How can I configure Outlook 2003 to block spam?
Microsoft Office Outlook 2003 includes features and functionality designed to help block much of the junk e-mail messages (or spam) that you receive. These features give you more control over the kinds of messages delivered to your Inbox, and from whom you want to receive messages. Although these features are not customizable in any way, they do provide a means for reducing the amount of incoming spam. In combination with good rules that you manually create – you can get a 80% spam blocking rate.
Update – Exchange Intelligent Message Filter
Microsoft Exchange Intelligent Message Filter (IMF) was first released at the end of May 2004.
Microsoft Exchange Intelligent Message Filter is a product developed by Microsoft to help companies reduce the amount of unsolicited commercial e-mail (UCE), or spam, received by users.
Intelligent Message Filter is based on Microsoft SmartScreen Technology from Microsoft Research. By using e-mail characteristics tracked by SmartScreen technology, Intelligent Message Filter can help determine whether each incoming e-mail message is likely to be spam. Based on this likelihood, you can choose to block e-mail messages at the gateway or at the mailbox store. Furthermore, users are able to view the Spam Confidence Level (or SCL) rating for each message, and thus determine the effectiveness of IMF. Read more about it on the Display SCL Level in Outlook 2003 page.
Exchange Server 2003 SP2 Update Note: IMF is now an integral part of Exchange Service Pack 2 (SP2). You can learn how to configure it on SP2 by reading Configure Intelligent Message Filter in Exchange 2003 SP2.
Read more about IMF in the Related Articles section below.
How Outlook 2003 Helps Block Junk E-Mail Messages
These Outlook 2003 features are designed to work together to help block unwanted e-mail messages.
- Junk E-Mail Filter: Outlook 2003 uses state-of-the-art technology developed by Microsoft Research to evaluate whether a message should be treated as a junk e-mail message based on several factors—such as the time the message was sent and the content and structure of the message. The filter does not single out any particular sender or type of e-mail message. Rather, it uses advanced analysis to determine how likely it is to be thought of by you as a junk e-mail message.
By default, this filter is set to a low setting designed to catch the most obvious junk e-mail messages. Messages caught by the filter are moved to a special Junk E-mail folder, where you can access them later. If you want, you can make the filter more aggressive (perhaps mistakenly catching more legitimate messages), or even set Outlook 2003 to permanently delete junk e-mail messages as they come in.
- Safe Senders List: If an e-mail message is mistakenly marked as a junk e-mail message by the filter, you can easily add the sender of that message to your Safe Senders List. E-mail addresses and domain names on the Safe Senders List are never treated as junk e-mail messages, regardless of the content of the message. Contacts are trusted by default and messages from them will never be treated as junk e-mail messages. When your company uses Microsoft Exchange Server, messages from within the organization will also never be treated as junk e-mail messages. You can configure Outlook 2003 to accept only messages from the Safe Senders List, giving you total control over which messages you receive.
- Blocked Senders List: E-mail messages from a certain e-mail address or domain name can easily be blocked by adding the sender to your Blocked Senders List. Messages from people or domain names on your Blocked Senders List will always be treated as junk e-mail messages, regardless of the content of the message.
- Safe Recipients Lists: An e-mailing list or group that you are a member of can be added to your Safe Recipients Lists. Any messages sent to the e-mail addresses or domain names on this list will not be treated as junk e-mail messages, regardless of the sender or content of the message.
- AutoUpdate: You can update your Junk E-Mail Filter with periodic updates from Microsoft so you have the latest methods to block unwanted messages. Microsoft is committed to providing periodic updates of the Junk E-Mail Filter. However, in Microsoft Office 2003 Beta 2 the AutoUpdate feature is not included.
Setting Junk E-Mail Filters in Outlook 2003
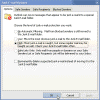
In Outlook 2003, the Junk E-Mail Filter is turned on by default. The first time Outlook 2003 moves a message to the Junk E-mail folder, it will notify you with a dialog box.
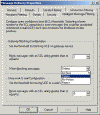
To change junk e-mail settings in Outlook 2003:
- On the Tools menu, select Options.
- In the Options dialog box, in the E-mail section, click Junk E-mail.
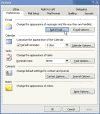
- Choose the level of junk e-mail message protection you want.
- You can also add or remove email addresses or sending domains to the Safe Senders list. That list can be exported and imported to another computer.
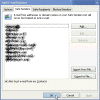
To add a sender to your Safe Senders List, Safe Recipients Lists, or Blocked Senders List:
- Right-click on a message from the sender.
- Point to Junk E-mail, and click either Add Sender to Safe Senders List, Add Sender to Blocked Senders List, or Add Recipient to Safe Recipients Lists.
To remove a sender’s address from the list of junk mail senders:
- Click on the message that you wish to mark as Not Junk
- Click on the Not Junk button in the Outlook toolbar.
Note: For versions of Microsoft Exchange Server without Cached Exchange Mode, junk e-mail filtering must be installed and configured on the Exchange Server.
Further Reading
You might also want to read the following related articles:
- Archiving the SCL Rating in Intelligent Message Filter
- Block Spam with Exchange 2003 Intelligent Message Filter
- Block Spam with Exchange 2003
- Bug in Intelligent Message Filter Interface
- Combating Spam in the Corporate Environment
- Configure Intelligent Message Filter in Exchange 2003 SP2
- Display SCL Level in Outlook 2003
- Display SCL Level in OWA 2003 SP2
- Download Exchange 2003 Intelligent Message Filter
- GFI MailEssentials for Exchange/SMTP – more info
- How to Post to Newsgroups Without Getting spammed?
- Installing Intelligent Message Filter with Exchange 2003 SP2
- Junk E-mail Reporting Tool for Outlook 2003
- Moving Intelligent Message Filter Archive Folder
- Sender Policy Framework
- Updating Intelligent Message Filter in Exchange Server 2003 SP2
- View Intelligent Message Filter Archive
Links
Prevent Junk E-Mail Messages with Outlook 2003
Exchange Intelligent Message Filter