Google offers several different solution sets for Android Enterprise device management. In addition to Mobile Application Management (MAM), work profile for Bring-Your-Own-Devices (BYOD) users, and dedicated device for handsets that fulfill a single-use case, fully managed device is a solution for company-owned devices. Organizations that opt to use the fully managed device solution can manage configuration needed to keep handsets secure while still allowing users to be productive.
Microsoft has been testing MDM for fully managed Android Enterprise devices in preview since January 2019. During the preview phase, a new redesigned lightweight app was introduced simply called ‘Microsoft Intune’. It doesn’t replace the Intune Company Portal app and it is only used in fully managed device scenarios. The app brings all the features from Company Portal to fully managed device handsets.
Intune can onboard devices that run Android 6.0 and later using the following methods:
- Knox Mobile Enrollment
- NFC
- QR Code
- Token Entry
- Zero Touch Enrollment
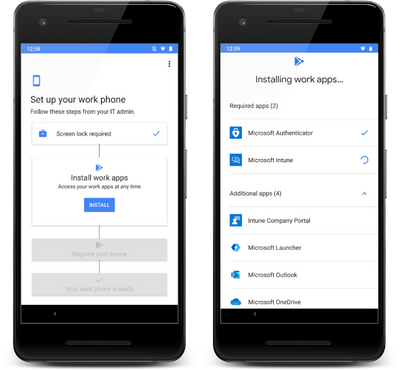
Microsoft says that the device provisioning workflow launches the out-of-box experience (OOBE) that then guides users through the steps needed to onboard the device. A PIN is set during this phase to make sure the handset is protected from the beginning. The new Microsoft Intune app, Microsoft Authenticator, and Company Portal app are automatically downloaded as part of the OOBE. A list of other mandatory apps that will be installed is also displayed to make the process more transparent to the user. Finally, devices are registered with Azure Active Directory (AAD) so that compliance requirements are met from the get-go to enable the device to connect to corporate resources.
Device Compliance and Security
Multifactor authentication is supported, as is the deployment of root and SCEP certificates. Other profile types are also there, including email, Wi-Fi, and VPN profiles. Users can’t sideload apps and organizations can enable the Managed Google Play store to distribute business apps. Optionally, it is possible to give users access to the public Google Play store as well. IT can also determine which Android system apps users can run.
Intune can be used to manage all the Android Enterprise Device Owner settings shown in the Intune console and you can create compliance policies, like enforcing PIN complexity requirements and specifying a threat level threshold for devices, and leveraging Mobile Threat Defense providers, such as Lookout and Symantec Endpoint Protection Mobile.
Microsoft Launcher for a Consistent End-User Experience
And if you want to turn Android into a Microsoft phone, you can use Microsoft Launcher to add your company branding and provide a consistent user experience by setting a wallpaper and defining the order in which applications are pinned to the home screen.
At the time of writing, there seem to be some issues publishing SCEP certificates. But hopefully that’s just teething trouble that Microsoft will sort out quickly. Microsoft says that there’s more to come as it prepares to support the full range of Android Enterprise scenarios in the coming months.



