What is an advanced security scenario in Windows Server 2012?
Windows Server 2012 introduces several improvements to the Advanced Security settings dialog when configuring NTFS access controls and auditing. In this Ask the Admin, I’ll look at how permissions configuration has been simplified for advanced security scenarios.
An example of an advanced security scenario is preventing users from accidentally deleting, moving, or renaming entire file structures. Administrators often configure NTFS permissions so that users can create, delete, and rename files, but not delete folders. While this doesn’t provide fool-proof protection, it does give a certain degree of damage limitation when simple finger trouble is the source of the problem.
Configure an Advanced Security Scenario in Windows Server 2012
Let’s configure the permissions set on a folder in Windows Server 2012, to see how the process is easier than in previous versions of Windows Server. Log on to a file server that’s joined to a domain with an account that has local administrator privileges.
- On the desktop, press the Windows key + E to open File Explorer.
- In File Explorer, right-click the folder you want to modify and select Properties from the menu.
- In the Properties dialog, switch to the Security tab.
- Click Advanced in the security tab.
- In the Advanced Security Settings dialog, click Disable inheritance.
- In the Block Inheritance dialog, click Convert inherited permissions into explicit permissions on this object.
In this example, I’m going to grant specific permissions for the Domain Users group. Before doing this, you should remove any existing permission entries for Domain Users.
- Click Add.
- In the Permission Entry dialog, click Select a principal.
- Type domain users in the Enter the object name to select box and click OK.
- Select Files only from the Applies to drop-down menu.
- Click Show advanced permissions.
- Under Advanced permissions, check all permissions apart from Full control, Change permissions and Take ownership.
- Click OK.
- In the Advanced Security Settings dialog, click Add again.
- In the Permission Entry dialog, click Select a principal.
- Type domain users in the Enter the object name to select box and click OK.
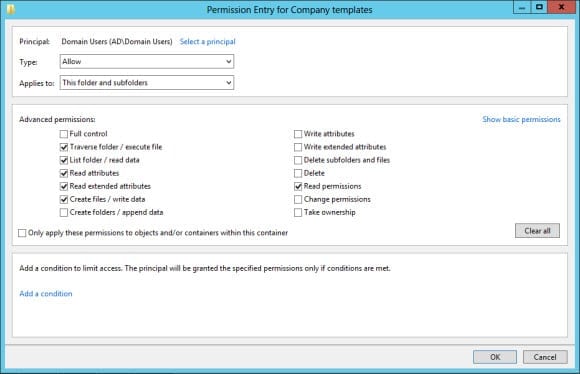
- Select This folder and subfolders from the Applies to drop-down menu.
- Under Advanced permissions, select: Traverse folder/execute file, List folder/read data, Read attributes, Read extended attributes, Create files/write data, and Read permissions.
- Click OK.
- Now you should see two entries for the Domain Users group in the Advanced Security Settings dialog. Click OK.
- Click OK in the Properties dialog.
That’s it! You’re done.