Sysprep Windows Server 2012 Faster with /mode:vm Switch
How can I use sysprep to quickly create images of Windows Server 2012 for virtual machines?
Windows Server 2012’s System Preparation Tool (sysprep.exe) contains a new switch that allows system administrators to generalize the OS (remove any installation specific configuration) faster than previous versions of the tool that were designed for use on physical hardware. In this Ask the Admin, I’ll explain the new functionality and how to use it.
The sysprep tool is used to remove system-specific information from the OS so that it can be used for imaging to multiple devices. For instance, you might install Windows Server, make some specific customizations, and prepare the OS so that it can be distributed to different hardware, without having to make the customizations individually on each server.
What’s New in Sysprep for Windows Server 2012?
The new VM-mode method for generalizing a Windows 8 or Server 2012 installation only works from inside a virtual machine. Once sysprep has completed the generalization and shutdown the VM, you can copy the VM’s .vhd file and attach it to a new VM in any system that uses the same hypervisor technology.
For example, if you create the VM image in Hyper-V and then use sysprep to generalize Windows, the .vhd file should only be attached to VMs running on Hyper-V with the same hardware profile as the original VM. The same applies to .vhd images generalized on VMware and any other hypervisor. Finally, the /mode:vm switch can only be used from inside a running VM.
Use Sysprep to Generalize Windows Server 2012 Running in a VM
You will need to use sysprep from the command line, as there is no option to enable VM mode in the GUI.
- Install Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012 (or later editions) in a virtual machine.
- Customize the operating system as required.
- Switch to the Start screen and type cmd. Make sure that Command Prompt is highlighted in the search results and press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to launch the process with administrative privileges. Give consent or enter credentials if prompted.
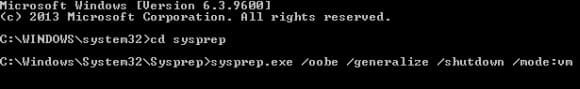
- Change the working directory to System32 by typing cd c:\windows\system32\sysprep and pressing Enter.
- To run sysprep with the standard GUI options, but also the /mode:vm switch, type sysprep.exe /oobe /generalize /shutdown /mode:vm and press Enter.
Once the VM has shutdown, you can create a copy of the .vhd file and attach it to new VMs in the same environment.



