If no DNS servers were detected during the initial configuration of Windows 2000 DNS, the system will typically designate the new DNS server as a “root server”, which is the ultimate authority for all naming resolution activities. As a result, the new DNS server will not be able to forward any name resolution queries that it is unable to resolve to another server or to the root servers on the Internet.
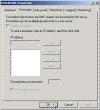
Consequently, a Windows 2000 DNS server that has been configured as a root server disables the options to add forwarders automatically.
Also, the Root Hints tab will be empty.
If, at a later date, you decide that this DNS server should be integrated into a larger DNS environment such as the Internet, you will need to remove the “root” forward lookup zone.
To remove the root forward lookup zone:
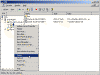
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click DNS to start the DNS Management Console.
- Click the DNS Server object for your server in the left pane of the console, and click the (+) PLUS sign next to the server object to expand the tree.
- Click the (+) PLUS sign next to Forward Lookup Zones to expand it.
- Click the zone that is marked with a (.) period, and then press DELETE.
- Click OK to confirm that you want to delete the zone.
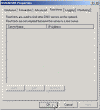
- Close the DNS Management Console and re-open it. Now the options to configure Root Hints or Forwarders are available.
After deleting the root zone you can now read Configure DNS Forwarding.