
Step Four – Configure your modem for PPP
You’ll have to disconnect from the ADSL service to configure the following settings, so maybe now’s a good time to print this screen.
Connect to the modem via the web interface on http://10.0.0.138.
You’ll get a screen like this one:
Go to the PPTP menu and remove all entries. Apply and Save the changes.
Go to the PPP menu and remove all entries. Apply and Save the changes.
Go to the Phone Book menu and remove all the entries. Apply and Save changes.
Go to the CIP Interfaces and delete all entries. Apply and Save all.
Go to the Bridging Ports menu and delete all entries. Apply and Save all.
Note: Setting the modem back to it’s default settings will also bring all the deleted items back. See the Reset Password for Alcatel SpeedTouch Pro page for info on how to reset the modem.
On the Phone Book menu and add a new entry with following details:
Name ‘MXS’ VPI=8 VCI=48 Type=ppp
Save the changes.
Note: Some European ISPs have other VPI/VCI settings. Please contact your ISP for more details if you cannot make it work with the above settings. Note that is you did get the settings right – they will have a yellow color. Furthermore, you cannot use the same settings twice even if they’re right. That’s why I asked you to delete all other entries.
Read the Upgrade from Alcatel SpeedTouch Home to Pro – Reader Notes article for more info on some of the most used settings for world-wide ISPs.
Go to the PPP menu screen and add a new entry for the ‘MXS’ with a type of ‘vc-mux’. Apply and Save.
Now go back to the PPP menu and configure the new ‘MXS’ entry with the following settings:
User=username@Iisp (CAPITAL ‘I’ and the name of your ISP) Password= (provided by your ISP) Connection Sharing = Everybody Destination networks = All networks Specific network = Address translation (NAT-PAT) = selected Primary DNS and Secondary DNS = (provided by ISP) Local IP and Remote IP = none Mode = ALWAYS-ON Idle time limit = LCP echo = selected PAP = ACCOMP = selected
Click Apply. You must now change the STATUS from ‘OFF’ to ‘ON’.
Notice how the STATE is now ‘TRYING’.
Apply and Save all changes. Go back to the PPP menu and see that the STATE is now ‘UP’. It can take a while before the modem connects and changes to the ‘ON’ status:
If it does not change, double-check your settings.
Step Five – Configure your computer’s NIC
The Alcatel modem is configured (by default) to run it’s own DHCP service. It will supply the needed IP addresses and other configurations to the workstation connected to it. If you have a HUB or SWITCH that’s connected to the modem then all computers that are connected to that HUB or SWITCH will receive IP addresses in the range of 10.0.0.0 from the modem.
Note: You can easily configure the DHCP service on the modem by going to the DHCP menu and looking around.
To configure a workstation to use automatically assigned IP addresses is easy. I think you know how to do that by now. If you’ve got amnesia here are a few screenshots of a Windows XP workstation. Figure it out on your own.
(don’t mind the rest of the icons…)
You can, of course, configure the workstation to have a static IP address. Since the Alcatel modem now acts as a router and it’s inner (LAN) IP address is 10.0.0.138, you need to configure all computers that are connected to it to have IP addresses that are on the same network ID as the modem – 10.0.0.0 with a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0 (Just don’t use 10.0.0.138 – it’s the modem’s IP address!). Make sure that all computers use the modem’s IP address as their default gateway.
Revert to the default settings if something goes wrong
I hope you won’t need it but if you do, you can simply reset the modem to it’s default settings by pressing the DEFAULTS button on the back of the modem. See the Reset Password for Alcatel SpeedTouch Pro page for info on how to reset the modem.
If you still have a http connection to the modem you can go to the System Setup menu and press Defaults. This will restore all settings to default.
All the changes will be lost except the version change – from 8604 to 8606 meaning you don’t have to go through steps 1-4 if you want to re-enable your modem.
If you still want to, you can revert to the basic configuration by telnetting to the modem and entering:
rip> drv_write 2 1 b 8604
And then reboot the box.
rip>exit >system system> reboot
That’s it.