Demoting a Windows Server 2016 Domain Controller
In this Ask the Admin, I’ll show you how to demote a domain controller and remove the Active Directory Domain Services server role.
Most Windows system administrators know how to promote a server to a domain controller. In older versions of Windows Server, this was easily achieved by running dcpromo. In newer versions, you add the Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) role using Server Manager. Once the role has been added, Server Manager prompts you to complete the process and opens a wizard that guides you through the installation of a domain controller.
There are several ways to demote a domain controller. Server Manager offers two ways to achieve this. The first, and maybe most obvious, is to use the Remove Roles and Features command in the Manage menu. If you try to remove the ADDS server role this way, you will be guided through the removal process by a wizard. Another way you can start the process is to click on Local Server in the left of Server Manager and then scroll down to ROLES AND FEATURES on the right. Then right click Active Directory Domain Services in the list of roles and click Remove Role or Feature in the menu.
- In the Remove Roles and Features wizard, click Server Selection on the left, and then click Server Roles below it.
- In the list of roles on the right, deselect Active Directory Domain Services.
- In the pop-up dialog, confirm that you want to remove associated roles, like the Active Directory DS tools, by clicking Remove Features.
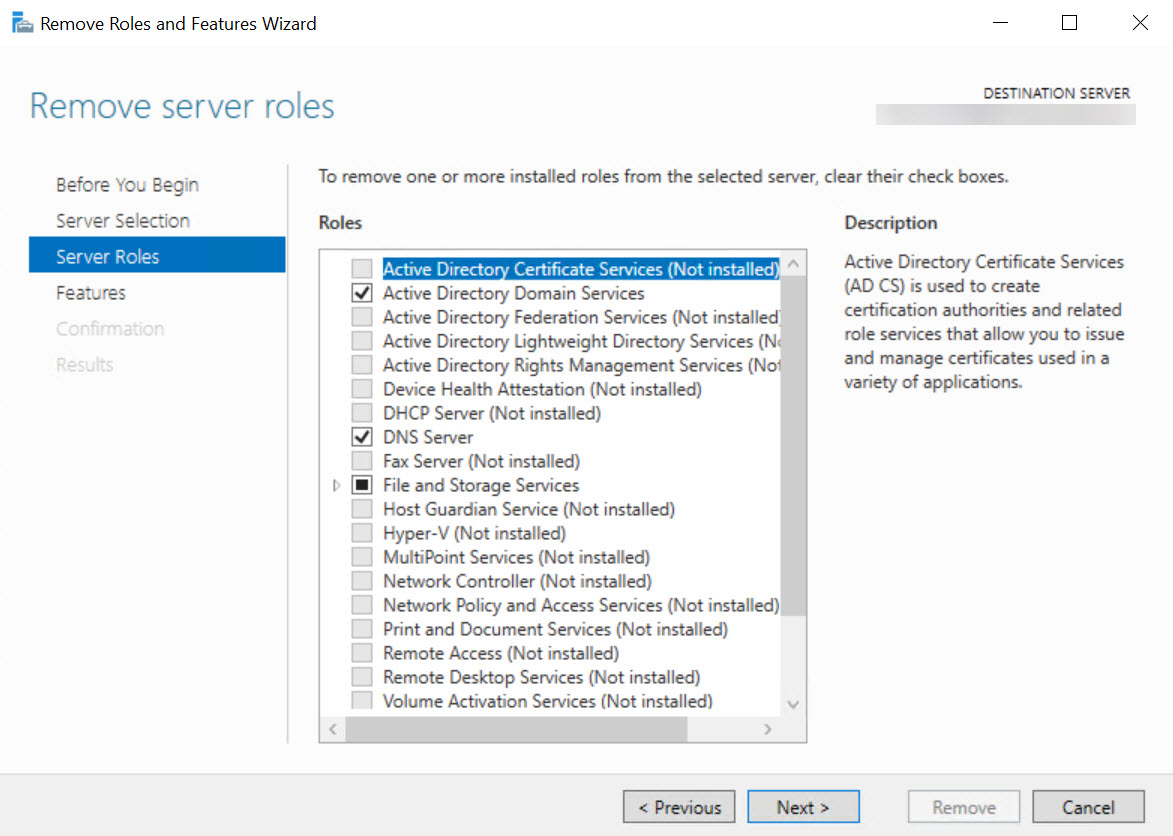
Before removing ADDS, Windows Server will perform a validation check. You won’t be able to remove the role until the domain controller has been demoted. The validation results will show a warning and provide a link that opens the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard.
- In the validation dialog, click Demote this domain controller.
- In the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard, check the details on the Credentials screen.
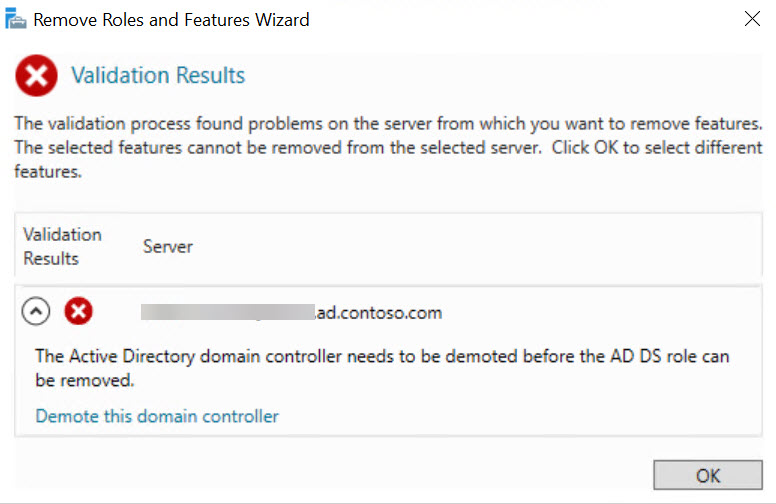
Checking Force the removal of this domain controller leaves the demoted domain controller’s object metadata in Active Directory. If the domain controller is the last in the domain, you will need to check Last domain controller in the domain before you can proceed. You can also change the credentials used for the demotion by clicking Change…
- Click Next.
- On the Warnings screen, check Proceed with removal and click Next. Here you are being reminded that the domain controller hosts DNS, and potentially a Global Catalog, and that other servers in the domain might rely on these services.
- On the Removal Options screen, you can choose to remove DNS zones, AD application partitions, and DNS delegation. Only the options applicable to the domain controller will appear on this screen. Check the items to be removed and click Next.
- On the New Administrator Password screen, type and confirm a new password for what will become the local administrator account once the server has been rebooted. Click Next.
- Finally, on the Review Options screen, check the options you have selected and then click Demote.
You’ll be prompted to reboot the server after a few minutes. At which point, you can complete the removal of the ADDS server role in Server Manager.
Demotion Using PowerShell
The above procedure can also be performed using two AD PowerShell cmdlets. The first step is to demote the domain controller to a member server. Open a PowerShell prompt and run the command as shown below. The AD Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) need to be installed before you can use the AD PowerShell module.
Uninstall-ADDSDomainController
Other parameters can be added to Uninstall-ADDSDomainController to reflect the options that are available in the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard.
Uninstall-ADDSDomainController -Credential (Get-Credential) -ForceRemoval
For a full list of available parameters, use Get-Help Uninstall-ADDSDomainController.
Once the server has been demoted and rebooted, run Uninstall-WindowsFeature to remove the ADDS server role:
Uninstall-WindowsFeature AD-Domain-Services -IncludeManagementTools
If you try to remove ADDS before demoting the domain controller, PowerShell will return an error.
In this Ask the Admin, I showed you how to demote a Windows Server 2016 domain controller and remove the Active Directory Domain Services role.
Follow Russell on Twitter @smithrussell.




