As you know by now, the system partition (meaning the partition on which the operating system is installed on) is a place that just begs for more space as time goes by. Hotfixes, Patches, Service Packs, installed applications such as Microsoft Office and many others – all consume a lot of space on that partition. The more it is used, the more space will be consumed by these apps.
Previous Microsoft operating systems had some internal mechanism to extend or expand partitions. But there were limitations on these operations, such as having the need for the disks to be configured as Dynamic Disks, and the fact that for a long period of time you could extend any partition as long as it’s not the system partition. Some 3rd-party applications could (and still can) be used to extend partitions, but in this article we want to focus on internal tools.
Unlike previous Microsoft operating systems, Windows 7 now allows for an easy, out-of-the-box method of expanding those partitions and making them larger, while reliving us of these previous limitations.
Note: Of course, extending a partition requires one thing, and if you don’t have it, there’s no point in talking or thinking about extending any partition. That thing is “Free, unused space on the hard disk where the partition exists“. You cannot extend a partition, any partition, if you’ve got nowhere to extend it to…
Extending a partition is done by using the Extend feature in Disk Management, or in the DISKPART command line executable.
Note: When you extend a partition, all data on the existing partition will NOT be erased, but it’s better to be safe than sorry, therefore I always recommend using a good backup procedure to back up your data, just in case.
Note: While this article is specifically discussing extending system partitions, the procedures outlined here can be used to extend ANY partition, not just the system partition.
Also note that extending the system partition does not require a reboot.
Basically, there are 2 methods of extending the system partition in Windows 7:
Method #1 – Extending the system partition by using the GUI
1. Log on as an Administrator.
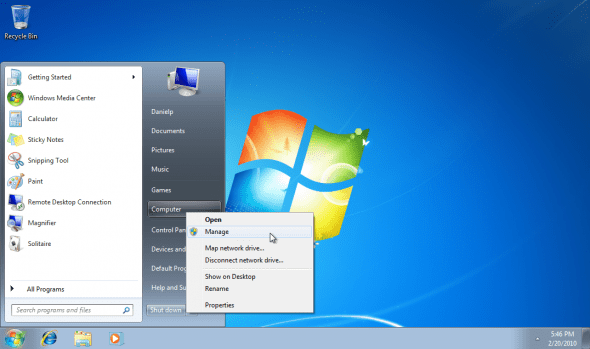
2. Go to Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Administrative Tools > Computer Management. You can also open the Computer Management application by using the Computer context menu. Select Computer Management.
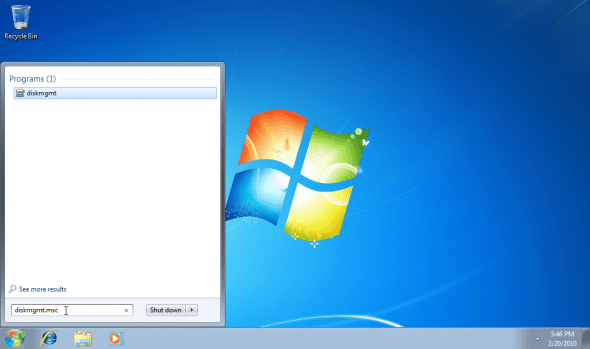
In fact, you can go directly to the Disk Management MMC snap-in by typing diskmgmt.msc in the Start’s search box or on the Run command.
If you’re prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
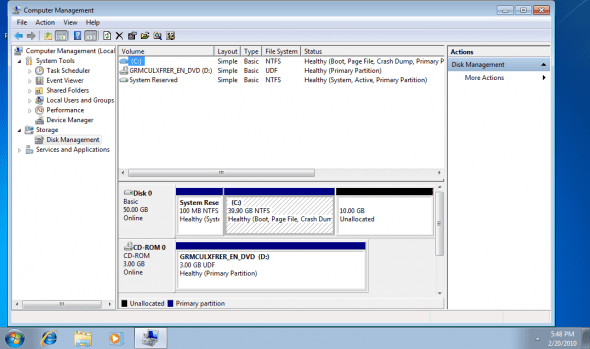
3. Expand the Storage section, and in it go to the Disk Management console.
4. Select the disk you want to extend, for example Drive C.
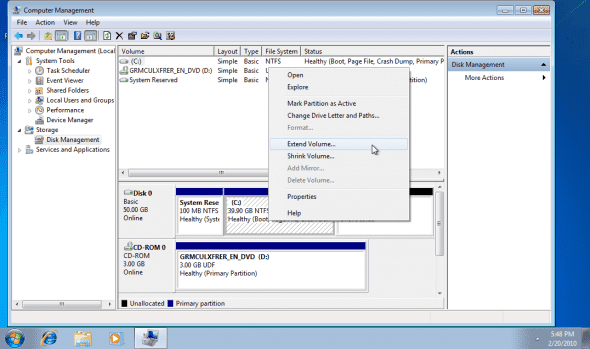
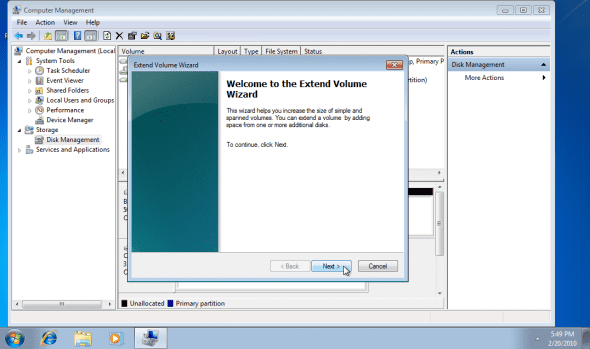
5. Right-click the disk and select Extend Volume.
6. Click on “Next”.
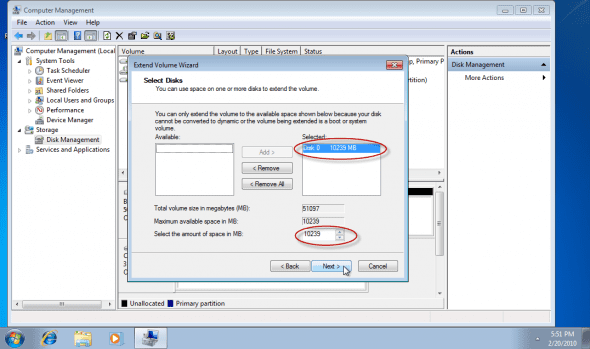
7. Windows 7 will tell you how much space can be added to the existing partition. You can manually enter the amount of space you want to add by changing the “Select the amount of space in MB” values. Note that you cannot enter a higher value than the value already present. Click on “Next”.
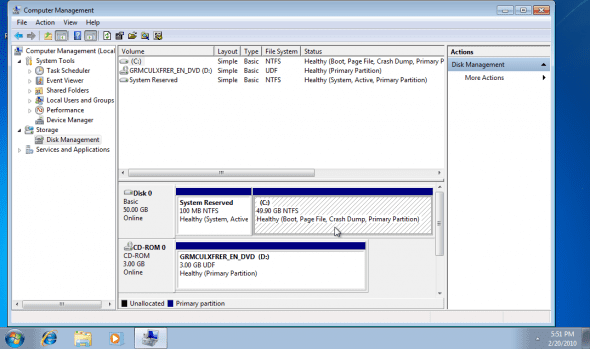
8. The process will finish quite quickly, and a reboot is NOT required. You can notice the new partition size.
Method #2 – Extending the system partition by using the command line
Extending a partition or volume can be done via the CLI, or command line interface. In order to do that perform the following steps:
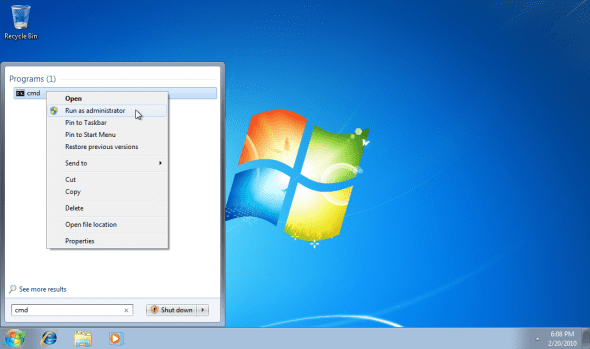
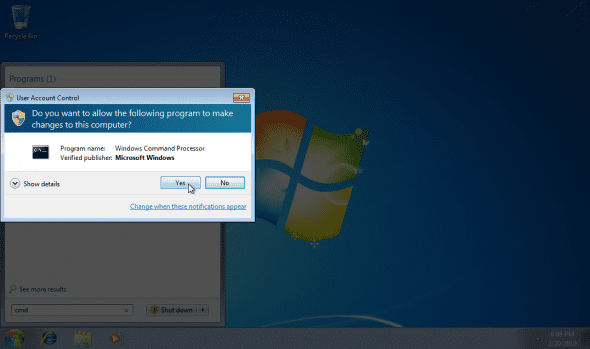
1. Click Start and type CMD, then press Enter. It is best to run the Command Prompt as an Administrator. To do so, right-click CMD and select “Run as Administrator”.
When prompted to allow the Command Processor to run, click on “Yes”.
BTW, you can also hover over the CMD line and press CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER to invoke the “Run as Administrator” shortcut.
2. In the command prompt type
Diskpart
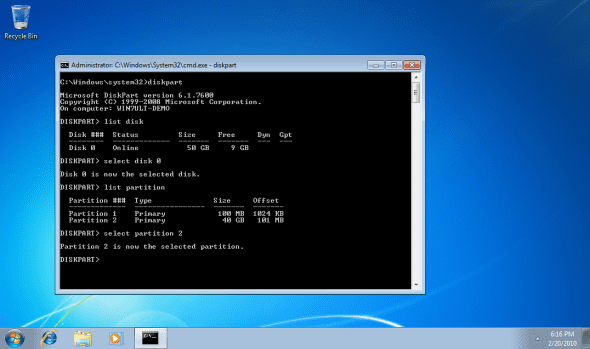
3. Select the right disk drive and partition to work on. Typically, in Windows 7, this should be disk 0 and partition 2, but please make sure you do select the right disk and partition before continuing. You can do so by performing a LIST operation to view your existing disks and partitions BEFORE attempting to expand the wrong partition.
List disk
Select disk 0
List partition
Select partition 2
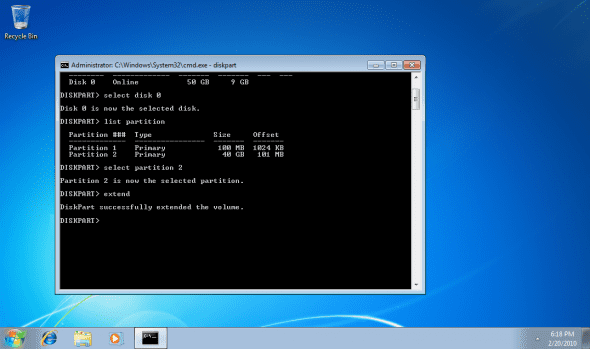
4. When the right disk and partitions were selected, run the EXTEND command. If you don’t specify the size to extend by, then the command will extend the partition by using all of the contiguous space available on that disk.
Extend size=500
The above command will extend the partition by 500 MB.
Extend
The above command will extend the partition by using all of the contiguous space available on that disk.
BTW, do not confuse the extend command with the expand command, which, in Windows 7, is used to expand the size of virtual disks.
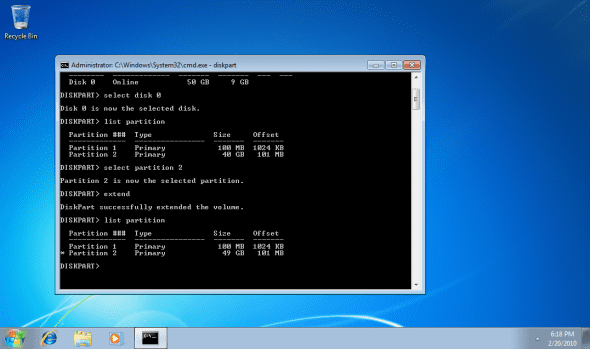
5. You may check the new partition size by running the list command, again.
List partition
6. You must now exit DISKPART by using the Exit command.
Exit
BTW, as a general tip and so that you know, you can use the above procedures also on Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2.