Enable Remote Management of Windows Server 2008 R2 Server Core
As you probably know by now, Windows Server 2008 Server Core installation provides a minimal environment for running specific server roles. This reduces the maintenance and management requirements, as well as the attack surface for those server roles. You can read more about Server Core on this site.
One of the challenges of using Server Core is the management aspect. Fortunately, most of the management pain has been solved by usage of local Command Prompt, PowerShell (new to R2 Server core), manually created scripts, 3rd-party graphical user interface tools, and recently in R2, a tool called SCONFIG. Read more about SCONFIG in my Manage Windows Server 2008 R2 Core with SCONFIG article.
Server Core is usually intended to be remotely managed. This makes your life easier, as you can manage remote servers and core installations on your Windows 7 workstation, in the comfort of your own office. To do that, you must first make sure that you initially configure the machine with a proper IP address, add it to a domain (if needed) and open the correct Firewall rules and ports. After doing that, you can relax and start using local GUI-based management tools to remotely manage the server, just like you would for any server.
So, how do you enable these rules? Read on.
The easiest method would be to use the built-in SCONFIG tool.
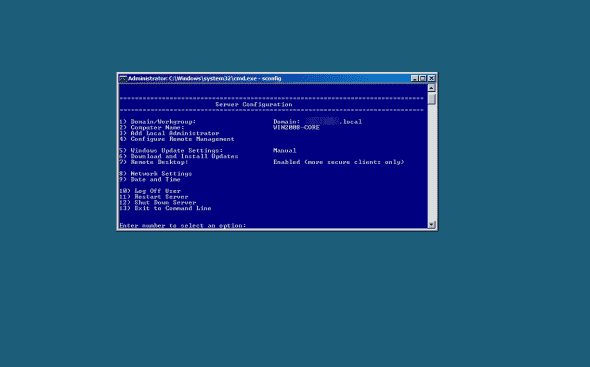
Log in to the core machine, and launch SCONFIG:
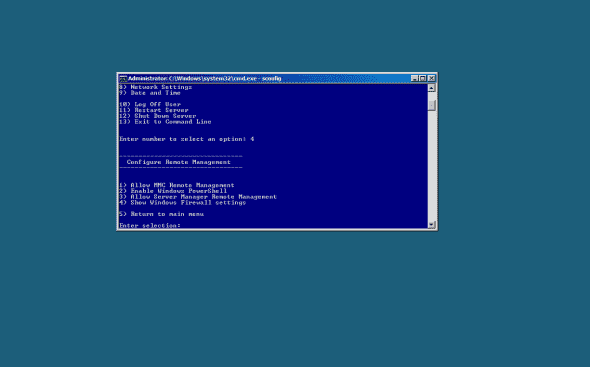
Assuming that the machine is properly joined to a domain, press 4 to enable remote management.
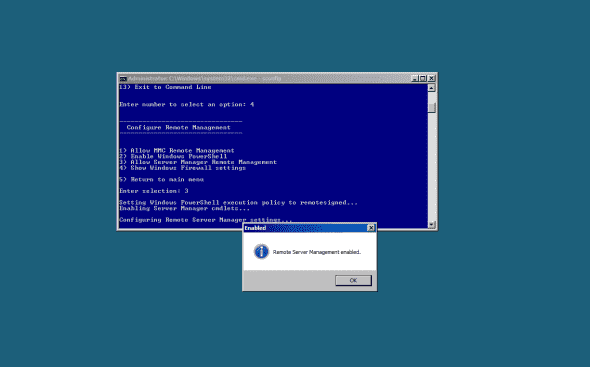
To allow remote management through Server Manager, press 3.
You’ll be notified when settings are completed.
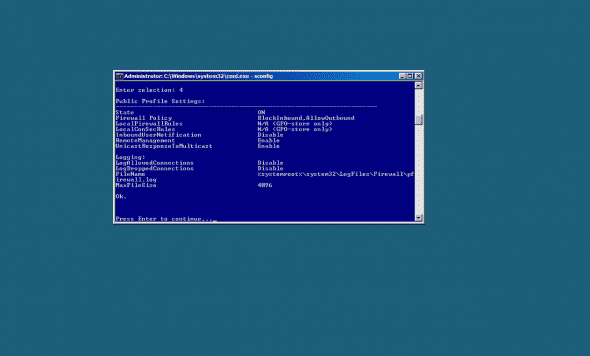
You can also press 4 to view the firewall settings, however, this is not necessary.
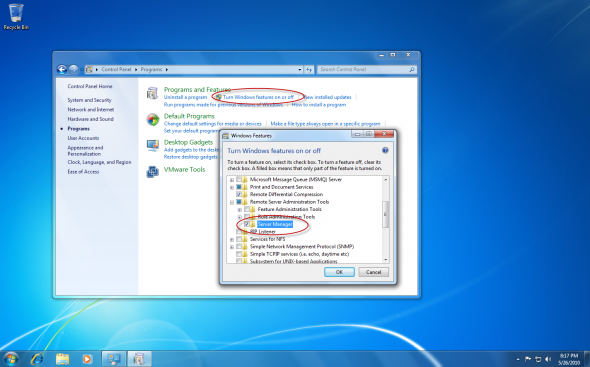
Next, head on to your Windows 7 workstation where you’ve got RSAT installed, and run Server Manager. If you do NOT have Server Manager installed, you must enable it (only after installing RSAT) by using the Turn Windows Features On or Off in Control Panel. For more information on installing RSAT, please read Installing Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows 7.
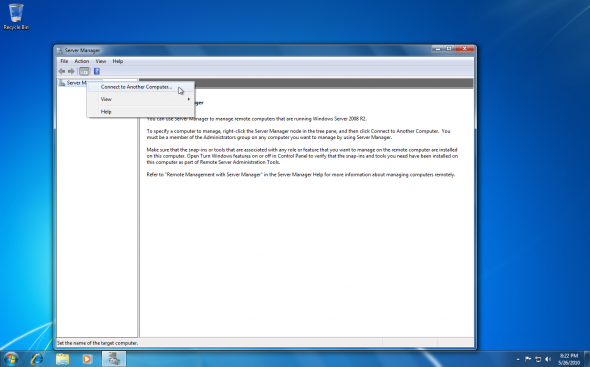
Assuming that both Windows 7 and the remote server core are members of the same Active Directory domain, all you need to do is to right-click on the Server Manager item and select “Connect to Another Computer“.
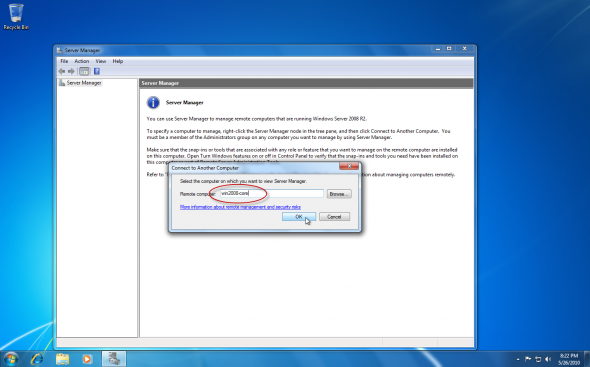
In the Connect to Another Computer window, type the name or browse to the server you wish to connect to.
Note: I strongly suggest you also read my Fix “RPC Server is Unavailable” Error in Windows Server 2008 R2 Remote Disk Management article, as it contains some important information about the firewall rules that need to be enabled on the local computer.
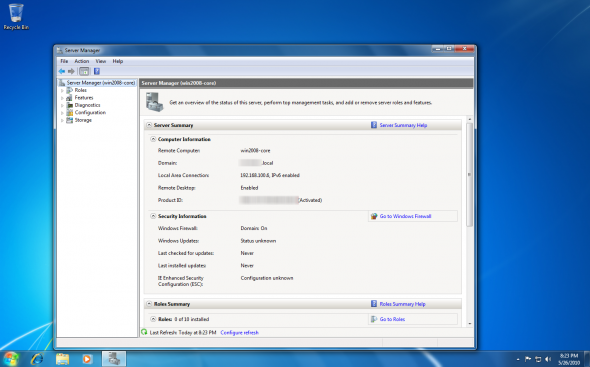
Bingo.