Managing Windows Server 2008 R2 from Windows 8
I know that the deployment drive for Windows 8 in the corporate environment is not as high as Microsoft would have wanted it, but even so, Windows 8 was released about a year ago, so by now you’d think you could use it to manage the servers in your organization. Well, at least that’s what I thought. I run a small Dell workstation in my work environment, and I decided I had enough of RDPing into the servers, either physical or virtual, just to manage some of their settings.
Server 2008 R2 Management from a Windows 8 Workstation
Before I go into the steps to do this, first I have a couple of points to make.
Note: With all said, there are several roles – most prominently the Hyper-V role – that still cannot be managed from a Windows 8 machine unless you run the Hyper-V server side on a Windows Server 2012 machine. Remember that while you can manage all remote Windows Server 2012 Roles and Features, when you’re connecting to a Windows Server 2008 R2 you can perform most management tasks, but you can’t perform role or feature installation or uninstallation.
Performance note: Server Manager can be used to manage up to 100 servers that are configured with a typical workload. The number of servers that you can manage with a single Server Manager console can vary depending on the amount of data that you request from managed servers, and hardware and network resources available to the computer running Server Manager. As the amount of data you want to display approaches that computer’s resource capacity, you can experience slow responses from Server Manager and delays in the completion of refreshes.
0. Make sure the Windows 8 workstation is joined to the domain
This is a prerequisite. Some roles can be managed by selecting how to authenticate to the target servers, but your life would be so much easier if you just make your machine a member of that domain. If you cannot/don’t want to do that, I suggest using regular RDP.
1. Download and install RSAT for Windows 8
First of all, we need to download and install the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) package for Windows 8. Both 64-bit and 32-bit versions of RSAT for Windows 8 are available to download.
Download Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 8 from Official Microsoft Download Center
Choose your version of RSAT, download it, and double-click on it to install it on your Windows 8 workstation.
2. Add remote servers to Server Manager
Once RSAT is installed, you need to add all the remote servers that you want to manage to Server Manager.
- First, open Server Manager from the Start screen.
- In the Server Manager dashboard, click Add other servers to manage.
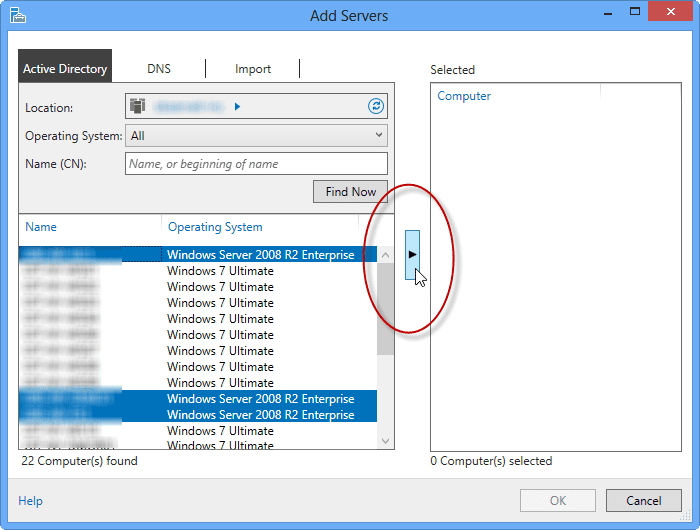
- In the Add Servers dialog, click Find Now to list all computers in your AD domain. If you want, you can specify a search criteria such as the operating system or machine name to narrow your search results. You can also use the CTRL key to make multiple selections.
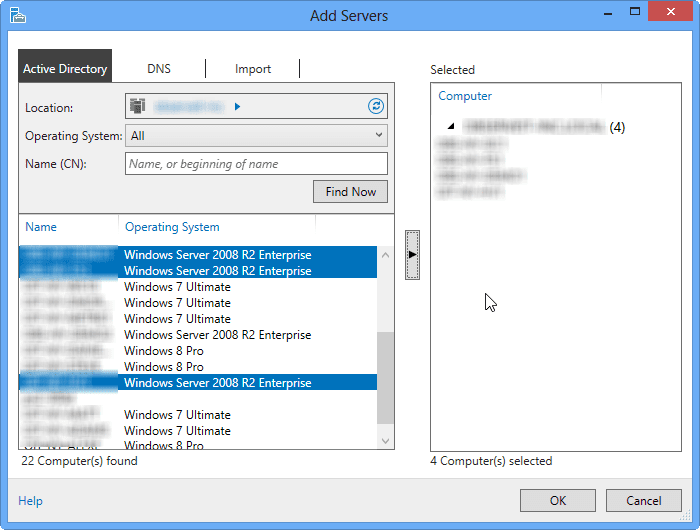
- Select the servers that you want to add to Server Manager, then click the arrow in the center of the dialog box and click OK. This will add them to the servers list.
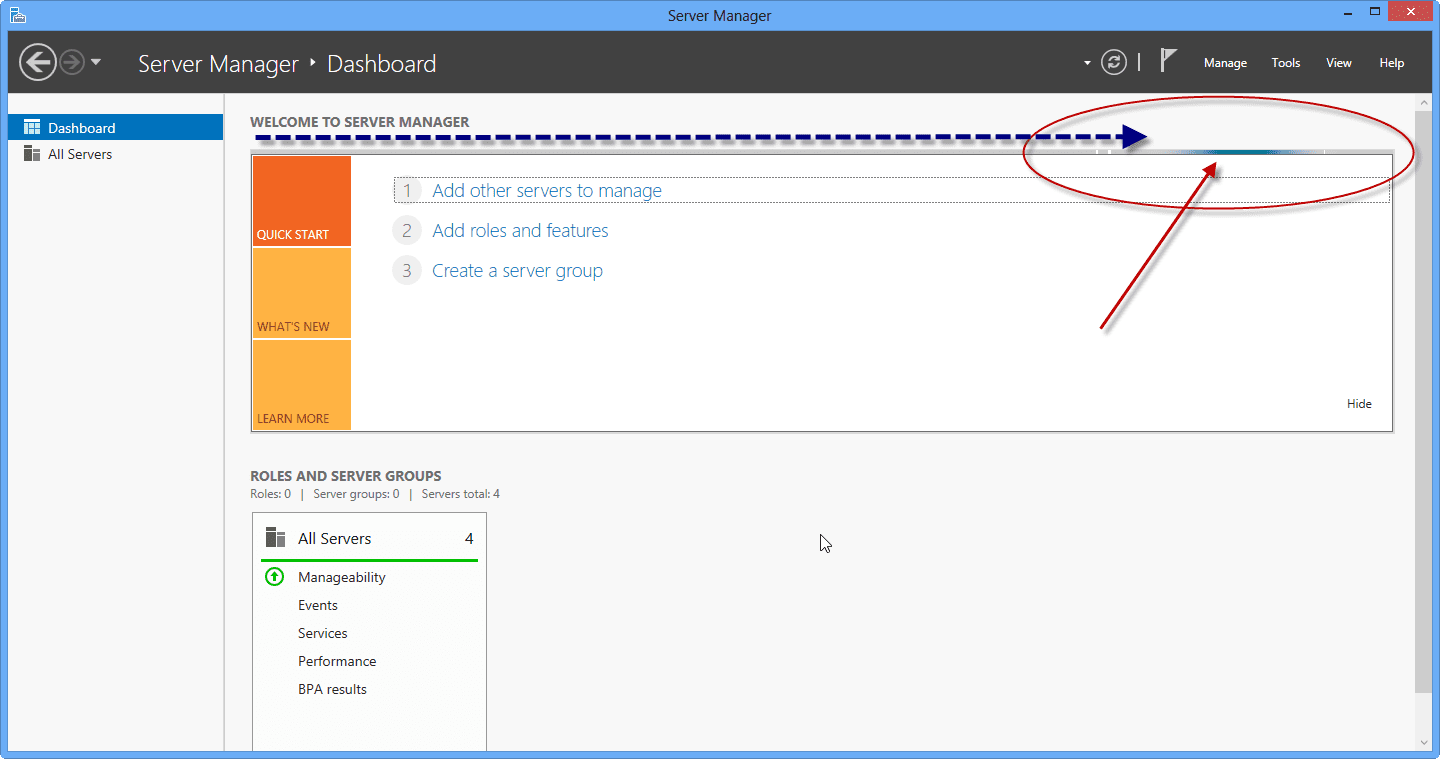
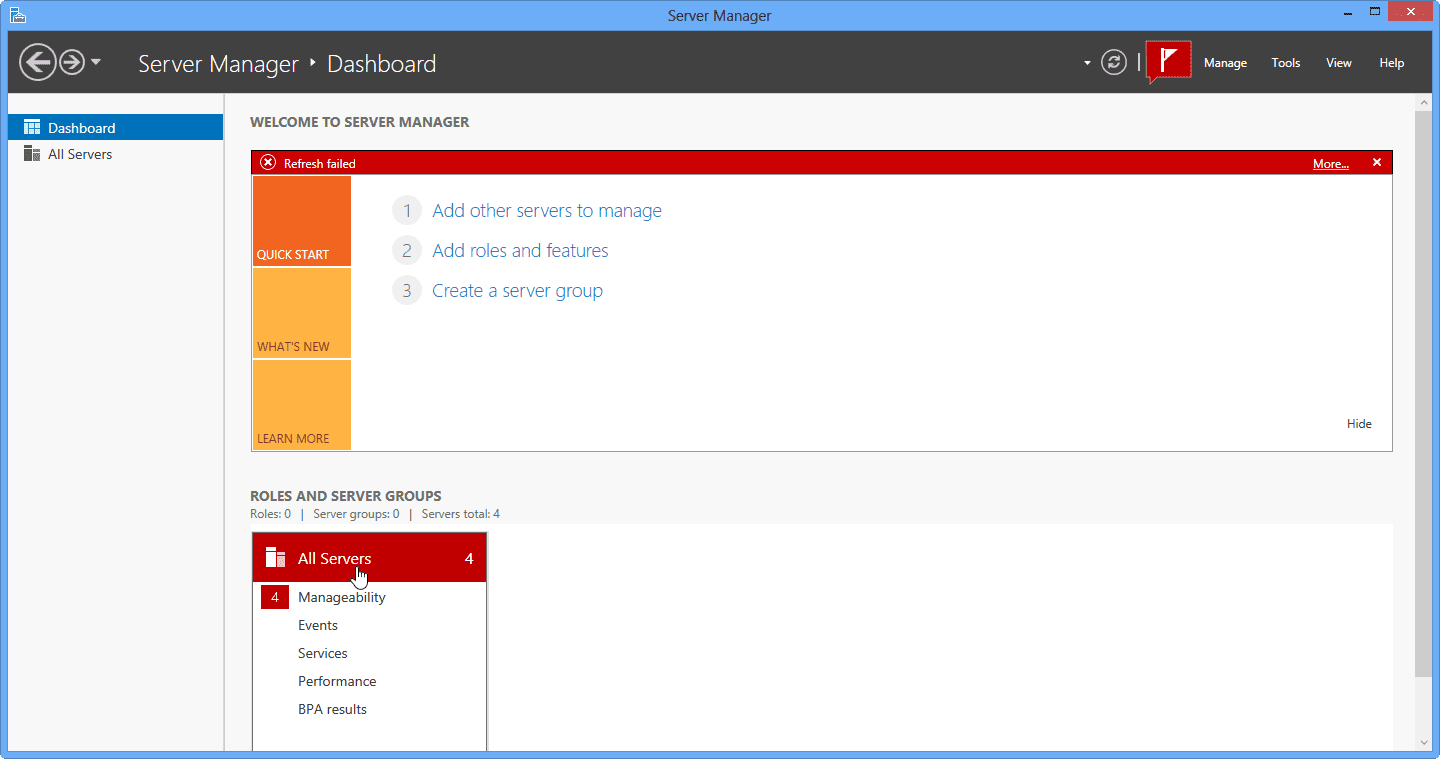
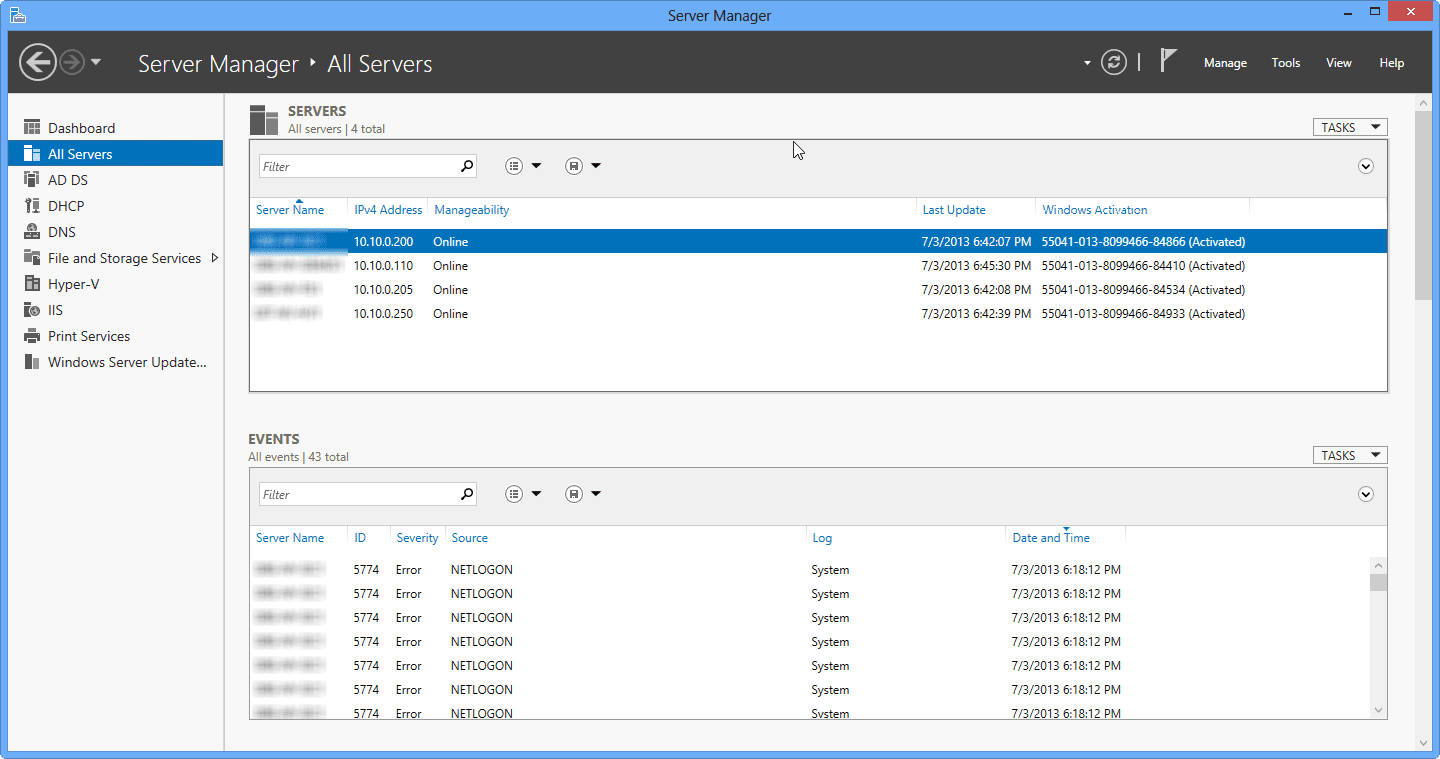
The selected servers should now be available to manage via Server Manager and other tools in RSAT. However, note that the refresh progress bar is extremely hard to spot, and you may think nothing is happening. If you note the red circle and arrow in the image below, the bar slowly moves from left to right, and it is the only indication that the Server Manager console is refreshing.
Now, if these were Windows Server 2012 servers, all would have been fine. However, since these are Windows Server 2008 R2 machines, you will get this error:
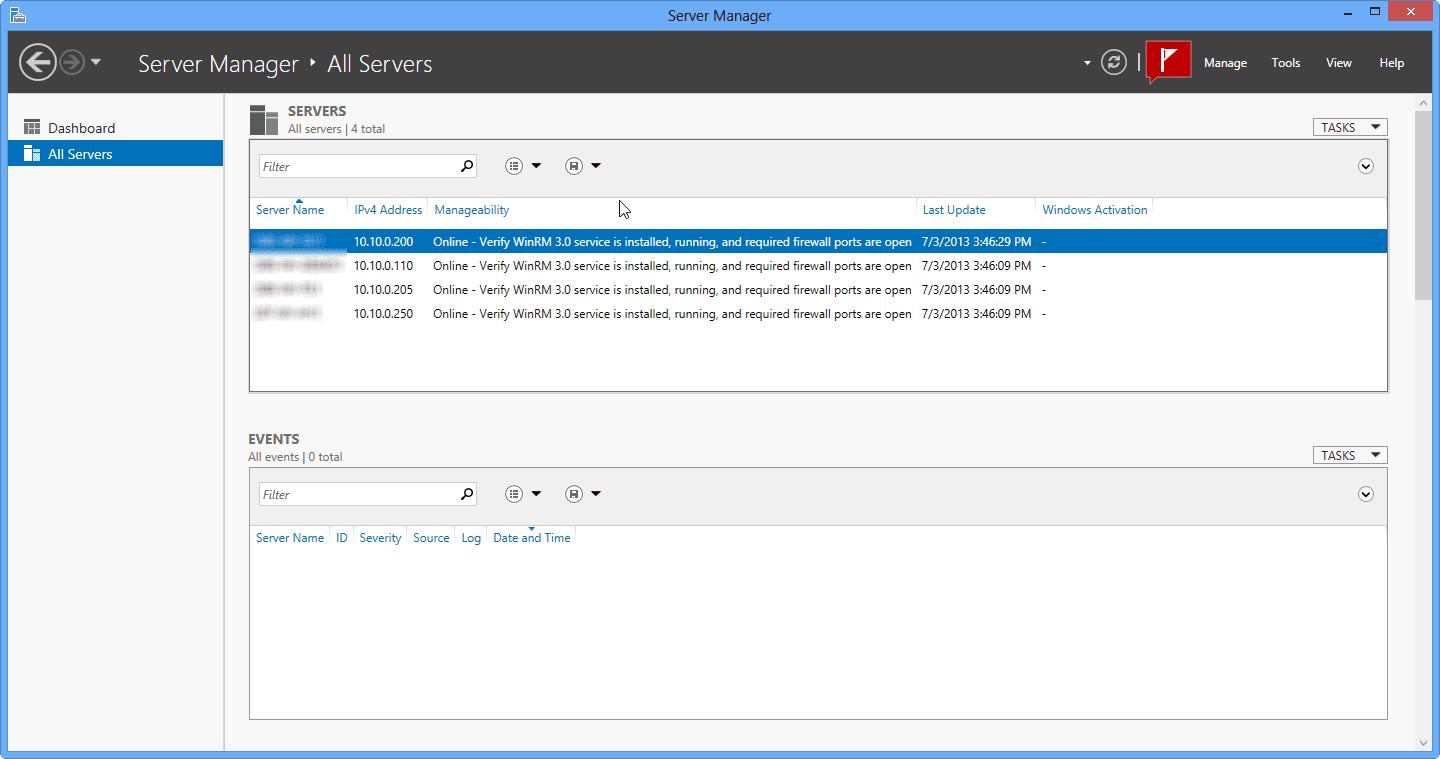
- And when you click on All Servers, you’ll see this:
In order to resolve this issue on the Windows Server 2008 R2 servers follow these steps:
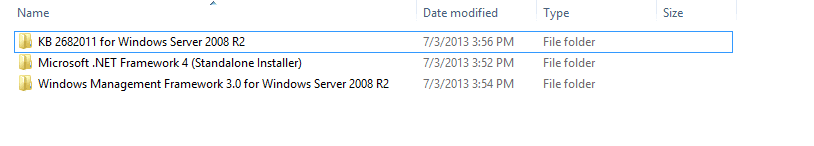
- Install the following components on the Windows Server 2008 R2 server(s) you want to manage:
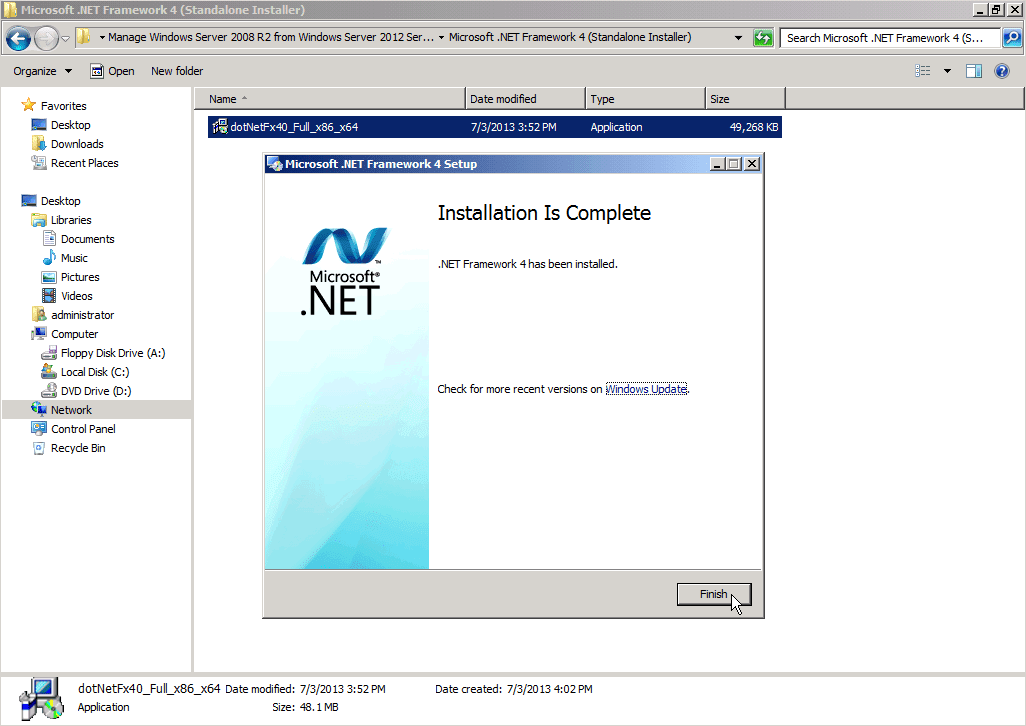
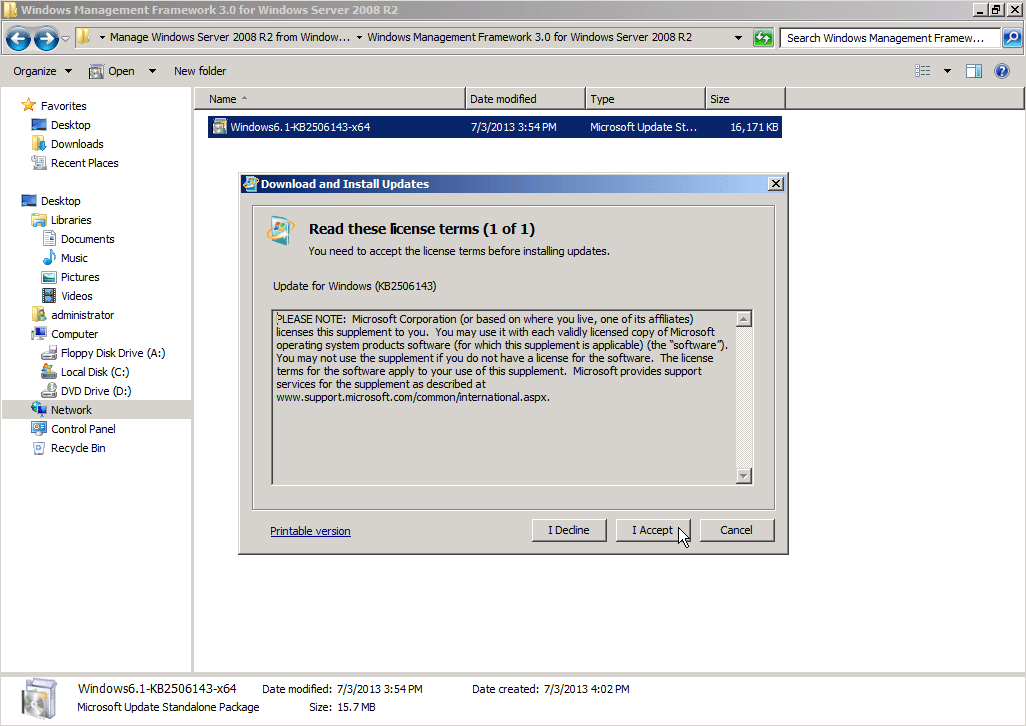
– Microsoft .NET Framework 4.0– Windows Management Framework 3.0– the KB2682011 update
- Place all the above in a folder, have them ready to install.
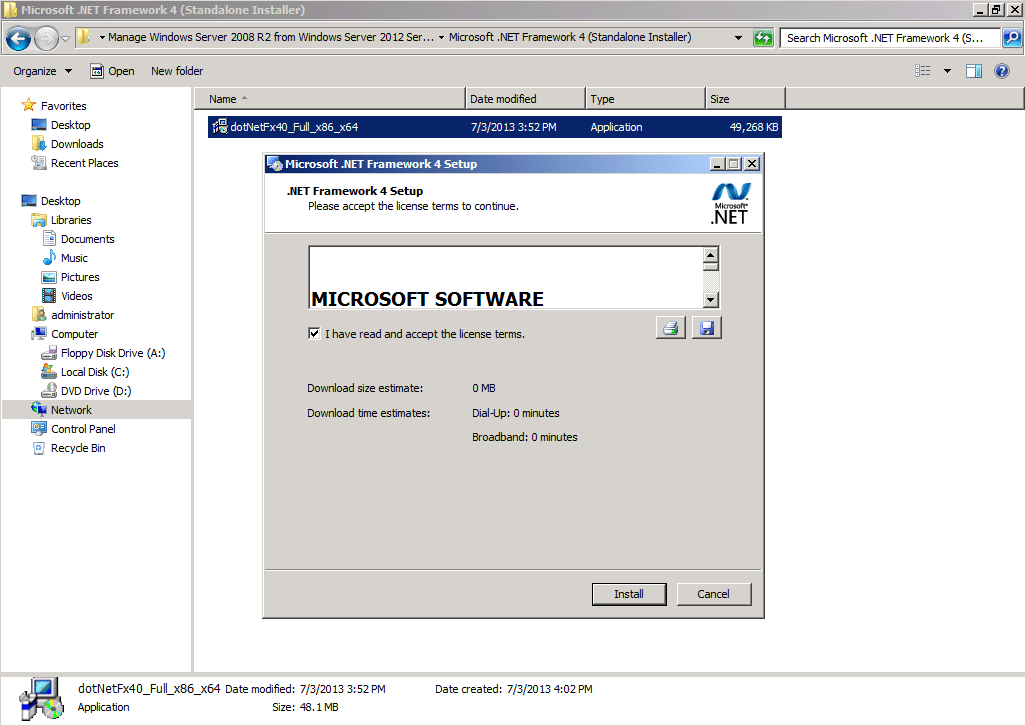
From my experience, in many cases .NET Framework 4.0 is already installed. But if it’s not, install it. While a reboot is mostly likely NOT required for this once you install it, you’ll get at least six new security updated from Microsoft’s Windows Update, so you will need to reboot after all.
- After that, install WMF 3.0. This one will require a reboot, so plan your actions accordingly, but you can wait with the reboot till the next step.
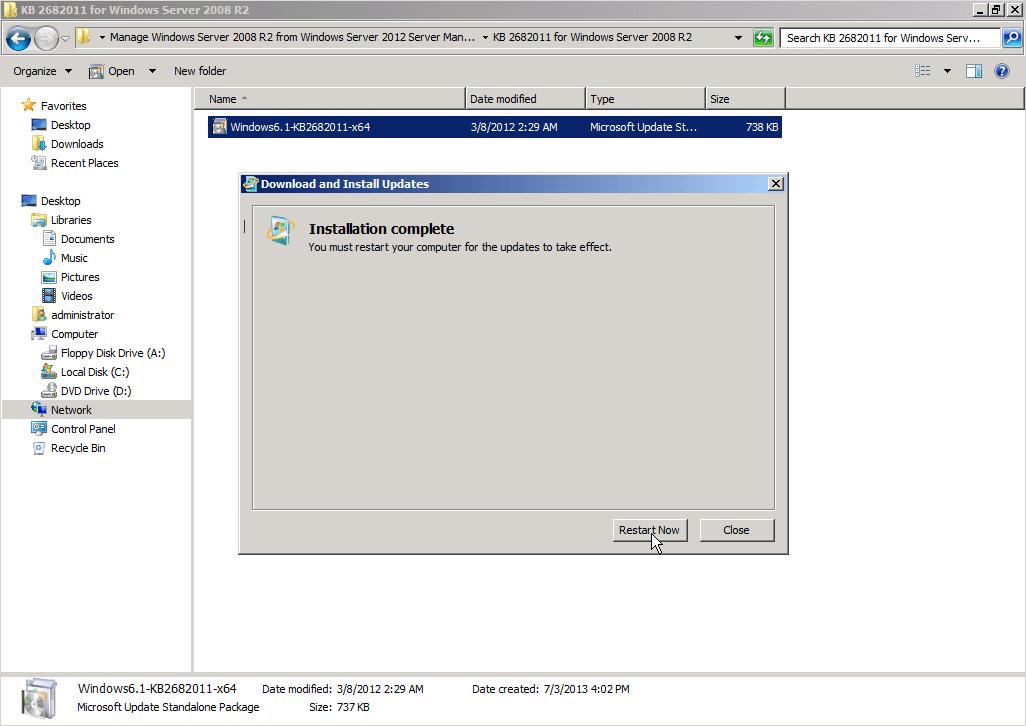
- Once installed, install the KB2682011 update. This too will require a reboot.
- You can now reboot.
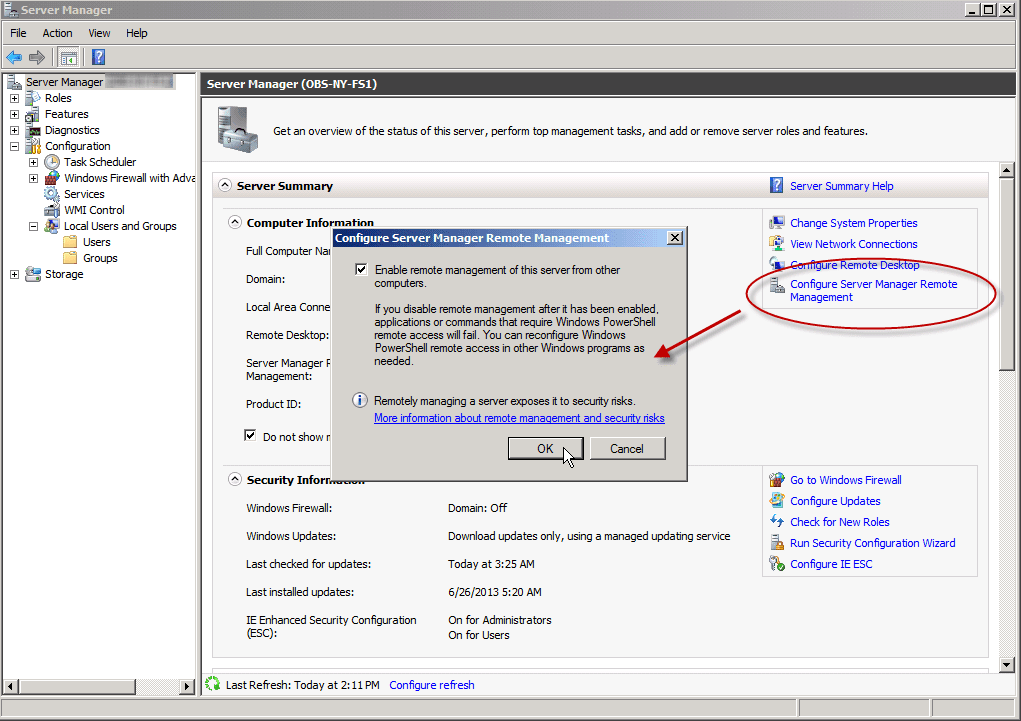
- Next, on the monitored servers open Server Manager and click on Configure Server Manager Remote Management. Click to select the Enable remote management… checkbox and click OK.
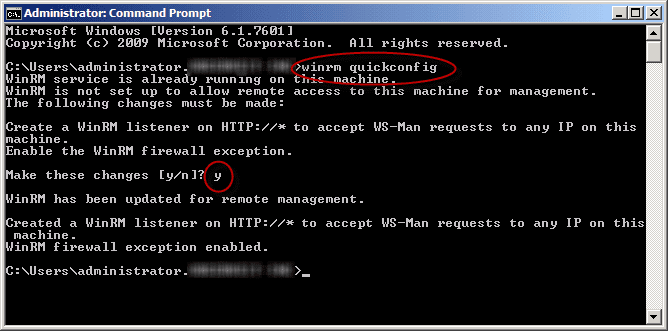
- This should take care of all firewall rules, but from my experience there were some servers that still did not let me connect to them. I also ran the following command from their elevated credentials (“Run As Administrator”) command prompt: winrm quickconfig
- Click Y when prompted.
- Now we’re all set. Back on your Windows 8 machine, refresh the “All Servers” view. This may take some time.
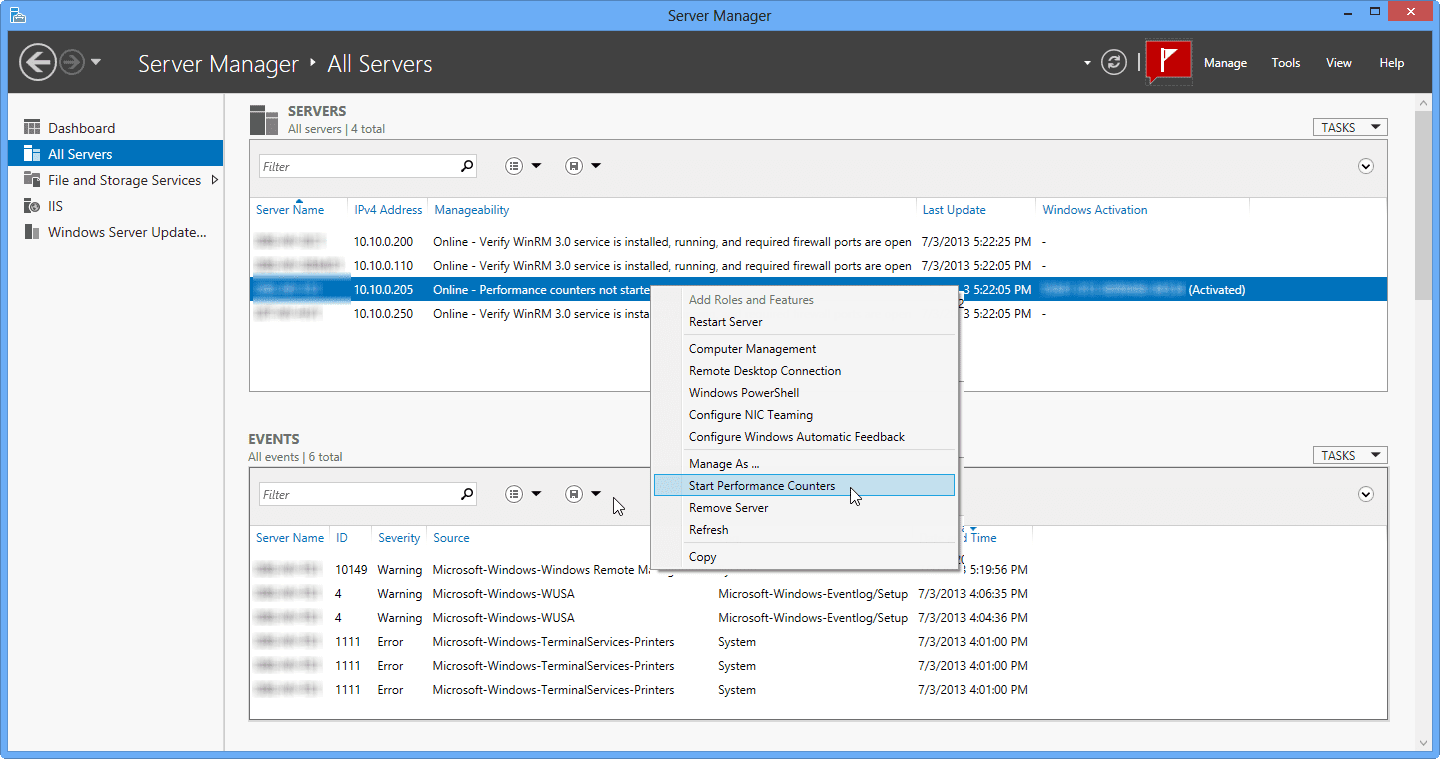
- Since performance counters on the remote servers were not yet started, you’ll see that in the view list. Right-click on the server and select Start Performance Counters.
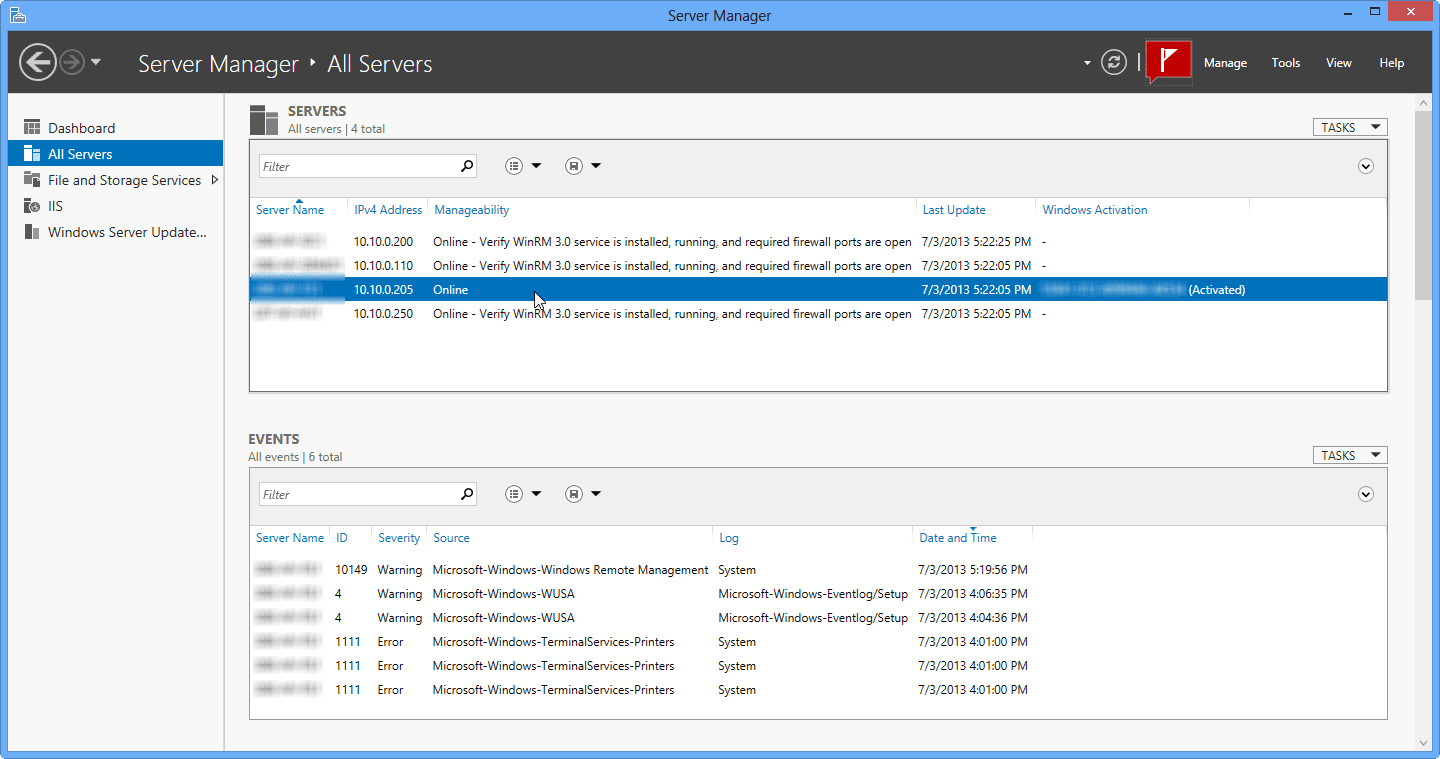
- If all is well, server status will turn into “Online” and it can now be managed.
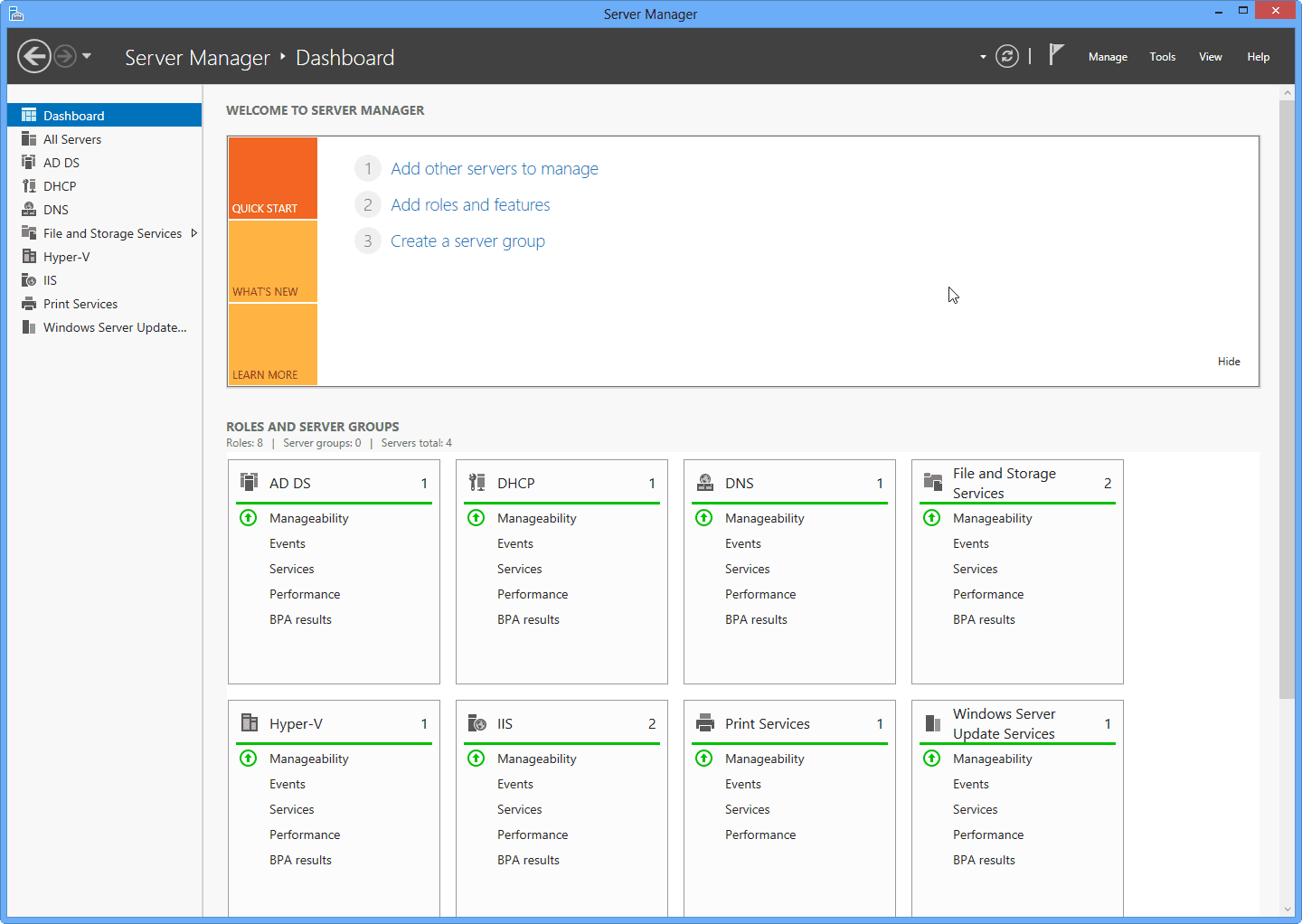
After all servers were added and configured, the dashboard gives you a nice breakdown of all server roles, allowing you to easily manage them.