How to Uninstall and Reset Windows Subsystem for Linux Distributions
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a compatibility layer for Windows 10 and Windows Server that allows users to run Linux binaries natively. WSL virtualizes a Linux kernel interface on top of Windows, so it only requires a minimal amount of RAM. And when not in use, the WSL driver isn’t loaded into memory, making it more efficient than a VM or container. In addition to giving access to the tools included with whichever Linux distro you choose to install, WSL can also run system level daemons (services) in the background. You can even install multiple Linux distributions and switch between them.
Linux distributions for use with WSL are managed via the Microsoft Store. At the time of writing, Ubuntu, openSUSE Leap, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, Kali Linux, and Debian can be installed from the Store. One of the advantages of using WSL is that you can reset Linux distributions back to their default settings, wiping any applications you’ve updated or installed. Resetting a distribution is faster than removing it and then reinstalling it using the Microsoft Store.
If you don’t already have a Linux distribution installed in Windows 10, check out How to Install Windows Subsystem for Linux on Petri.
Reset a Linux Distribution
For the purposes of this article, I’m going to use Windows 10 version 1809. You might find that the following instructions don’t work in earlier versions of Windows 10. For example, prior to the Fall Creators Update, it wasn’t possible to remove a Linux distribution using the Microsoft Store.
I have Ubuntu Linux installed on my Windows 10 PC. The instructions that follow can be used to uninstall any Linux distribution.
- Type apps & into the search box in the bottom left of the taskbar.
- Click Apps & features in the search results. The Settings app will open.
- On the Apps & features page in the Settings app, type Ubuntu, or the name of the Linux distribution you want to reset, in the ‘Search this list’ box.
- Ubuntu, or the name of your Linux distribution, will appear. Click it and then click Advanced options.
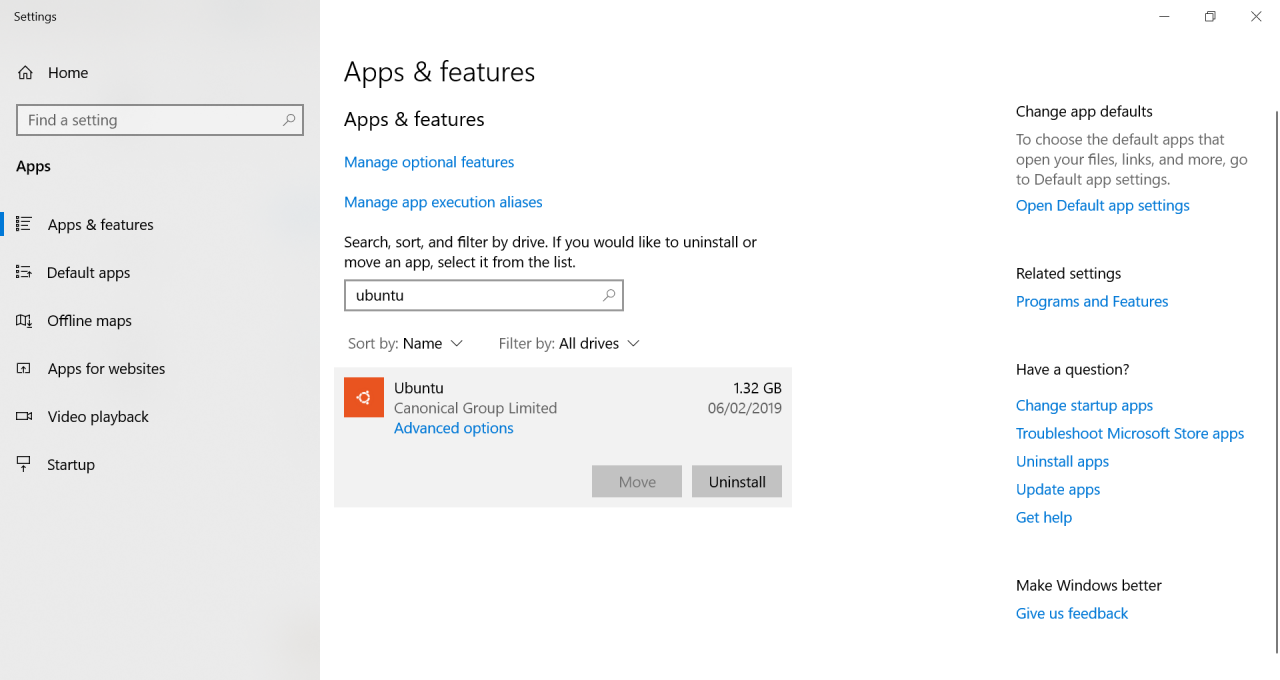
- In the Settings app, scroll down the list of options until you see Reset. There are two options, Repair and Reset. We want to reset our distribution, so click Reset.
- You will see a warning that resetting the app will permanently delete its data and sign-in preferences. Click Reset again in the pop-out dialog.
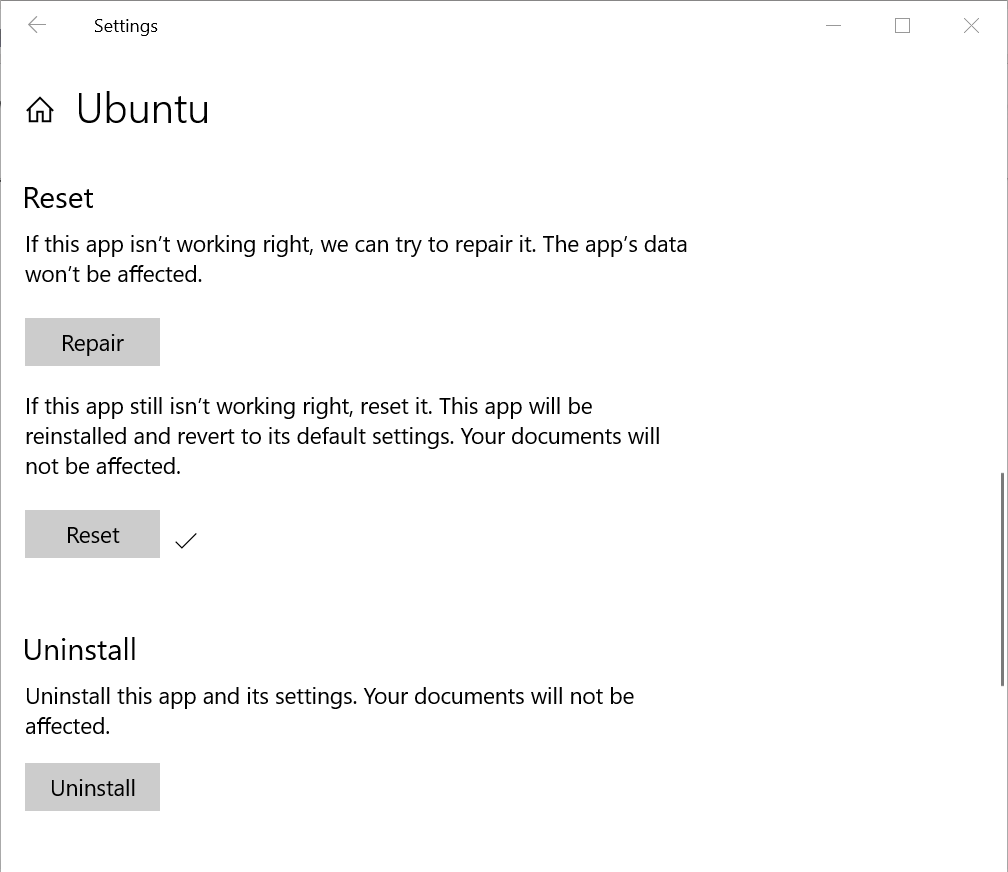
- The resetting process will take a few seconds. Once it’s complete, a tick icon will appear to the right of the Reset button.
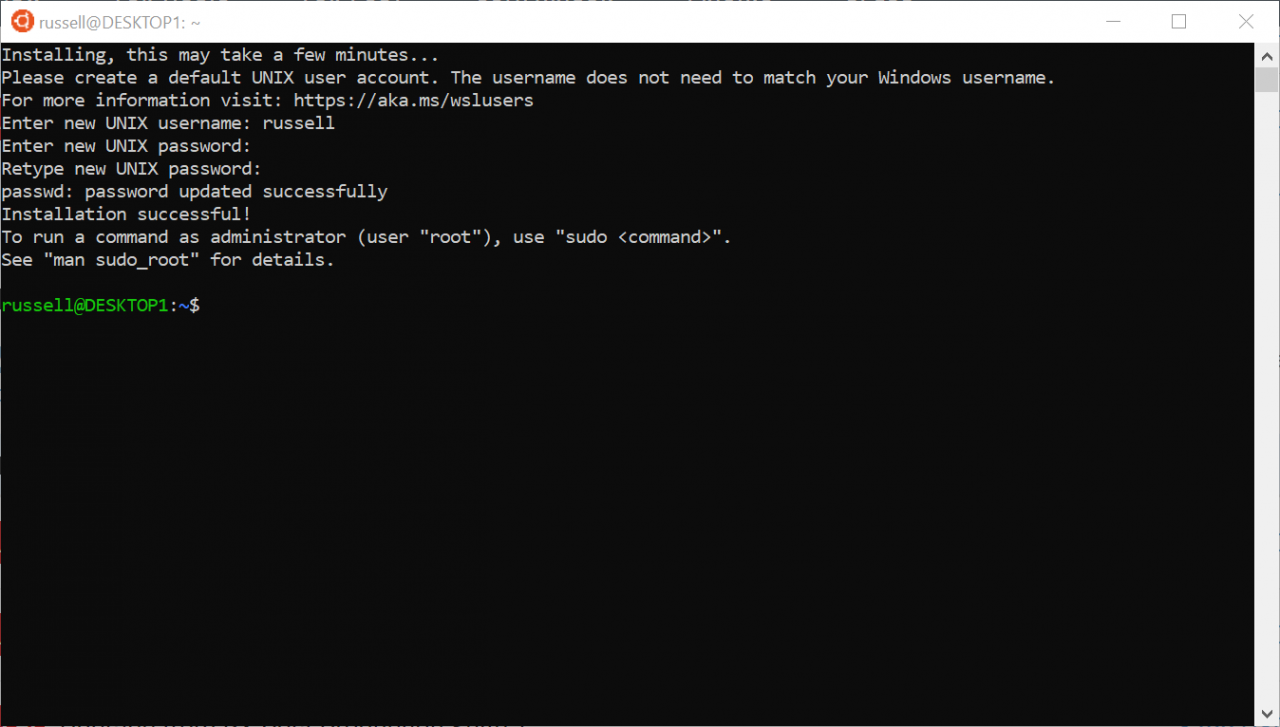
Now start your Linux distribution. It will take a few minutes to reinstall Linux and you’ll be prompted to set up a new user.
Uninstall a Linux Distribution
Removing a Linux distribution is just as easy as performing a reset. Follow the instructions above for resetting Linux until you get to the distribution’s advanced options page in the Settings app. Then continue as shown below:
- In the Settings app, scroll down the list of options until you see Uninstall.
- Click Uninstall.
- You will see a warning stating that you are about to remove the Linux distribution from Windows. Click Uninstall
Removing and resetting Linux distributions with the Windows Subsystem for Linux is easy using standard Microsoft Store app management controls in the Settings app. In an upcoming article, I’ll show you how to manage multiple Linux distributions on the same Windows 10 PC.




