Joining Windows Server 2012 to a Domain
How do I join Windows Server 2012 to a domain?
Before you start on your quest to join Windows Server 2012 to a domain, make sure that you can resolve the Active Directory (AD) domain name using DNS. Pinging the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) ensures that at least one domain controller (DC) is available to process your domain join request.
Check DNS resolution
- Open a command prompt window on Windows Server 2012 by clicking the blue PowerShell icon on the desktop Task Bar or by typing CMD on the Start screen and pressing ENTER.
- In the command prompt window, type ping <FQDN>, replacing <FQDN> with the Fully Qualified Domain Name for your Active Directory domain. For instance, this might look like ad.contoso.com. Note that there’s no need to include the name of any particular domain controller.
If you don’t get a reply from the ping command, check that DNS is set up correctly on the machine that you are trying to join to the domain. There should be at least one DNS entry in the network card’s IP configuration settings. You can check the network adapter’s IP address configuration by typing ipconfig /all in the command prompt, where you should see at least one DNS server address listed. If a DNS server is present in the configuration but you still can’t successfully resolve the domain’s FQDN, you will need to do some more DNS and/or network troubleshooting.
Join the computer to a domain
- Once you have established that DNS resolution is working correctly, open Server Manager from the icon on the desktop Task Bar or from the Start screen.
- In Server Manager, select Local Server in the left pane.
- In the right pane of Server Manager under Properties, click WORKGROUP.
- In the System Properties dialog on the Computer Name tab, click Change.
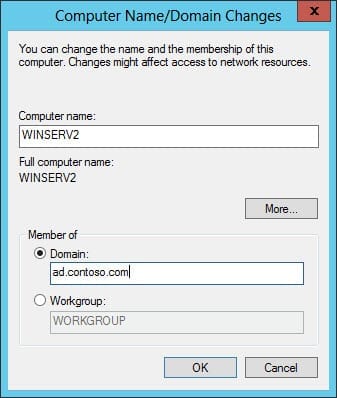
- In the Computer Name/Domain Changes dialog, click Domain, type the FQDN of your Active Directory domain and click OK.
- In the Windows Security dialog, type a domain administrator username and password, or the credentials of another user account with permission to add computers to the domain, and click OK.
- You should then see a welcome message to the domain. Click OK in the message dialog box.
- When prompted to restart the computer, click OK.
- Close the System Properties dialog.
- Click Restart Now in the Microsoft Windows dialog.
Log on as a domain user
Once the computer has rebooted, log on as a domain administrator by clicking the Switch User arrow on the logon screen and then select Other user. You can then log on to the server as a domain user. If you want to log on with a domain user that happens to have the same name as a local user, type the domain username with the domain’s FQDN suffix, such as [email protected]