This document describes how you can configure an Alcatel SpeedTouch Pro ADSL modem not to use NAT anymore, and not to perform the dialing to the ISP.
Note that you’ll need a software login method to achieve a connection to ADSL. Alternatively, there are many relatively cheap and/or better Routers on the market which perform these “port forwarding” requirements in a much easier and reliable manner.
This process is often called BRIDGING. The Alcatel modem will not receive the true IP address from the ISP, instead it will be sent to your machine or Internet Gateway box (or router). BRIDGING in the case of the Pro, is just a fancy name for turning it into an ordinary ADSL modem and switching off the Security and Internet Sharing features. This often becomes necessary when trying to allow services like MSN Messenger, VPNs or even running certain Servers.
The difference between BRIDGING and DHCP SPOOFING (described here Configure Alcatel SpeedTouch ADSL for DHCP Spoofing) is that with bridging the end-machine/router does the dialing, and so it gets the real IP address from the ISP. With spoofing the modem dials for you, receives the IP address from the ISP, and then gives it to the end-machine/router.
As stated, this process will therefore eliminating NAT on the Alcatel modem. It is also useful for setups where combination of an Ethernet gateway routers which have PPTP dialer support are in placed. Doing so will enable you to configure an internal router or a server that has routing software installed and have it receive an IP address from your ISP – instead of having the modem obtain the address for you.
This method will work if one of the following assumptions is true:
- Your modem is connected to the Internet and another computer is connected to your modem.
- Your modem is connected to the Internet and you have a router that is connected to the modem. This router must have NAT capabilities and PPPoE dialing capabilities. The router will then be connected to a hub/switch, and to it other computers will connect.
- Your modem is connected to the Internet and you have a server computer that is connected to the modem. This server must have Routing and NAT capabilities and will be configured to dial to the Internet. The server will then be configured with another NIC, and to it you connect another computer.
- Your modem is connected to the Internet and you have a server computer that is connected to the modem. This server must have Routing and NAT capabilities and will be configured to dial to the Internet. The server will then be configured with another NIC, to which you will then connect a hub/switch, and to it other computers will connect.
Make a note of the fact that the modem will stop acting as a router with NAT/PAT which means that you’ll have to connect it to a router or server that has NAT capabilities. Without such configuration you won’t be able to connect to the Internet.
Note: This configuration tip will only work in the PRO modem or on a HOME modem that was upgraded to PRO: Upgrade from Alcatel SpeedTouch Home to Pro.
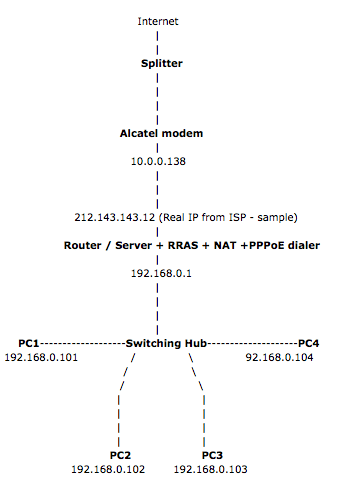
Proposed layout:
- The ADSL cable goes to the splitter.
- The ADSL modem is connected to the splitter.
- The ADSL modem is configured as PRO.
- NAT is disabled on the modem.
- The Ethernet cable from the modem is connected to the router (or server with RRAS and NAT
- The router / server is connected to the switching hub.
- All PC’s are connected to the switching hub.
Disclaimer & Warning
Messing with the software settings of your modem and/or messing with the registry or internal settings of your operating system can render your modem or operating system useless. Read the whole article and manual before you do any changes. Following these steps might work for you. It did for me and for many others, but that does not necessarily mean they will! I take no responsibility for anything bad that might happen to your OS or modem, and since you’re on your own – Do not ask me for help! It’s your modem!
Applying this hack will definitely VOID WARRANTY! If you are not experienced with tricks like these STOP NOW! Besides, some ISPs might stop supporting you if they find out that you messed up with your modem.
Configure your modem as Pro
You’ll have to configure the modem as Pro. If you have an Alcatel SpeedTouch Home please follow this guide before going on with the upgrade to 510: Upgrade from Alcatel SpeedTouch Home to Pro.
Step One – Configure your modem
You’ll have to disconnect from the ADSL service to configure the following settings, so maybe now’s a good time to print this screen.
Connect to the modem via the web interface on http://10.0.0.138.
You’ll get a screen like this one:
Go to the PPTP menu and remove all entries. Apply and Save the changes.
Go to the PPP menu and remove all entries. Apply and Save the changes.
Go to the Phone Book menu and remove all the entries. Apply and Save changes.
Go to the CIP Interfaces and delete all entries. Apply and Save all.
Go to the Bridging Ports menu and delete all entries. Apply and Save all.
On the Phone Book menu and add a new entry with following details:
Name=’BRIDGING‘ VPI=8 VCI=48 Type=bridge
Save the changes.
Note: Some European ISPs have other VPI/VCI settings. Please contact your ISP for more details if you cannot make it work with the above settings. Note that is you did get the settings right – they will have a yellow color.
Go to the Bridging menu screen and add a new entry for ‘BRIDGING’ with following details:
Bridge Port=’BRIDGING‘ Encap=LLC/SNAP FCS=No State=Forwarding
Apply and save these changes.
Step Two – Configuring the workstation / router / server
Don’t forget that the modem will now no longer login by itself, and will require another (better equipped) Router, or software method to connect to and share ADSL.
If it’s a workstation that’s connected directly to the modem you should then configure it with a dialer (described below). You configure the DNS server to be the same as the IP address of your ISP’s DNS server, or if you want – to be the same as the inner IP address of the modem itself. If that computer also acts as a DC then it must already have an installed DNS service. With that said all you have to do is to configure forwarding between the DNS and the DNS server of your ISP.
To configure a dialer (in Windows XP) do the following:
- Open Network Connections from the control Panel and click Create a New Connection.
- In the Welcome to the new connection wizard click Next.
- In the Network Connection Type window select Connect to the Internet. Click Next.
- In the Getting ready windows select Set up Connection Manually. Click Next.
- In the Internet Connection windows select Connect using a Broadband… Click Next.
- In the Connection name windows enter the connection’s name. Click Next.
- In the Connection Availability window select Anyone’s Use (if you want to). Click Next.
- In the Internet Account Information window enter your ISP-given username and password.
Enable this connection to be the default connection, enable ICF and allow connecting without the need to prompt for a username and password – if you want. Click Next.
- In the final window select to create a desktop shortcut (if you want) and click Finish.
- A connect ISP PPPoE window will appear. Try to connect.
- Go back to the Network Connections window and see your new icon. You can change it’s properties by right-clicking on the icon.
Warning: There is also no more protective NAT layer (firewall) provided by the Alcatel in bridging mode, so be sure to take care of this in another manner as well, such as installing a 3rd-party firewall or by (at least) enabling ICF on the dialer.
If it’s a server then you have to configure it as a router (which is beyond the scope of this lesson) with NAT capabilities and a dialing software.
If it’s a router – you configure the WAN interface to dial in to the Internet and obtain and IP address automatically. On the LAN interface you either manually configure the IP network ID etc, or you deploy a configured DHCP with all their needs.