
Microsoft has partnered with Google, AMD, and NVIDIA to create a new open specification for a silicon Root of Trust (RoT), dubbed Caliptra.
What is silicon root of trust?
Silicon root of trust, sometimes referred to as hardware root of trust, creates a chain of trust starting in the hardware used to boot a device. For example, if the firmware that’s used to start the operating system bootloader is trusted, then the subsequent code, in this case the OS bootloader, can use the same credentials because they are already trusted. The credentials are passed on to run the next piece of code, probably Windows or another operating system.
Caliptra Open-Source Root of Trust
Caliptra is designed to meet the enhanced security requirements of modern Edge and confidential computing scenarios.
“Caliptra is a forward-looking approach casting transparency into hardware security. As a reusable open source, silicon-level block for integration into systems on a chip (SoCs)—such as CPUs, GPUs, and accelerators—Caliptra provides trustworthy and easily verifiable attestation,” explained Rani Borkar, CVP for Azure Hardware Systems and Infrastructure.
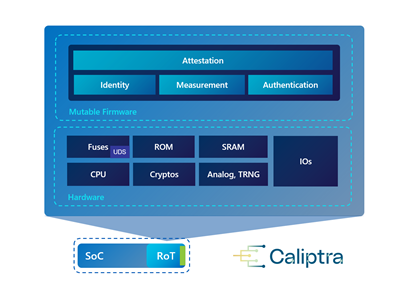
Microsoft highlights that Caliptra offers essential security properties that boost the integrity of security protections for confidential workloads. It helps to ensure that only trusted firmware can execute on the chipset. The list of security properties includes Identity, Compartmentalization, Measurement, Renewable security, Ownership, and Attestation.
According to Microsoft, the Caliptra RoT standard is a significant improvement over previous standards that had a separate implementation from the SoC. Moreover, it will help to standardize the security architecture of cloud-based servers. The Caliptra 0.5 specification is available to download now, and the company plans to launch the final standard in early 2023.
Microsoft launches a new secure Baseboard Management Controller, “Hydra”
Microsoft has teamed up with Nuvoton to introduce a new Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) called Hydra. It’s a specialized service processor that lets customers remotely monitor the physical state of servers, computers, and other hardware devices. Microsoft’s new security-focused BMC provides support for “TCG DICE identity flows with hardware engines” to let users quickly perform cryptographic operations.
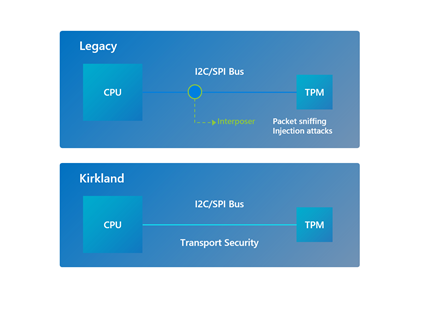
Project Kirkland protects the bus between the CPU and TPM
Finally, Microsoft has collaborated with Google, Intel, and Infineon to launch Project Kirkland. It leverages standard-based firmware techniques to protect the bus between the CPU and the TPM against eavesdropping and substitution attacks.
Project Kirkland uses cryptography for caller authentication and protects the transmission of sensitive information through the bus, and you can find more details in the official blog post.



