Windows 7 Backup and Restore is the long awaited backup replacement for Vista’s Backup Status and Configuration tool which lacked many important features. When using the Backup and Restore tool, an important aspect of the backup job is the proper selection of backup target.
While Backup and Restore can use several types of hardware for the backup destination, where you save your backup depends on the hardware that you have available, the information you are saving on your backup, and how you want to interact with the backup wizard.
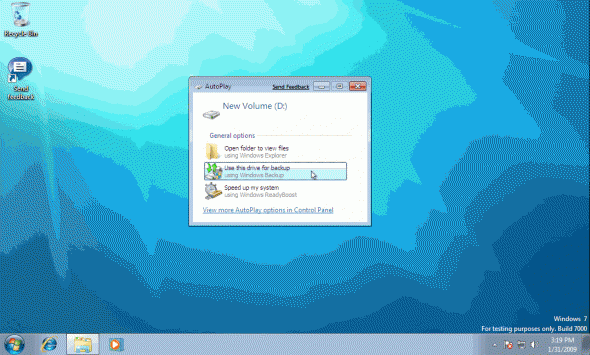
BTW, when you insert a new hard drive (such as an external USB drive) and Windows 7 recognizes it, it will prompt you if you wish to use it as the target for your backups. This can be changed later, but if you do select it, the Backup Files will begin.
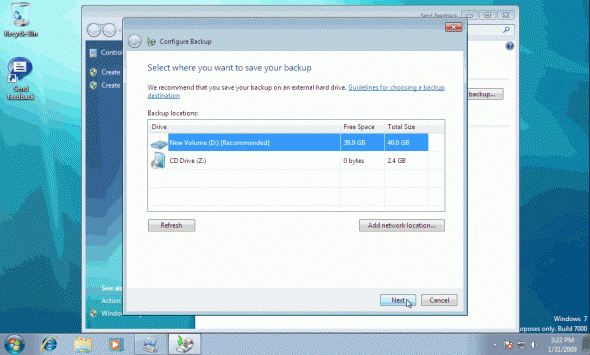
When you choose a destination to save your backup to, the wizard searches your computer and displays a list of all destinations that you can use. The following list describes the types of backup destinations that Backup and Restore supports:
- Internal hard disk – In the past years, hard disks became relatively inexpensive. This makes them the best option for backup media targets. If you have a problem with your operating system and cannot boot your computer up anymore, you can use the hard disk in another computer and you will still have access to the backups. Note: You should also never back up files on the same drive that Windows is installed on because if your computer gets infected by a virus or has a software failure, you might have to reformat the drive and reinstall Windows to recover from the problem and then, again, you would lose your backup data. This risk can be mitigated by using a different partition for the backup target.However, installing another hard disk in your computer is NOT the same thing as adding an additional partition to an existing hard disk (if it has enough free space in it). If you use a partition on an disk for your backups and that disk were to fail, you would lose your backups.Hard disks do have some disadvantages, with the most prominent being the fact that since the hard disk is installed inside your computer, you can’t store it in a location separate from your computer, such as a fireproof safe. Furthermore, hard disks, being delicate in their mechanical aspects, are prone to hardware malfunctions and might be ruined when moved from one location to another.
- External hard disks – An external hard drive can easily be attached to your computer using a USB or Firewire port. Like internal hard disks, external hard disks can hold a lot of information based upon their size. Unlike internal hard disks, external hard disks can be stored in a separate physical location from your computer. This can help protect your backup.External disks are as delicate as internal ones so be careful when moving them from one location to another, and protect them from strong magnetic fields. In addition, USB-attached disks tend to have a slower data transfer rate than internal disks, which, in turn, might cause longer backup times.
- Writeable CDs or DVDs – If you have a CD or DVD burners installed in your computer, you can use it for your backup target. Being cheap to buy and offering cheap media, these make a good choice for mobilizing your backup media to locations that are separate from your computer, such as a fireproof safe.However, note that you can’t save a system image on a CD or DVD, and, depending on how much data you have, it might take several CDs or DVDs to hold your backup and you would need to store and keep track of all of them. In addition, CDs and even the larger DVD medias can store only a fraction of the amount of data that can be stored on a hard disk.
- USB flash drives – Becoming cheaper from day to day, you can use external USB flash drives to store your backups. Like CDs and DVDs, you can store a flash drive in a location that is separate from your computer, such as a fireproof safe.To save a backup on a flash drive, it must be larger than 1 GB. Here too, like CDs and DVDs, current technology limits USB flash drive sizes and you can store only a fraction of the amount of data that can be stored on a hard disk. However unlike hard disks, USB flash drives have no moving parts, making them ideal for moving around.
- Network locations – A shared folder or mapped drive on the network can be a convenient place to save your backups and they can be added as more storage space is required.However, the network location must be available at the time the backup is scheduled to occur and the user name and password that you provided when you set up your backup needs to still be valid for the network location, and other people who have access to the network location might be able to access your backup. Needless to say, a network location cannot be moved around. However being a “network” location, this means that it does not necessarily need to be close next to the computer you’re backing up, and with some limitations, it can be located in a separate physical site.
You cannot use any of the following destinations:
- The destination is a tape drive. Backup and Restore cannot save backups to tapes.
- The destination is the disk that you are trying to back up. You can’t back up a disk to itself.
- The destination is a CD-ROM drive or a DVD-ROM drive. You must use a CD or DVD burner, also known as a CD-R/CD-RW or DVD-R/DVD-RW drive.
- The destination is not formatted as NTFS, FAT, or Universal Disk Format (UDF).
- The destination is either the system disk or the boot disk.
- The destination is a network location on a computer running Windows XP Home Edition.
- The destination is a recovery partition created by your computer manufacturer that contains files and tools that you can use to return your computer to the manufacturer’s settings if it stops working correctly.
- The destination is locked by BitLocker Drive Encryption.
As a general recommendation in regard to using Windows 7 as a client operating system, use either internal hard disks, separate from the one Windows is installed on. Alternatively, use an external USB hard disk and make sure you disconnect it after you perform your backup.