Add Pop-Up Tips for PowerShell WinForms Script
- Blog
- PowerShell
- Post
IT pros who have taken the leap and dived head-long into PowerShell will eventually find themselves creating graphical PowerShell scripts and tools. This often means using Windows Forms, which is also known as WinForms. You can create some very complicated graphical tools and often IT pros do just that, where these tools are delegated for administration. I would expect the form interface to be intuitive most of the time, but perhaps you might want to add a little interactive help. You can use the ToolTip control to accomplish this.
Using a WinForms-Based PowerShell Script
Here’s a simple WinForms-based PowerShell script:
#demo-winform.ps1
[void][reflection.assembly]::loadwithpartialname("System.Windows.Forms")
# create form 1
$form1 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.Form
$form1.text = "Computer Name"
$form1.height = 250 #120
$form1.width = 250
$form1.formborderstyle = 3
# create OK and cancel scriptblocks
$oksb = {
$form1.dialogresult = 1
$form1.hide()
}
$cancelsb = {
$form1.dialogresult = 2
$form1.hide()
}
# create OK button
$okbutton1 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.Button
$okbutton1.text = "OK"
$okbutton1.height=25
$okbutton1.width=75
$okbutton1.top= 121 #51
$okbutton1.left=105 #147
$okbutton1.add_click($oksb)
$form1.controls.add($okbutton1)
# create Cancel button
$cancelbutton1 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.Button
$cancelbutton1.text = "Cancel"
$cancelbutton1.height=25
$cancelbutton1.width=75
$cancelbutton1.top= 121 #51
$cancelbutton1.left= 15 #66
$cancelbutton1.add_click($cancelsb)
$form1.controls.add($cancelbutton1)
# create label
$label1 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.Label
$label1.text = "Enter computer name:"
$label1.left=12
$label1.top=9
$label1.width=205
$label1.height=13
$form1.controls.add($label1)
# create text box
$text1 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.TextBox
#create a default value
$text1.Text=$env:computername
$text1.left=15
$text1.top=25
$text1.height=20
$text1.width=205
$form1.controls.add($text1)
#create some check boxes
$check1=New-Object system.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$check1.width=150
$check1.Text= "OperatingSystem"
$check1.Top=50
$check1.Left=15
$check1.Checked=$True
$form1.Controls.add($check1)
#create some check boxes
$check2=New-Object system.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$check2.width=150
$check2.Text= "ComputerSystem"
$check2.Top=70
$check2.Left=15
$check2.Checked=$False
$form1.Controls.add($check2)
#create some check boxes
$check3=New-Object system.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$check3.width=150
$check3.Text= "BIOS"
$check3.Top=90
$check3.Left=15
$check3.Checked=$False
$form1.Controls.add($check3)
# show form 1
if ($form1.showdialog() -eq 2) {
# cancelled
break
}
# get computer info
$result=@()
if ($check1.Checked) {
$data = Get-WmiObject -class win32_operatingsystem -ComputerName $text1.text
$result+= $data
}
if ($check2.Checked) {
$data = Get-WmiObject -class win32_computersystem -ComputerName $text1.text
$result+= $data
}
if ($check3.Checked) {
$data = Get-WmiObject -class win32_bios -ComputerName $text1.text
$result+= $data
}
# create results form
# create form 2
$form2 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.Form
$form2.text = "WMI Results: " +($text1.text).toUpper()
$form2.height = 250
$form2.width = 400
$form2.formborderstyle = 3
# create OK and cancel scriptblocks
$oksb2 = {
$form2.dialogresult = 1
$form2.hide()
}
# create OK button
$okbutton2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$okbutton2.text = "OK"
$okbutton2.height=25
$okbutton2.width=75
$okbutton2.top=150
$okbutton2.left=147
$okbutton2.add_click($oksb2)
$form2.controls.add($okbutton2)
# Create a new text box
# create text box
$text2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$text2.left=15
$text2.top=9
$text2.height=100
$text2.width=360
$text2.multiline = $True
$text2.scrollbars = "Vertical"
$text2.Font="Lucida Console"
$text2.wordwrap = $True
$text2.text = ($result | Out-String).Trim()
$form2.controls.add($text2)
$form2.showdialog() | Out-Null
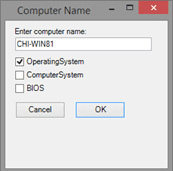
The script will present a simple form with a few check boxes.
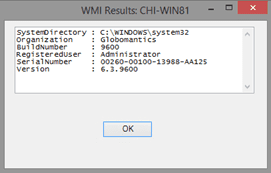
Click, OK and a few WMI queries will run, presenting the results in a new form.
This isn’t especially complicated, but let’s add some help. The way I handle this in my forms is to display the help when the user hovers the mouse over a given control. The help text is displayed in the ToolTip control. First, let’s add the control to the script.
$tooltip1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.ToolTip
When working with WinForms in a PowerShell script, we have to connect some PowerShell action with some event from the form, such as clicking a button or hovering the mouse.
In my projects, I define these actions in scriptblocks. I’m going to write a scriptblock to display the pop-up help for selected controls.
$ShowHelp={
#display popup help
#each value is the name of a control on the form.
Switch ($this.name) {
"text1" {$tip = "Enter the name of a computer"}
"check1" {$tip = "Query Win32_OperatingSystem"}
"check2" {$tip = "Query Win32_Computersystem"}
"check3" {$tip = "Query Win32_BIOS"}
}
$tooltip1.SetToolTip($this,$tip)
} #end ShowHelp
The scriptblock includes a switch statement that looks at a string and depending on what it matches, in this case text1 or check2, it assigns a value to the variable $tip and applies the value to the ToolTip object. The $this refers to active control. For each control in my form, I’ll add a connection for the _MouseHover event.
#give the control a name
$text1.name="text1"
#connect the ShowHelp scriptblock with the _MouseHover event for this control
$text1.add_MouseHover($ShowHelp)
$form1.controls.add($text1)
When the form detects that event, it will run the associated command, which in my script is the $ShowHelp scriptblock. If the user hovers on the $Text1 control, then $this will be that control. You must make sure you give each control a name in order for the switch statement to work. The control name doesn’t have to match the variable name, but mine just happens to. I can repeat this process for the other controls in my form. Here is my revised script:
#demo-winform-with-tooltip.ps1
[reflection.assembly]::loadwithpartialname("System.Windows.Forms") | Out-Null
#define a tooltip object
$tooltip1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.ToolTip
<#
define a scriptblock to display the tooltip
add a _MouseHover event to display the corresponding tool tip
e.g. $txtPath.add_MouseHover($ShowHelp)
#>
$ShowHelp={
#display popup help
#each value is the name of a control on the form.
Switch ($this.name) {
"text1" {$tip = "Enter the name of a computer"}
"check1" {$tip = "Query Win32_OperatingSystem"}
"check2" {$tip = "Query Win32_Computersystem"}
"check3" {$tip = "Query Win32_BIOS"}
}
$tooltip1.SetToolTip($this,$tip)
} #end ShowHelp
# create form 1
$form1 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.Form
$form1.text = "Computer Name"
$form1.height = 250 #120
$form1.width = 250
$form1.formborderstyle = 3
# create OK and cancel scriptblocks
$oksb = {
$form1.dialogresult = 1
$form1.hide()
}
$cancelsb = {
$form1.dialogresult = 2
$form1.hide()
}
# create OK button
$okbutton1 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.Button
$okbutton1.text = "OK"
$okbutton1.height=25
$okbutton1.width=75
$okbutton1.top= 121 #51
$okbutton1.left=105 #147
$okbutton1.add_click($oksb)
$form1.controls.add($okbutton1)
# create Cancel button
$cancelbutton1 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.Button
$cancelbutton1.text = "Cancel"
$cancelbutton1.height=25
$cancelbutton1.width=75
$cancelbutton1.top= 121 #51
$cancelbutton1.left= 15 #66
$cancelbutton1.add_click($cancelsb)
$form1.controls.add($cancelbutton1)
# create label
$label1 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.Label
$label1.text = "Enter computer name:"
$label1.left=12
$label1.top=9
$label1.width=205
$label1.height=13
$form1.controls.add($label1)
# create text box
$text1 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.TextBox
#create a default value
$text1.Text=$env:computername
$text1.left=15
$text1.top=25
$text1.height=20
$text1.width=205
#give the control a name
$text1.name="text1"
#connect the ShowHelp scriptblock with the _MouseHover event for this control
$text1.add_MouseHover($ShowHelp)
$form1.controls.add($text1)
#create some check boxes
$check1=New-Object system.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$check1.width=150
$check1.Text= "OperatingSystem"
$check1.Top=50
$check1.Left=15
$check1.Name = "check1"
$check1.add_MouseHover($ShowHelp)
$check1.Checked=$True
$form1.Controls.add($check1)
#create some check boxes
$check2=New-Object system.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$check2.width=150
$check2.Text= "ComputerSystem"
$check2.Top=70
$check2.Left=15
$check2.Name = "check2"
$check2.add_MouseHover($ShowHelp)
$check2.Checked=$False
$form1.Controls.add($check2)
#create some check boxes
$check3=New-Object system.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$check3.width=150
$check3.Text= "BIOS"
$check3.Top=90
$check3.Left=15
$check3.Name = "check3"
$check3.add_MouseHover($ShowHelp)
$check3.Checked=$False
$form1.Controls.add($check3)
# show form 1
if ($form1.showdialog() -eq 2) {
# cancelled
break
}
# get computer info
$result=@()
if ($check1.Checked) {
$data = Get-WmiObject -class win32_operatingsystem -ComputerName $text1.text
$result+= $data
}
if ($check2.Checked) {
$data = Get-WmiObject -class win32_computersystem -ComputerName $text1.text
$result+= $data
}
if ($check3.Checked) {
$data = Get-WmiObject -class win32_bios -ComputerName $text1.text
$result+= $data
}
# create results form
# create form 2
$form2 = New-Object system.Windows.Forms.Form
$form2.text = "WMI Results: " +($text1.text).toUpper()
$form2.height = 250
$form2.width = 400
$form2.formborderstyle = 3
# create OK and cancel scriptblocks
$oksb2 = {
$form2.dialogresult = 1
$form2.hide()
}
# create OK button
$okbutton2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$okbutton2.text = "OK"
$okbutton2.height=25
$okbutton2.width=75
$okbutton2.top=150
$okbutton2.left=147
$okbutton2.add_click($oksb2)
$form2.controls.add($okbutton2)
# Create a new text box
# create text box
$text2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$text2.left=15
$text2.top=9
$text2.height=100
$text2.width=360
$text2.multiline = $True
$text2.scrollbars = "Vertical"
$text2.Font="Lucida Console"
$text2.wordwrap = $True
$text2.text = ($result | Out-String).Trim()
$form2.controls.add($text2)
#display form 2
$form2.showdialog() | Out-Null
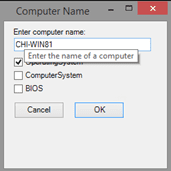
Now when the user hovers the mouse over one the defined controls, the Tooltip control displays my defined help message.
When the mouse moves away, the tooltip automatically goes away. Controls without the attached event will have no popup help. I hard coded my popup help, but it wouldn’t be that difficult to read help strings from an external source. This would be especially helpful if you need to provide localized popup text.
You can do all of this manually for simple forms. However, IT pros rarely take the simple approach. A popular tool for creating WinForm-based PowerShell scripts is a commercial tool from SAPIEN called PowerShell Studio. Because this product is widely used, I’ll demonstrate how to add tool tips to a PowerShell Studio project in a future article.