Introduction
I recently ran into an “Access Denied” error message when I was trying to access administrative shares on a Windows 7-based computer from another Windows 7-based computer that was a member of a workgroup.
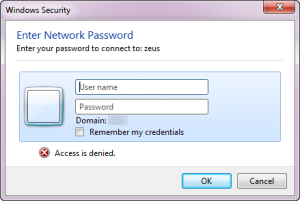
This issue usually occurs when you attempt to use one computer running either version of Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 to access a remote administrative share (C$, D$ etc.) that resides on another Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 machine, and both machines are part of a workgroup (and not an Active Directory domain!).
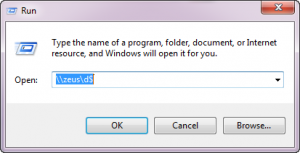
When attempting to use Windows Explorer (or the Run command) you receive the following error message:
Logon unsuccessful:
Windows is unable to log you on.
Make sure that your user name and password are correct.
If you try to map a network drive to the administrative share by using the Net Use command, you get the following error message after providing the correct credentials:
System error 5
has occurred. Access is denied.
For example (remote computer name is ZEUS):
Troubleshooting Checklist
Stuff you need to check before proceeding:
- We’re talking about any combination of Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 and/or Windows Server 2008 R2.
- Both computers are members of a workgroup.
- The workgroup’s name is “Workgroup”.
- From one of the computers, you try to access an administrative share that is located on the other computer.
- When you are prompted for your user credentials, you provide the user credentials of an administrative user account on the destination computer.
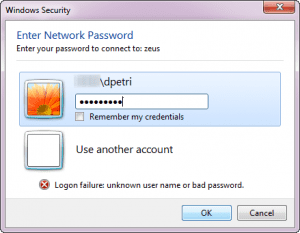
- This also happens when you have the same exact user name and password combinations on both machines. For example, you use DPETRI as the user name on both machines, and the password is identical. Note that this is not a must, but then you will need to enter the correct user name and password as the connection credentials. When using the NET USE command, you must also provide the correct user name and password.
- Although you can specify a remote domain name, since both machines are not members of any domain, you need to specify the remote machine’s name as the domain. For example, if the machine’s name is ZEUS and the username is DPETRI, you enter ZEUS\DPETRI as the credentials.
- We assume that there are no connectivity issues between the computers (can you PING by computer name? Can you PING by IP address?)
- We assume that the Windows Firewall is either disabled on both machines, or that an appropriate rule is used to open the relevant ports.
- We assume that both computers’ network settings are set to “Work” or “Home”, and not “Public”.
Getting Rid of the “Access Denied” Error Message
To solve this issue you need to make a small registry modification on the TARGET computer.
Please carefully read the following warning:
Warning!
This document contains instructions for editing the registry. If you make any error while editing the registry, you can potentially cause Windows to fail or be unable to boot, requiring you to reinstall Windows. Edit the registry at your own risk. Always back up the registry before making any changes. If you do not feel comfortable editing the registry, do not attempt these instructions. Instead, seek the help of a trained computer specialist.
1. Start Registry Editor (Regedit.exe). If you get the UAC prompt, acknowledge it.
2. Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System
3. On the Edit menu, select New and then click DWORD (32-bit) Value.
4. Type LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy to name the new entry, and then press Enter.
5. Right-click LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy, and then click Modify.
6. In the Value data box, type 1, and then click OK.
7. Exit Registry Editor. There is no need to reboot the machine.
Note: To revert to the original setting, change the LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy value to 0 (zero).
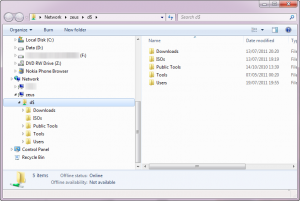
Next, try to access the administrative share on the remote machine. This time you should succeed.
Case solved.